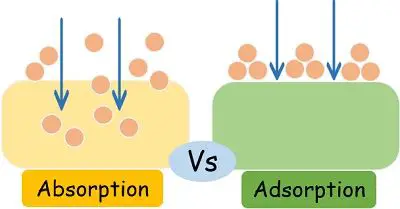
People frequently get confused between absorption and adsorption as they spell similar. But the mechanism by which two substances interact with each other clearly differentiates these two physio-chemical processes.
On one hand, absorption refers to the distribution of one substance throughout the area of the second substance. In contrast, adsorption refers to the adhesion of one substance over the surface of the other one.
In simple words, absorption takes the molecules, ions or particles inside its physical structure. While adsorption only attaches them to the surface without taking them inside.
This implies that the absorption relates to the volume while the adsorption remains associated with surface tension. The process of absorption involves phenomena like dissolution and diffusion.
Whereas adsorption involves the adhesion of the molecule.
In absorption, the particles of liquids or gases are soaked by the solid instead of any molecular forces. While in adsorption, there are intermolecular forces that bind molecules to the surface.
Here, we will discuss some of the key differences that exist between absorption and adsorption.
Content: Absorption Vs Adsorption
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Absorption | Adsorption |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The condition in which any substance (atoms, ions or molecules) is taken by or absorbed by another substance, especially in the solid or liquid material. | In this condition the substances like gas, liquids or dissolved solids loosely adhere or stick to the surface of another substance which can be solid or liquid. |
| Kind of phenomenon | Bulk phenomenon | Surface phenomenon |
| Reaction Rate | The reaction occurs at the uniform rate. | The reaction rate increases slowly and attains equilibrium. |
| Heat exchange process | Endothermic process. | Exothermic process. |
| Concentration | Does not change is constant throughout the medium. | The concentration changes from bulk to the bottom of the absorbent. |
| Temperature | No effect of temperature. | Adsorption works at the lower temperature. |
| Application | Cold storage, ice production, turbine inlet cooling, refrigerants. | Air conditioning, water purification, synthetic resin, chillers. |
What is Absorption?
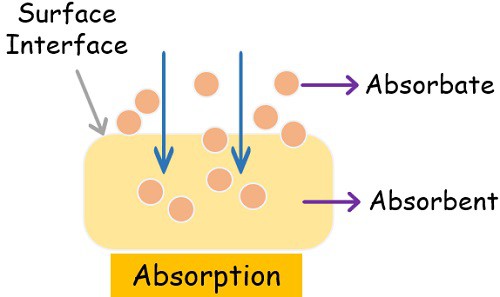
Absorption is a very common term and well-known phenomenon. It is a simple process where particles of one substance enter into the empty space of the other substance.
The absorbed material remains intact within the empty spaces of other substances without any chemical interaction with the absorbing material.
It may or may not require energy. For instance, absorption via diffusion doesn’t need energy, but active transportation requires energy.
Definition of Absorption
“The bulk process where one substance enters inside the physical structure of another substance is adsorption.”
Components involved in absorption
There are two main components in the process of absorption- absorbate and absorbent.
- Absorbate: The substance that gets absorbed in the empty spaces of the other substance is absorbate.
- Absorbent: The substance that provides empty space for other substances to enter is absorbent.
Do you know?
- Most of the time, the absorbate and adsorbent are in different phases.
- The absorbate enters wholly inside the absorbent, unlike adsorption. (Where only some amount of adsorbate adheres to that of the adsorbent).
- The absorbent can be solid, liquid or gas by nature.
Rate of Absorption
The rate of absorption varies as per the following elements:
- Time of contact
- Nature of absorbate
- Nature of absorbent
- Pressure
- Quantity of absorbate
- Surface area of contact
Uses of Absorption
- Industrially it is used in liquid-liquid extraction.
- Our body performs absorption for the intake of the nutrients extracted from the digested material.
- The plants absorb sunlight in order to perform photosynthesis.
- The process of absorption of gases in carbonated beverages.
- The liquids absorbed using a cloth or sponge.
- The body absorbs drugs and medicines in the bloodstream via absorption only.
- The oxygen dissolved in water is used by aquatic organisms.
What is Adsorption?
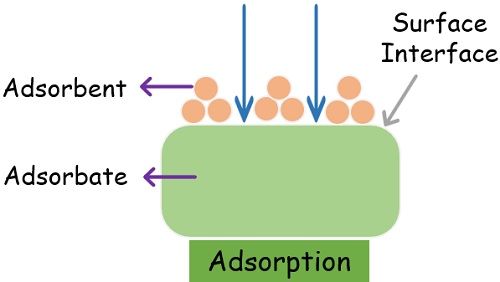
Adsorption is strictly a surface phenomenon that is completely different from absorption. It is a simple mechanism by which particles of one substance get attracted to the particles of another substance. As a result of this attraction, the former particles adhere to the surface of the other substance.
While adsorption, a relatively small amount of the substance experiences molecular forces and gets attracted to the exterior surface of the bulk substrate.
Do you know?
- Adsorption is an exothermic process. It results in a reduction of forces exerting between adsorbate and adsorbent at interphase.
- Viruses use the adsorption process to adhere to the surface of their host prior to the entry.
Definition of Adsorption
“The phenomenon where the particles of gas/liquid substances adhere on the surface of other liquid/solid substances is known as adsorption.”
Components involved in Adsorption
The process of adsorption involves two main components- adsorbate and adsorbent.
- Adsorbent: The bulk component that attracts the adsorbate particles is the adsorbent. Its particles attract and force the adsorbate to come close and adhere to its surface.
It also provides the interphase for the adsorption process. - Adsorbate: The component that gets attracted is Adsorbate. Its particles adhere to the surface of the adsorbent as soon as they come into contact.
Mechanism of Adsorption
The mechanism of adsorption is similar to that of surface tension. The energy of the adsorbent particles and adsorbate neutralizes when they come in contact at the interphase.
The adsorption occurs as a result of the forces acting on the surface. Particles at the interior of the adsorbent remain surrounded by more atoms on their upper side.
But this is not the same condition for the atoms at the surface as they have no outer layer.
As a result, the inner particles remain balanced while the outer ones are unbalanced. Consequently, the unbalanced forces attract adsorbate particles to establish the required balance. This leads to the phenomenon of adsorption.
Types of Adsorption
There are three types of adsorption:
- Physisorption
- Chemisorption
- Electrostatic adsorption
1. Physisorption: It is the physical adsorption that occurs due to the weak Van der Waals forces between the particles of adsorbate and adsorbent. For instance, when the gases such as hydrogen and nitrogen get adsorbed on the surface of the charcoal, it is physisorption.
2. Chemisorption: It is chemical adsorption because of the strong chemical interactions between adsorbate and adsorbent. Here, particles of both adsorbate and adsorbent develop chemical forces or bonds at the interphases.
For instance, when the gases like hydrogen and nitrogen get adsorbed over the surface of the substances like ferrous sulphate, chemical bonding occurs. It is a type of chemisorption.
3. Electrostatic Adsorption: Oppositely charged functional groups of adsorbate and adsorbent give rise to electrostatic adsorption. The charged clouds of the adsorbate and adsorbent produce electrostatic interactions that cause the adsorption.
Examples of some most commonly used adsorbents
- Silica
- Activated charcoal
- Activated alumina
- Zeolites
- Polymers and resins
- Clay
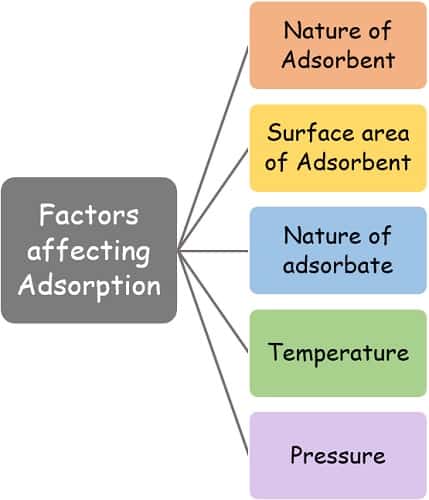
Factors affecting Adsorption
Applications of Adsorption
The adsorption process is useful in varied sectors, including domestic, medical, industrial and biological.
Some of the basic applications are as follows:
- The processes like air purification, water purification, air conditioning, and adsorption chilling rely on the adsorption phenomenon.
- Pharma industries use the adsorption process to practice prolonged exposure to various drugs and chemicals.
- Also used to produce non-stick coatings by the adsorption of polymers on the surface.
- The silica gel pouches adsorb the humidity and moisture of bags, medical kits, shoes etc.
- The gas mask used by the labourers and workers at chemical industries and mines adsorbs the harmful gases and minute particles.
- In paint producing industries, the adsorption process removes the remaining moisture from paints so that they can adequately adhere to the surface of the wall.
- The mechanism of chromatography solely relies on the adsorption phenomenon to separate various components of one substance.
- The cleansing mechanism of the soaps and detergents all depends on the adsorption phenomenon.
For example, when a chalk stick comes in contact with ink, its molecules adhere there due to the adsorption. But as the time passes, the chalk stick starts getting the colour of ink. This is because of absorption.
Key Differences Between Absorption and Adsorption
- Absorption is the phenomenon where one substance soaks the second substance in the space within. Whereas adsorption is the surface phenomenon where one substance adheres to the surface of another substance.
- Absorption is a bulk phenomenon. Whereas adsorption is a surface phenomenon.
- Absorption is an endothermic process. In contrast, adsorption is an exothermic process.
- In absorption, the concentration of the absorbate does not change instead it remains constant throughout the absorbent. But in adsorption, the concentration of the adsorbent changes, it decreases from the surface to the bottom of the absorbing material.
- The rate of reaction gradually increases thereby reaching equilibrium.
- Absorption works in the processes like cold storage, ice production, turbine inlet cooling, and refrigerants. While air conditioning, water purification, synthetic resin, and chillers are the area of applications of adsorption.
Conclusion
Absorption and adsorption are the kinds of homophones, but their meaning and application differ. This content will brief the major differences between these two processes with a comparison chart, diagrams and examples.



Daphne Gilpin says
It was helpful to me when you explained that adsorption includes the accumulation of the substance on the surface of the adsorbent. I’ve been wanting to learn more about adsorption because we’re considering investing in an air gas liquid drying system at my workplace. Your article was interesting to me because you explained adsorption in a way that was easy for me to understand!