A habitat is a place that provides the organism with its basic need of air, water, food and shelter. The organism living in a particular habitat utilises all the resources available in the surrounding for survival.
Whereas the niche is the sub-part of any habitat. It is a small place or position that a particular species holds in the ecosystem according to its functional role. It basically defines how an organism responds to the availability and distribution of resources, predation, competition etc.
You can understand habitat as the address of a species while niche as the profession or occupation of the organism in that particular ecosystem.
The habitat can have several numbers of niches as its sub-unit. In contrast, the niches don’t have any further smaller units. The habitat supports more than one species at a time. But the niche specifically deals with single species at a time.
The following section aims to demonstrate the key differences between a habitat and a niche.
Content: Habitat Vs Niche
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Habitat | Niche |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A habitat is an area, where a species lives and interact with the other factors. | A niche is an ideology, of how an organisms lives or survive in the provided environmental conditions. |
| Consist of | Habitat consist of numerous niches. | Niches does not contains such components. |
| It includes | Affect of temperature, rainfall and other abiotic factors. | Flow of energy from one organisms to other through ecosystem. |
| Examples | Desrets, oceans, forest, rivers, mountains, etc. are examples of habitat. | It is a part of habitat only, where shelter for living being can be furnished. |
| Supports | Habitat supports numerous species at a time. | Niche supports a single species at a time. |
| What it is | Superset | Subset |
| Nature | Habitat is a physical place. | Niche is an activity performed by organisms. |
| Specificity | Habitat is not species specific. | Niche is species specific. |
What is a Habitat?
The earth with shifting landscapes imparts numerous challenges for the creatures that make it their home. This home can be any specified ecological area that helps to meet the organism’s basic needs for survival.
Although all the living entities live on this same planet, they prosper in a very particular location only. This acts as their respective ecological habitat.
You can understand it as how some flora and fauna can survive in the least availability of water. At the same time, some others can only live inside the water. It implies that the needs, body structure, and ability to adaption decide the habitat of an organism.
Definition of Habitat
The term habitat has its origin in the Latin word ‘Habitare”, which means “To live or dwell in”.
“Any location or ecological area, big or small, warm or cold, dry or wet that supplies the organism with its primary needs of air, food, water and shelter can be a habitat”.
Characteristics of Habitat
- Habitat reflects the organisms’ way of living.
- It gets influenced by the biotic as well as abiotic elements present there.
- It consists of several big, small niches that act as the organisms’ unique habitat based on their role.
- Continuously has an impact of fluctuating temperatures, amount of rainfall, sunlight exposure etc.
- A habitat supports an enormous number of species at a single time.
- It is a physical place that can be the external environment or can be a place inside a living body.
- It is not species-specific; thus, animals and plants sharing common needs live in the same environment.
Selection of Habitat
The habitat indicates the environment of any species i.e., the one it has chosen to live. The organism deliberately selects the space that can serve the role of its shelter and can elevate its rate of survival. It also relies on what potentially suits the fitness of a particular species.
Habitat and Adaptation
As per the habitat and the fluctuations in the environmental conditions, a living body tries to modify itself accordingly. This process is known as adaptation.
The level of adaptation increases the chances of survival of any species. It not only enhances the growth rate but also helps the organism to protect itself from danger.
For instance, the octopus has evolved itself as per the deep-diving underwater settings. It has eight arms that aid him to propel throughout the seabed. Also, they help it climb and crawl over the rocks, swim in deep waters and feel its path.
There are numerous receptors all around its body surface. They are the taste receptors, just like having tongues all over the body.
Octopus has adapted the defensive mechanism immensely and is often referred to as the “Master of Disguise”. Since it is spineless without a single bonny component, it can easily squeeze itself into a tight small structure and rapidly disappear through narrow orifices whenever required.
Examples of Habitat
1. The Northland Brown Kiwis have dense rainforests as their habitat. They dwell in the damp and moist gullies where they can quickly get the earthworms to feed on. As their eating habits demand a humid place, thus they have chosen the rainforest as their habitat.
2. The size of the habitat can dramatically vary as per the needs of the organism.
For instance, a Pistol Shrimp found in deep down waters; spends most of its lifetime in small burrows at the waterbed. It hangs out only with its close friend, goby fish, in a limited arena for some time and comes to the burrow again.
Contrastingly, the Hawk has a much larger habitat in the form of the sky. This is because of its ability to adapt anywhere, anything.
3. The Polar bear, Panda bear and Grizzly brown bear are assumed to be distantly related, having common ancestry. And even with the interrelated lineage, they are so extremely different from each other concerning their external appearance as well as their habitat.
This evidently manifests the fact that they have adapted themselves according to the surrounding environment. The polar bears near the poles have adapted their bodies to the freezing cold environment. Their white coat makes them less visible in the icy background as there are very few places to hide. This thick fur repels water and cold; thus, they can easily swim for days in the icy water.
Similarly, the Panda bears have comparatively larger heads than other bears. Also, they possess strong jaw muscles so that they can easily chew tough bamboo.
Brown grizzly bears have adapted themselves for the seasonal availability of food. They are mainly located in grasslands where there is plenty of food in summers and no food in winters. Thus, in summers, they eat excessively, while they go to hibernation in winters.
What is a Niche?
The term niche was first time used by ‘Grinnell’ in 1971. To understand the concept of niche, you will have to consider all the interactions and relationships the organism persists with its surrounding factors.
An organism decides its niche based on its functional position in a specified ecosystem. It may also rely on the sort of response it generates to the availability of resources, predation, competition etc.
Definition of Niche
“Niche is the distributional unit, where organisms live within their constitutional and instigative boundation”.
Selection of Niche
Each specific species has a different set of adapting abilities. Thus, they never directly compete for all the same resources.
The idea of ecological niche can be understood by the following factors:
- On what does it feed on?
- Where does it shelter?
- How many mating partners are present?
- What is the reproductive ability of the organism?
- How does the organism respond and interact with biotic factors like predators, competitors, parasites etc.?
- How does the organism react and adapts to the availability of the abiotic resources?
Distribution of Species in Niches
All the organisms react differently to the biotic and abiotic factors until they occupy their unique niche. This distribution accounts for basic requirements and the level of adaptation of an individual species.
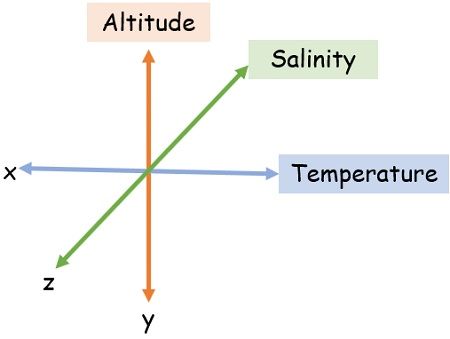
For instance, some of the organisms survive in some range of temperature, while others might live at a certain range of altitude or salinity. In this way, these small points of distinction segregate the organisms into different niches.
Characteristics of Niche
- You can understand it as the unique the adaptation; the more unique the niche will be.
- The more diverse the habitat is, the greater number of niches it will have.
- Niches allow and promote the fittest species to grow and survive.
- Niches are the sub-part of habitats that are highly specific.
- They support only a single species at a time for survival.
- Reduce the amount of competition by segregating the organism based on their elementary needs.
- As soon as the niche is vacant, other organisms can fill that position.
- The niche should be specific to each species, which means no two species can share the same niche.
Types of Niches
Three types of niches are as follows:
a) Spatial or habitat niche: Deals with the physical space occupied by the organisms.
b) Trophic niche: It differs on the basic food level of an organisation.
c) Multidimensional or Hypervolume niche: Complex to understand and explainable using fundamental and realised niches.
Advantages of Niche
In an ecosystem, many numbers of an organism can coexist peacefully because of their unique niches. Although their habitat is the same, the separation at the niche level makes it easier for them to adapt and grow in the limited but specified units of resources.
For the successful survival of the species, it is highly advantageous to occupy a unique niche. This is because taking a specific niche decreases the amount of competition for the available resources.
Examples of Niches
1. A teacher, Mr Zabir, teaches in Sun International School. He has taught several classes in the same classroom, and thus, it has become his habitat.
But he specializes in English subject, and thus it has become his niche. Similarly, various teachers teaching different subjects have their own unique niches.
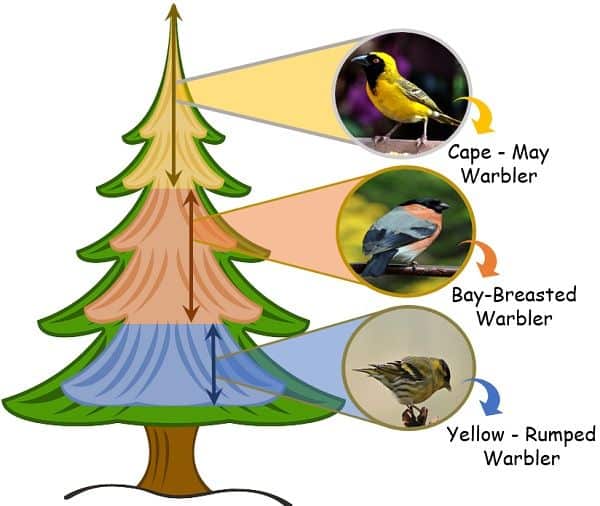
2. The Galapagos Islands located approx. 605 miles away to the west side of S. America have birds called finches. These islands are specialised as the main habitat for these birds.
But, different species of finches have their unique beak. This beak structure is responsible for their distribution in the niches. Separated niches allow them to prosper and survive in the same habitat.
The Warbler finches have thin beak as it eats insects.
Whereas the ground finches have short beaks as they feed upon the seeds left on the ground.
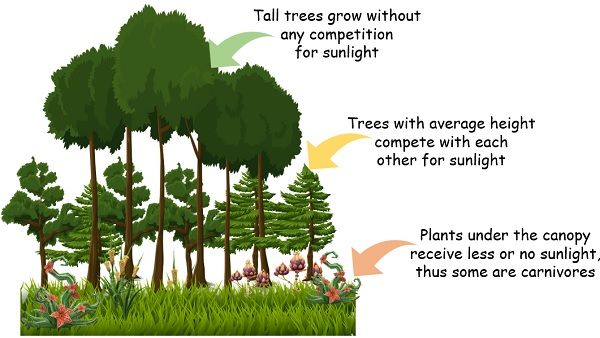
3. Rainforests are popular for their wide range of biological diversity. And because of this, it provides immense numbers of niches.
Like, tall plants spend most of their energy growing big so as to absorb the light without any competitors.
Whereas the plants present further down with average height invest large amounts of their energy in competing with others for the resources.
While the lowest plants below the canopy are specialised plants such as vines and carnivore plants.
Here, it is clearly visible that the unique the adaptation is, the more unique the niche will be.
4. Birds differ in their eating habits; where some birds eat only insects, some only fruits, and some can eat anything they come across. So here we can conclude that these birds being of the same habitat differ in their niches because of different eating habits.
Key Differences Between Habitat and Niche
Following are the substantial difference between habitat and niche.
- A habitat can be defined as an area, where different species lives and interact with the other factors, while niche is an ideology, of how an organism’s lives and survive in the provided environmental conditions.
- Habitat consists of numerous niches; Niche does not contain any such components.
- Habitat includes the effect of temperature, rainfall, and other abiotic factors; Niche includes the flow of energy from one organism to another through the ecosystem.
- Examples of habitat include deserts, oceans, forests, rivers, mountains, etc.; Niche is a part of habitat only, where a shelter for living beings can be furnished.
- Habitat supports numerous species at a time; Niche supports a single species at a time.
- As said above habitat is a superset of niche and niche is a subset of habitat, which means niche is a part of the habitat.
- A habitat is a physical place in nature, while a niche is a kind of activity performed by organisms.
- Habitat is not species-specific while niche is species-specific.
Conclusion
Hence we can say that there are many definitions of niche, defined by different ecologists, but the basic idea of niche lies between the interaction of different ecological factors and organisms in the ecosystem.
On the other hand, habitat is the natural environment inhabited by any organisms whether a plant or an animal or any other microorganisms. As both the terms are closely related, hence it is important to understand them precisely and mark the difference.





Negin says
Hi
thanks for these much useful information.
would you please mention the source of these information?