Both the food chain and food web are the systems that portray the actual energy flow process in an ecosystem. The existence of our earth relies on this energy circulation between different organisms.
The food chain is a simple representation that illustrates the linear passage of nutrients and energy. The producers initiate this energy flow and it ends with the apex consumers. In contrast, the food web is a detailed presentation that depicts the interconnection between several food chains.
In a food chain, one trophic level’s organism solely depends upon the single preceding trophic level. Here, every particular organism has its specified consumer. Thus, if any of the organisms is removed, it might disturb the whole energy flow. For this reason, the chances of instability in the environment increase.
Whereas, in food webs, one trophic level never completely gets dependent on a single species. Here, the one organism serves multiple roles, i.e., of a producer or a consumer. Thus, the removal of a species never causes significant damage to the ecosystem.
This section will emphasize key differences between the food chain and the food web.
Content: Food Chain Vs Food Web
- Comparison Chart
- How does Energy Flow in the Ecosystem?
- What is a Food Chain?
- What is a Food Web?
- Key Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Food Chain | Food Web |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The flow of energy through a single straight pathway from the lower trophic level to the higher trophic level is called food chain. | The interconnected, numerous food chains through which the energy flow in the ecosystem is called food web. |
| Number of chains | It consists of only one straight chain. | It consists of many interconnected food chains. |
| Stability | The instability increases due to increasing number of separate and confined food chains. | The stability increases due to the presence of the complex food chains. |
| Disturbances arises due to | Even if the one group of an organism disturbs, the whole chain will be affected. | The food web does not get disturbed by the removal of one group of organisms. |
| Feed upon | Usually, member of higher trophic level depends or feed upon the single type of organisms of the lower trophic level. | In the food web, the members of higher trophic level depend or feed upon many different types of the organism of the lower trophic level. |
| Trophic level | Food chain consists of only 4-6 trophic levels of different species. | Food web contains numerous trophic level also of different populations of species. |
| Types | 1.Grazing food chain. 2. Detritus food chain. | No type |
How does the energy flow in the ecosystem?
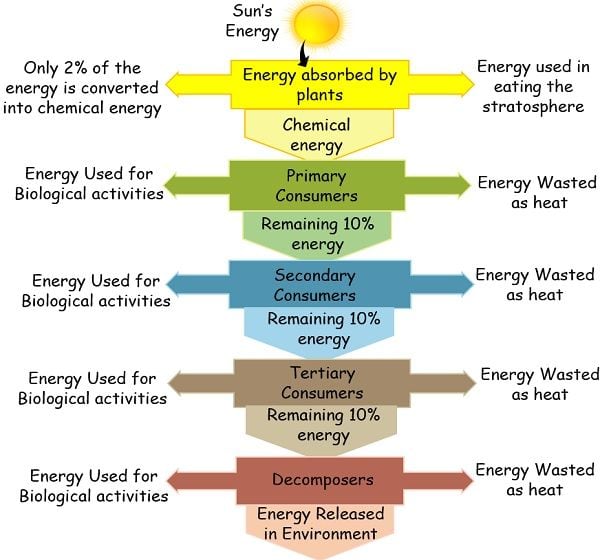
Energy is the ultimate need of all living organisms on the earth. The absence of energy will cease all the metabolic, physiological and physiochemical activities of the living world. The energy constantly flows from one trophic level to another in the ecosystem. This proportion of energy that circulates defines the energy flow or calorific flow.
For any ecosystem, the sun serves as the primary energy source that possesses 100 % energy. The sun supplies about 85 % of its energy to the plants. Of which, plants only absorb 1-2% of the energy to perform photosynthesis.
The plants convert the sun’s energy into chemical energy. This chemical energy is utilized by the primary consumers that are herbivores. Similarly, the primary consumers act as the energy source for secondary consumers. This process continues repeatedly, and the circulation of energy goes on.
Note
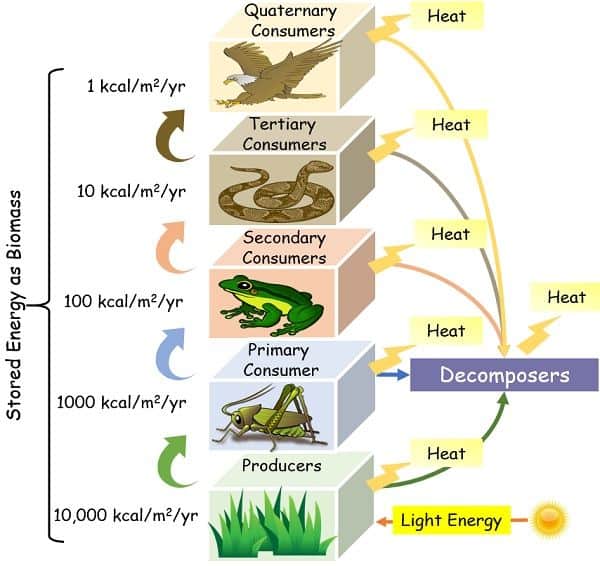
Ten % law: This law proposes that a large proportion of energy deteriorates in the form of heat at every trophic level. And only 10 % of the actual is transferred to the subsequent trophic level.
What is a Food chain?
The food chain is the most elementary and uncomplicated way to represent the energy flow. It is a linear pathway that manifests the movement of nutrients and energy from one trophic level to the next.
Almost all the food chains begin with the producers that are at the basal level. These producers are generally green plants that are capable of performing photosynthesis.
Sun provides its solar energy to the plants which they convert into chemical energy. This chemical energy is then transmitted to the succeeding trophic level. And this way, the flow of energy goes on.
This sequence or series of events depicting who eats whom in a hierarchical way is known as the Food chain.
Definition of Food Chain
We can define the food chain as:
“A simple sequence of energy flow from lower trophic levels to the higher trophic levels by the repeated events of eating and being eaten”.
Characteristics of Food Chain
- The food chain is an uncomplicated pathway that summarizes who eats whom very simply.
- The autotrophs or producers always occupy the first trophic level in the food chain.
- A single food chain may consist of 4-6 trophic levels. These levels consume the energy as per the hierarchic division.
- At every level, some amount of potential energy is wasted as heat. It implies that the fewer the number of trophic levels, the more efficient the energy transfer will be. Thereby, shorter food chains generate greater biomass.
- In this type of energy flow, a single organism or a species cannot perform many functions. That means they cannot dwell at multiple trophic levels simultaneously.
For example: If a goat is eating grass and a tiger is eating a goat, then the goat will only ever be below the tiger, and the grass will always be under the goat.
- Since one organism survives wholly and solely on another, thus removal of a single species will cause a severe disturbance in the ecosystem. Due to this reason, there is a perpetual risk of instability in the environment.
For example, if the tiger only survives over deer, then the decrease in the number of deers will immensely influence the tiger population.
Types of Food Chains
There are three types of food chains:
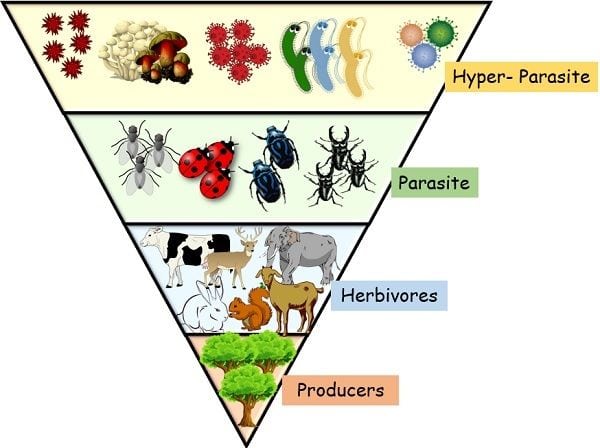
- Predator Food Chain: This is a typical food chain. It begins with plants and continues from lower predators to the higher. This type of food chain involves autotrophs, herbivores, carnivores and omnivores at 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th trophic levels. Here, the predator size is increased at every succeeding level ranging from smallest to biggest.
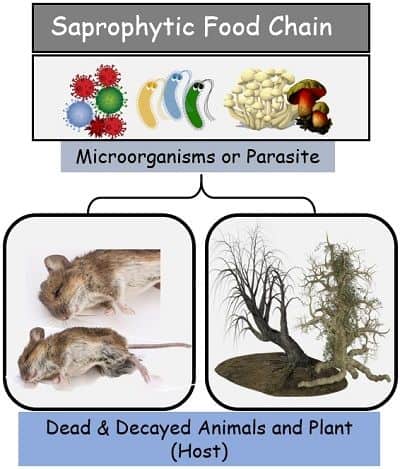
2. Parasitic Food Chain: Here, the food chain begins with herbivores and ends with the smaller parasites. The energy flows from larger organisms to smaller organisms, i.e., from host to parasite.
3. Saprophytic Food Chain: It displays energy flow from dead organic material to the micro-organism.
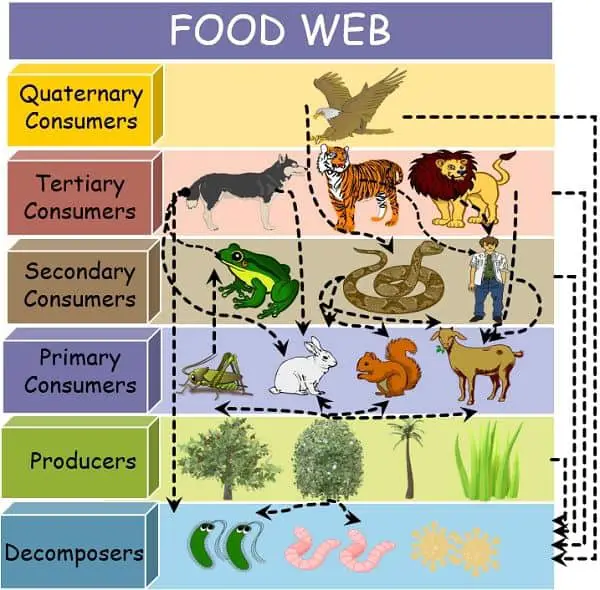
What is a Food Web?
The food web is a complex representation of the energy flow that summarizes all kinds of basic food chains. It portrays the actually occurring interactions among the various species in the real world.
It is a more realistic and dynamic tool to reveal the several different approaches by which the biotic factors stay connected. The food web is not an isolated or linear sequence in any ecosystem. Instead, it is interconnected and interlocked and has multiple trophic levels at the same time.
The Food web is often referred to as a consumer-resource system. It is formed when various food chains operate simultaneously.
Definition of Food Web
We can define the food web as:
“A complex zigzag representation that exhibits the energy circulation between the multiple trophic levels all at once”.
Characteristics of Food Web
- The food web creates an intricate but accurate network between already existing food chains in the ecosystem.
- Here, a single species can perform different roles and can be present at multiple trophic levels. Thus, it is a more precise display of what really occurs in the environment.
- It provides the optimum conditions for any species to enhance adaptability and competitiveness. This increases the organism’s probability of survival.
- The food web is exceptionally stable as no one organism solely relies only on one species for food. Thus, the elimination of one organism will not cause a severe disturbance in the operations of the food web.
- The food web is complicated due to the presence of variety in taste, preference, availability, and many related factors. It doesn’t obligate any organism to follow a strict diet completely.
For example, the tigers do not consume aquatic species like fish, crabs in the forest. But in Sundarbans, the tigers have adapted themselves to survive over the easily available aquatic fauna. - Food seasonality also influences the working of the food chain.
- Food webs consist of some particular species that are keystone species. We refer to these top predators as apex predators.
Food seasonality
It infers the availability of biotic communities on the basis of abiotic factors like temperature, photoperiod, etc.
For example, Certain species are seasonal specialists. They decouple themselves from the food chain for their survival. Like in winters, migrating to different places arresting their metabolic action through
- Hibernation
- Senescence
- Diapause
Or through aestivation in summers.
This food seasonality impacts the other group of species as they are now bound to feed on the available sources.
Keystone species
These are certain species that decide the stability and sustainability of the ecosystem. Elimination of these organisms might lead to the collapse of the food web.
For example, Grizzly bears are among the top predators in forest ecosystems. The collapse in their number will severely impact the food web.
Importance of Food Web
- The food webs make it very convenient to understand interactions and interrelations among the various species.
- We can easily define the energy circulation within the ecosystem with the help of the food web.
- It is helpful in understanding the disastrous consequences of the entry of toxins or any poisonous elements in the food chain.
- The food web also exhibits the natural selection process very efficiently. We can monitor the influence of environmental problems on natural flora and fauna with the food web.
For example
- Scarcity of food
- Overhunting
- Poaching
- Urbanization
- Population explosion
Key Differences Between Food Chain and Food Web
Given below are the important point which differentiates the Food Chain and Food Web:
- The food chain is a simple pathway that defines energy flow from lower to higher trophic levels. Whereas, the food web is a complex representation of the energy flow between the multiple trophic levels.
- In the food chain, a single series shows the interaction between the organisms of succeeding trophic levels. In contrast, there are numerous food chains summarized in a food web.
- One group of organisms strictly depend on the other. And thus, disruption in a single trophic level might collapse the whole food chain. In the food web, there is a multi-dependency among the trophic level. Thus, there will be no significant damage to the entire structure of the food web.
- One trophic level of a food chain relies on the preceding trophic level for food and energy. While in the food web, a single trophic level can depend on many other trophic levels for its food.
- There is always a risk of instability and unsustainability in the case of the food chain. But there is an immense amount of stability and sustainability in the food web.
- A typical food chain comprises about 4-6 trophic levels. In contrast, a food web constitutes several trophic levels.
Conclusion
Food chain and food web are ecological food maps that define the direction of energy flow. Both of them serve the purpose of understanding the relations between the biotic community. These concepts determine the real picture of the interaction in the environment. But their use might slightly vary as per your need.
You should study a food chain if you are trying to gain basic knowledge about the energy flow. Whereas, if you want to learn about the complex relations among the multiple trophic levels you should study a food web.

Kashish says
Very nice and useful answer…thk uh vry much
Rupchan Hussain says
It is very helpful for everyone, Thank you
Jewel Ahmed says
Thank you for sharing.
Reha says
Well was very productive work .
Gay Bish Boi says
Thank you
Puseee says
This was really helpful ty 🙂 great job!