Osmosis and Diffusion both depict the movement of particles from higher concentration to lower concentration. However, osmosis is a type of diffusion that is limited to fluids. Whereas, diffusion is not restricted and is prevalent in solids, liquids and gases.
The passage of the solvent molecules in osmosis occurs through a selectively permeable membrane. In contrast, for diffusion, the membrane is not mandatory. It can spread the particles directly within the given medium.
Osmosis establishes an equilibrium between osmotic pressures of solutions on both sides of the membrane. Diffusion also creates equilibrium. And thus, it continues until all the particles are equally distributed in the given area.
In this context, we will provide you with key differences between osmosis and diffusion.
Content: Osmosis Vs Diffusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Osmosis | Diffusion |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The movement of liquid (solvent) especially water from the higher region concentration to the region of lower concentration, through the semipermeable membrane is called osmosis. | The movement of molecules (solid, liquid or gases) from a region of higher concentration to the lower region concentration, but not necessarily through a semi-permeable membrane is called diffusion. |
| Semi-permeable membrane | The motion is through the semi-permeable membrane. | The motion is direct and does not require the semi-permeable membrane. |
| Medium | This process undertakes in the liquid medium. | This process undertakes in any medium (solid, liquid and gases). |
| Type of diffusing molecule | The movement is basically of solvent (water). | The movement can be in solid, liquid, or gases. |
| Rate of process | Osmosis is a slow process. | Diffusion is the fast process. |
| Free-energy | Osmosis is dependent on one solvent to the another for the reduction of free energy. | It is the movement of molecules from the area of their higher free energy to the area of the lower free energy. |
| Importance | 1. Osmosis is important in animals for maintaining the water at the cellular level, also in transporting the nutrients, cell-cell diffusion. 2. In plants, it is helpful in maintaining the turgidity, provides mechanical support, prevents excess water loss, and responsible for absorption of water from the soil. | Diffusion is important in animals at the time of creating energy, during respiration it helps in exchange of gases, while in plants it is also helpful in the process of transpiration and photosynthesis. |
What is Osmosis?
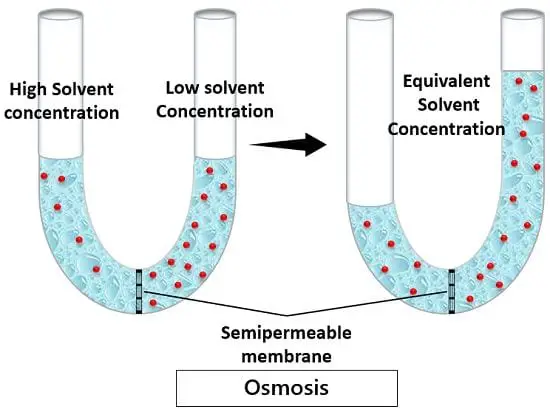
Osmosis is the phenomenon that depicts the movement of water or solvent. It is often considered a special sort of diffusion. This movement occurs across a selectively permeable membrane.
Osmosis is a mode of passive transport. And thus, no energy, i.e., ATP, during osmosis. It is a spontaneous phenomenon that works upon the driving forces.
History
Osmosis was first observed in 1826 by the French physiologist RJH Dutrochet (1776-1847).
Definition of Osmosis
We can define osmosis as:
‘A spontaneous process by which the water travels from the site of higher chemical concentration to the site of lower chemical concentration across a selectively permeable membrane’.
In other words,
‘Osmosis is the phenomenon where the water passes from the low osmotic pressure region to the higher osmotic pressure region through a biologically selective membrane’.
How does the osmosis exactly occur?
Movement during osmosis relies on the concentration gradient and pressure gradient. The direction and the rate of net movement depend on these gradients.
Any solution has its two prime components- solute and solvent. Concentrated solutions have a greater amount of solute than solvent. Thus you can say that they have a higher concentration of solute and a lower concentration of solvent.
Whereas the solutions with a greater amount of solvent than that of solute are dilute in nature. Thus, they contain a higher concentration of solvent and a lower concentration of solute.
In this way, osmosis aids the passage of solvent molecules from a dilute solution to the concentrated solution with a semi-permeable membrane.
Why does osmosis occur?
Osmosis obeys the laws of thermodynamics. It tends to establish an equilibrium between two concentration gradients. Osmosis balances and equalizes concentration of solutions on either side of the membrane. The movement of the solvent molecules continues until the equilibrium is attained. As the solution reaches equilibrium, it becomes more stable. And thus, the movement of molecules is ultimately ceased.
Requirements for Osmosis
The occurrence of osmosis necessitates three things:
1. Net downhill movement of solvent molecules: Solvent molecules tend to move from concentrated to diluted regions. This is a downhill movement. In the case of zero downhill movement, no osmosis can occur.
2. Osmotic Gradient: It is the difference between the concentrations or pressure of solutions on either side of the membrane. This osmotic pressure difference is a must for the process of osmosis.
3. Semi-permeable membrane: It is a thin film of biological material that acts as a sieve. It allows the passage of certain selective molecules across it. Thus, is a selectively permeable membrane.
Types of Osmosis
There are two significant types of osmosis:
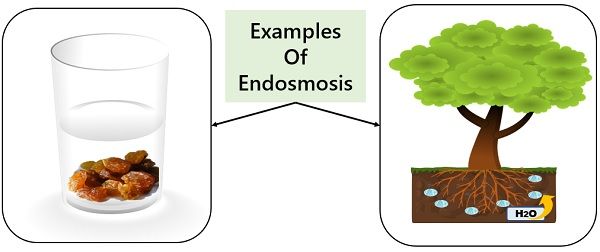
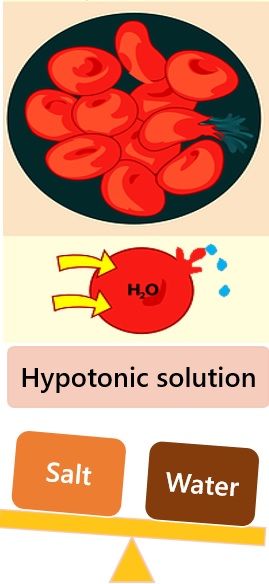
1. Endosmosis: Suppose you kept a cell in a hypotonic solution that has a higher potential of solvent than that of the cell. Then, the solvent molecules will travel from the external environment into the cell.
Due to endosmosis, the cell will get deplasmolyzed and will become turgid.
Example of Endosmosis
- Raisins soaked in water
- Plants absorbing water from the soil
- Blood in freshwater
- Absorption of nutrients in intestines
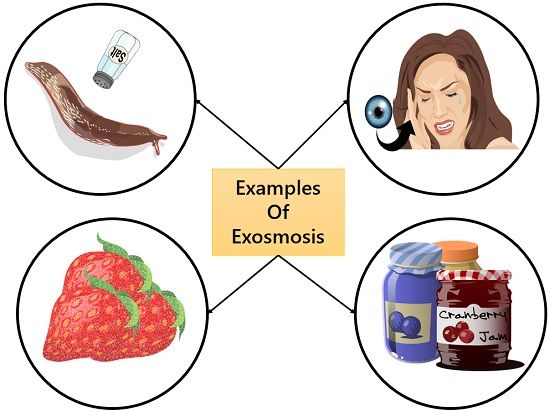
2. Exosmosis: If a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution with a lower potential of solvent than that of the cell. Then, the solvent molecules inside the cell will move in the external environment.
Due to exosmosis, the cell shrinks as it loses its solvent content and becomes flaccid. This means it undergoes plasmolysis.
Example of Exosmosis
- Food preservation techniques
- Salt on sluggish animals kills them
- Sugar on strawberries
- The use of contact lenses causes dryness the eyes
- Sore throat feels relieved with salt water gargles
What is Osmotic pressure?
It is the lowest amount of pressure required to stop the flow of solvent molecules across the pressure gradient. The concentration of the solute molecules governs it.
During osmosis, the solvent will move from dilute solution to concentrated solution. This movement will stop as the solution will reach towards equilibrium. This will determine the equalization of pressure on both sides.
We can calculate osmotic pressure:
π = iCRT
Where,
π = Osmotic pressure
i = Van’t Hoff factor
C = Molar concentration of the solute in the solution
R = Universal gas constant
T = Temperature
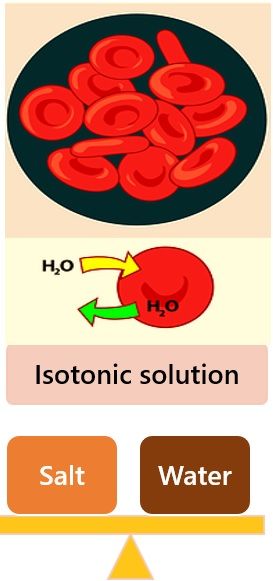
Types of Osmotic Conditions
The three types of osmotic conditions are as follows:
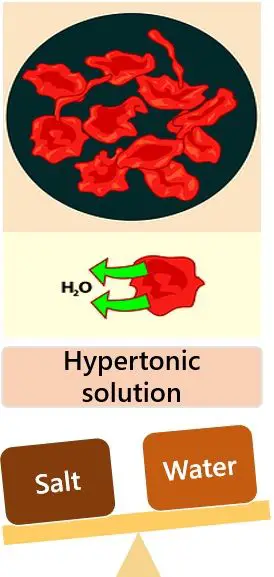
- Hypertonic Solution: Solution with relatively higher osmotic pressure and high solute concentrations. Here cells shrivel due to loss of water.
- Isotonic Solution (iso-osmotic): Solution with equal osmotic pressure and concentration of solute and solvent are at the same level. Thus no changes in cell volume and shape.
- Hypotonic Solution: Solution with relatively low pressure and high solvent concentration. Here cells absorb water, swell, and burst.
Factors affecting osmosis
- Diffusion distance
- Concentration gradient
- Temperature
Osmosis in Daily Life
- Transfusion: Used in hospitals to treat burns, dehydration, etc.
- Fluid balance and blood volume: Osmosis balances the fluid content in all the cells of the body. Also, it determines the blood volume of the organism.
- Oedema due to hypoalbuminemia: Oedema occurs due to the lower oncotic pressure of plasma. It results in the accumulation of fluid in tissue spaces.
- Red blood cells and fragility: It prevents from rupturing of the RBC i.e., haemolysis.
Other Types of Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis
In regular osmosis, the osmotic pressure triggers the process of osmosis. RO moves the solvent across the differential gradient from higher to lower concentration. But in RO, the movement is reversed from lower to higher concentration. Increased atmospheric pressure reverses the flow of solvent against the normal hydraulic pressure.
It is generally used for filtering water with a very low amount of impurities. The applied pressure forces the water molecules on one side of the membrane. While the remaining solute impurities will stay on the opposite end. In this way, the water becomes free from contaminants.
Forward Osmosis:
Forward osmosis is also based on pressure application. But this pressure is the natural osmotic pressure. It needs about 90% lesser energy than RO to drive the process.
Instead of pushing the water to either side of the membrane, FO pulls the water molecules. FO induces the passage of solute particles from lower to higher solute concentrations.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is a much simpler process that frequently occurs around you. For instance, the fragrance of room freshener scatters everywhere as soon as you spray it. Or you might have seen the dispersal of ink in water. Thus, you can say that diffusion is nothing but freely spreading the particles in the given space.
Definition of Diffusion
We can define diffusion as:
“The phenomenon of movement of particles from their higher concentration to lower concentration”.
Example
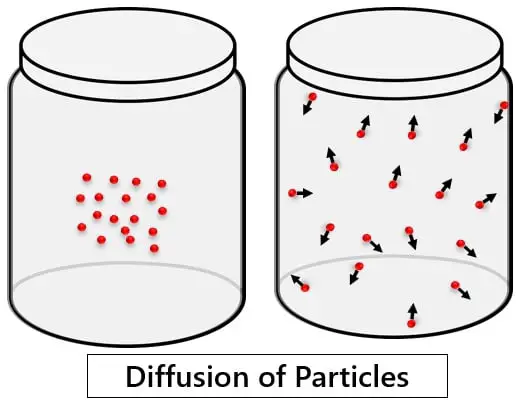
Suppose you filled a container with gas. But the particles are concentrated to a particular area only. Over a while, these particles will scatter in the entire container due to their random motion. This is diffusion.
Characteristics of Diffusion
- It may occur directly or via some substances like membranes. In a biological system, particles move within the cell or from one to another cell via a plasma membrane. This is because of diffusion.
- The movement of particles with diffusion is a mode of passive transport. Thus there is no energy expenditure.
- The diffusion of particles is due to the random motion of the molecules. This randomness drives the particles to move from a concentrated to a less concentrated area.
- The diffusion process is not restricted to liquids but also occurs in the case of gases.
- The process of diffusion will continue until all the particles are equally distributed. That means the same number of particles are present in every unit area. Thus, you can say that diffusion establishes the equilibrium of particles.
- It is a slow process and doesn’t rely on other living systems.
Other Types of Diffusion
- Surface Diffusion: It refers to the particle’s movement on the surface of solid material. You can assume it as jumping of particles to the adjacent adsorption site but only on the surface.
- Brownian Diffusion: The random jiggling movement of a particle in the still air or liquid. It results in continuous bombardment among the surrounding particles. For example, particles observed under a microscope skip, slip and dart within a liquid.
- Collective Diffusion: Many interacting particles collectively diffuse within a liquid.
- Osmosis: The diffusion of a solvent through a semi-permeable membrane.
- Effusion: Effusion occurs when the size of the hole is smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. It happens as a gas disperses through small holes.
- Electron Diffusion: It is the movement of electrons resulting in the production of electric current.
- Knudsen Diffusion: Here, the flux of diffusion decreases with an increase in particle’s molecular mass. This is because the increased molecular weight reduces molecular velocity.
- Momentum Diffusion: It is the spread of momentum between particles, mainly in liquids. It can take place in any direction.
- Photon Diffusion: Movement of photons within a material without getting absorbed. Instead, they repeatedly scatter, changing their direction. Used in medical tests as diffused optical imaging.
- Reverse Diffusion: Occurs in the opposite direction of the normal flow, i.e., from lower to higher concentration. It is carried out by using external pressure. Reverse osmosis is the best example of reverse diffusion.
- Self-Diffusion: It indicates the spontaneous motion of the particles to a new site within their crystal.
Factors affecting Diffusion
- Molecular weight: The larger the molecular weight, the slower will be the movement of the molecules.
- Concentration gradient: The higher the concentration gradient, the quicker the movement of molecules will occur.
- Pressure: Higher the pressure, the lower the rate of diffusion will be. This is due to the increase in the number of a collision.
- Temperature: Higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion will be.
- Surface Area: Larger surfaces will expose more molecules for diffusion. Thereby larger surface areas will increase the diffusion rate.
What is Facilitated Diffusion?
The rate of diffusion across the membrane depends on two essential factors:
Size of the particle: The smaller molecules like ions, water, glucose etc., tend to pass easily through the membrane. Whereas the larger ones like complex sugars and some amino acids are unable to diffuse.
Solubility of the particle: Similarly, the membrane’s outer surface being hydrophobic favours the passage of lipids and fat molecules. And the hydrophilic moieties are stuck at the membrane.
To overcome these issues, cell membranes have specialized proteins. These proteins aid the passage of the larger and hydrophilic molecules across the membrane. This is ‘facilitated diffusion’.
Facilitated transport cannot cause the movement from lower to higher concentration. Thus, even in facilitated diffusion, the presence of a concentration gradient is necessary. Porins and aquaporins are examples of facilitating proteins.
The facilitated diffusion has three major conditions:
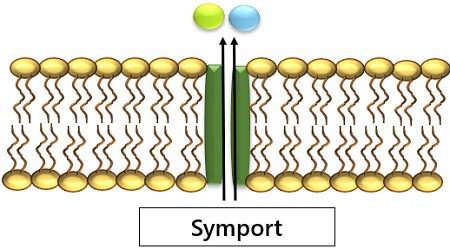
1. Symport: Movement of molecules in the same direction across the membrane.
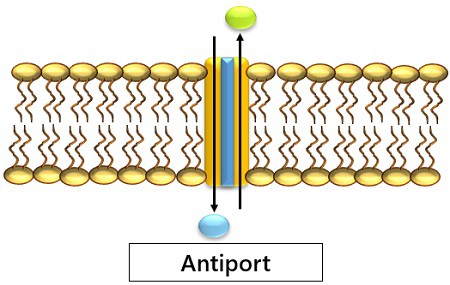
2. Antiport: Here, the molecules pass in opposite directions. That is, one move outwards and the other moves inwards.
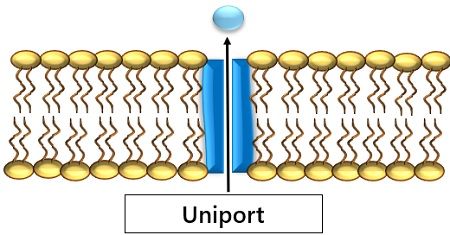
3. Uniport: Movement of a molecule irrespective of the motion of any other molecule.
Diffusion in Daily Life
- The gastrointestinal tract absorbs the nutrients through diffusion.
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs occurs through diffusion.
- Plants also intake carbon dioxide and release oxygen with the help of diffusion.
- Passage of waste products in the renal tubules occurs due to diffusion.
- Passage of waste products in the renal tubules occurs due to diffusion.
Key Differences Between Osmosis and Diffusion
Following are the substantial difference between osmosis and diffusion:
- Osmosis is the movement of liquid (solvent) especially water from the higher region concentration to the lower region concentration, through the semi-permeable membrane. Diffusion can be defined as the movement of molecules (solid, liquid or gases) from a region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration, but not necessarily through a semi-permeable membrane is called diffusion.
- The motion of molecules is through the semi-permeable membrane in osmosis, whereas in diffusion motion is direct and does not require a semi-permeable membrane.
- Osmosis undertakes in liquid medium only, whereas the process of diffusion undertakes in any medium (solid, liquid and gases).
- Water is only the diffusing molecule in osmosis; On the other hand, the movement can be in solid, liquid, or gases in the process of diffusion.
- Osmosis is a slow process and diffusion is a fast process.
- Osmosis is dependent on one solvent to another for the reduction of free energy, whereas in the case of diffusion the movement of molecules is from the area of their higher free energy to the area of the lower free energy.
- The process of osmosis is important in animals in maintaining the water at the cellular level, in transporting the nutrients, cell-cell diffusion. In plants, it is helpful in the maintenance of turgidity, provides mechanical support, prevents excess water loss, and is responsible for the absorption of water from the soil.
Whereas the process of diffusion is important in animals at the time of creating energy, during respiration it helps in the exchange of gases, while in plants it is also helpful in the process of transpiration and photosynthesis.
Conclusion
So in general terms, we can say that the intermingling of the molecules, for maintaining the equilibrium is the naturally occurring process in the body, and are termed as osmosis and diffusion. Through this physical process is sometimes confusing also. But has a significant value in the field of science.
In order to maintain the homeostasis of the body and also to balance the various internal mechanisms through internal cellular functioning, these concepts are regularly compared and discussed. And so we can say that in the osmosis process only water molecules can show the motion across the semi-permeable membrane and in the diffusion liquids and gases can move.



nandini says
very nice