The solute and solvent are the two prime components of the solution. The solute is one that gets dissolved. While the solvent is one in which the former dissolves. In other words, the solute is dissolved matter, and the solvent is the dissolving medium.
The solutes are present in all three states, i.e., solid, liquid and gas. But the solvents are generally fluid state. The quantity of solute is always less while that of solvent is more in a solution.
The boiling point of solute is greater while that of solvent is lower.
The following article will briefly showcase the elementary differences between solute and solvent.
Content: Solute Vs Solvent
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Solute | Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The substance that gets dissolved in the solvent in a solution is called as the solute; the solute is present in the lesser amount than the solvent. | The substance that dissolves the solute in a solution is called as the solvent; the solvent is present in the higher amount than the solvent. |
| Boiling point | The boiling point is higher than solvent. | It is lower than that of solute. |
| Physical state | Found in solid, liquid or gaseous state. | Mainly in the liquid state, but can be gaseous as well. |
| Dependability | Solubility depends on the properties of the solute. | Solubility depends on the properties of the solvent. |
What is a Solute?
In a solution, a solute is a substance that gets dissolved in the solvents. As soon as it comes in contact with the appropriate type of solvent, it starts undergoing the process of dissolution.
Note: The dissolution is the act of dissolving a solute in the solvent.
During the dissolution process, solvent breaks the molecules of solute apart and disperses them uniformly. This generates a homogenous mixture which we refer to as a solution.
Measurement of solute in the solution
We estimate the quantity of solute in a solution based on its concentration. This concentration is nothing but the amount of solute present in the total volume of solvent. This is easily calculated by using the molarity.
We can define solute concentration as:
“The moles of solute dissolved per litres of the solution”.
The concentration of solution also relies on the concentration of the solute. The more the solute, the higher will increase the concentration of solute.
The solvent can dissolve the various quantities of solute based on its strength of dissolution as well as the tendency of the solute particles to move apart. We refer to this property of solute as ‘Solubility’.
Process of Dissolving
The process of dissolution depends upon the ability of the solute molecules to come apart by overcoming the attractive intermolecular forces. The molecular force is strong to keep the solute molecules intact with each other in their position.
Thus, in order to form a solution, the attractive forces applying externally to the solute must be greater than the already existing force. And as soon as the solute-solute bonding breaks, the solute-solvent bonding begins.
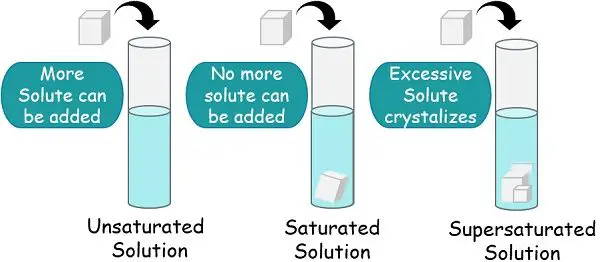
Saturation of Solute
As per chemistry, Saturation refers to the condition of equilibrium that balances the opposite forces, thereby equalizing the reaction rate. A solution is considered saturated when no further amount of solute can be added to it.
When the solvent has dissolved, the solute particles are up to their maximum limit and have no further space for more solute molecules. This is the process of Saturation, and the solution is a saturated solution.
Characteristics of the Solute
- Solute has higher boiling points than solvent.
- They can be in any state- solid, liquid or gas.
- A solution will always contain a lower quantity of the solute than that solvent.
- The heat gets transferred to the solute.
- The chemical structure and properties also determine the solute’s ability to solubilize. For instance, a polar solute will readily dissolute in a polar solvent and vice versa.
- As the surface area of the solute particle increases, its solubility increases automatically.
- Besides this, the volume and temperature also play a part in the level of dissolution.
- In the case of gaseous solutes, the solubility gets affected by the pressure, besides the volume and temperature.
Examples of Solute: Salt in Water
When we add a spoonful of salt, i.e. solute, to a glass of water, i.e., solvent, we can see that the salt directly collects at the bottom. It doesn’t directly start diluting in the water, and even if started at the molecular level, it is not visible to your eyes.
Now the question arises of what actually happens at the molecular level. So, as you know, the oxygen atom of a water molecule is negatively charged while the hydrogen is positively charged. The NaCl (salt) molecules possess ionic bonds consisting of a positive sodium ion and a negative chloride ion.
At the time of dissolution, the negative oxygen ion attracts the positive sodium. While the positive hydrogen ion attracts the negative chlorine ions. In this way, the hydrogen and oxygen ions of the water pull NaCl ions apart. And later, disperse them uniformly throughout the dissolving medium.
Note: As discussed above, the surface area determines the solubility. Thus, when we dissolve the coarse salt, it will expose a lesser area for the dissolution. And here, the time required for solution formation is also more. Whereas, if you take fine salt, it will lead to the exposure of more area. This will allow the solute particles to diffuse fast and uniformly throughout the solution.
What is a Solvent?
The solvent is that component of the solution which dissolves the solute. It can break the molecular interaction between solute-solute molecules and suspend the free solute molecules evenly to make a solution.
The major proportion of the solution remains occupied by the solvent. This is because its amount is always greater than that of the solute.
The solubility phenomenon relies on one basic factor “Like Dissolves Like”. This means solvents with the same chemical properties as solute will have a greater affinity toward solute particles. Due to this, the solution will be uniform, and the time required for solution formation will be less.
Water: A Universal Solvent
On our planet earth, if something is in abundance, that is – water. It is the most common liquid around us, used to perform activities for living.
It possesses a remarkable quality by which it can dissolve many substances within it. Due to this unique ability, we refer to water as a universal solvent.
Characteristics of the Solvent
- Solvent has a low boiling point and gets easily evaporated.
- Solvent exists as liquid mostly but can be solid or gaseous as well.
For example, Brass is a homogenous solid solution with having solid solvent. - Solvents containing carbon are organic solvents, while others without carbon are inorganic.
- In a solution, Solvent transfers the heat.
- All proportions of the solvent will have the same concentration of solute.
- Solvents are also used to regulate the temperature in a solution, either to absorb the heat generated during some chemical reaction or to enhance the reaction speed with the solute.
Types of Solvent
We can divide solvent into two basic categories:
- Polar Solvents
- Non-polar Solvents
Polar solvents
Polar solvents possess a positive and a negative charge that acts as two oppositely charged poles. They can dissolve polar compounds by dissociating the ionic interaction between solute-solute particles.
They have a high dielectric constant and have one or more electronegative atoms like N, H or O.
Alcohols, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amides are common examples of the functional group present in polar solvents.
We can divide polar solvents into polar protic solvents and polar aprotic solvents.
- Polar Protic Solvents: Water and methanol are polar protic molecules as they can form the hydrogen bond with the solutes.
- Polar Aprotic Solvents: They cannot form the hydrogen bond with the solute but create dipole-dipole interactions with the ionic solutes. For example, acetone is a polar aprotic solvent.
Non-polar solvents
They contain bonds with similar electronegative atoms like C and H. They consist of non-polar molecules that can dissolve non-polar compounds or solutes.
Key Differences Between Solute and Solvent
Given below are the key differences between solute and the solvent:
- The solute can be defined as the substance that gets dissolved by the solvent in a solution, while the substance that dissolves the solute is called the solvent. Therefore the solute is present in a lesser amount than the solvent.
- The solute can be found in a solid, liquid or gaseous state, while the solvent is mainly found in the liquid state, but can be solid or in the gaseous
state as well. - The boiling point is higher for the solute than the solvent. The properties of both solute and solvent are interdependent on each other.
Conclusion
Solutes and solvents are substances not used only in chemical laboratories, but they are part of the day to day life. A solution contains only two components, which are solute and solvent. Solvent has the capability of dissolving the solute in a homogenous solution.
We discussed the characteristics of both the substances and concluded that in one solvent there can be different types of solutes and can form a homogeneous solution.

Leave a Reply