Covalent bond occurs between the two non-metals, metallic bond occurs between two metals and the ionic bond occurs between the metal and the non-metal. Covalent bond involves the sharing of electrons, while metallic bonds have strong attractions and ionic bonds involve the transferring and accepting of electrons from the valence shell.
The adhering property of an atom, in order to arrange themselves in a most stable pattern by filling their outermost electrons orbit. This association of atoms forms the molecules, ions or crystals and is referred to as chemical bonding.
There are two categories of chemical bond on the ground of their strength, these are primary or strong bonds and secondary or weak bonds. Primary bonds are covalent, metallic and ionic bonds, whereas secondary bonds are the dipole-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonds, etc.
After the introduction of quantum mechanics and the electrons, the idea of the chemical bonding was put forth during the 20th century. With the discussion on the chemical bonding, one can get the knowledge of the molecule. The molecules are the smallest unit of the compound and provide information regarding the compounds.
On the way of highlighting the difference between the three types of bonds, we will be reviewing about their nature along brief description.
Content: Covalent Vs Metallic Vs Ionic Bonds
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Covalent Bond | Metallic Bond | Ionic Bond |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | When there is a strong electrostatic force of attractions between two positively charged nuclei and the shared pair of electrons is called the covalent bond. | When there is the strong electrostatic force of attractions between the cation or atoms and the delocalized electrons in the geometrical arrangement of the two metals, is called a metallic bond. | When there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between a cation and an anion (two oppositely charged ions) of elements is called the ionic bond. This bond is formed between a metal and a non-metal. |
| Existence | Exist as solids, liquids and gasses. | Exist in the solid state only. | They also exist in the solid state only. |
| Occurs between | Between two non-metals. | Between two metals. | Non-metal and metal. |
| Involves | Sharing of electrons in the valence shell. | The attraction between the delocalized electrons present in the lattice of the metals. | Transfer and accepting of electrons from the valence shell. |
| Conductivity | Very low conductivity. | High thermal and electrical conductivity. | Low conductivity. |
| Hardness | These are not very hard, though exceptions are silicon, diamond and carbon. | These are not hard. | These are hard, because of the crystalline nature. |
| Melting and Boiling Points | Low. | High. | Higher. |
| Malleability and Ductility | These are non-malleable and non-ductile. | Metallic bonds are malleable and ductile. | Ionic bonds are also non-malleable and non-ductile. |
| Bond | They are the directional bond. | The bond is non-directional. | Non-directional. |
| Bond energy | Higher than the metallic bond. | Lower than the other two bond. | Higher than the metallic bond. |
| Electronegativity | Polar covalent: 0.5-1.7; Non-polar<0.5. | Not available. | >1.7. |
| Examples | Diamond, carbon, silica, hydrogen gas, water, nitrogen gas, etc. | Silver, gold, nickel, copper, iron, etc. | NaCl, BeO, LiF, etc. |
Definition Covalent Bonds
The covalent bond is observed in an element which lies towards the right of the periodic table which is non-metals. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of the electrons between the atoms. The pairing of the shared electron, produce a new orbit around the nuclei of both the atoms referred to as molecule.
There are strong electrostatic attractions between the two nuclei of an atom and the bond is formed when the total energy while bonding is lower than the energy which was earlier as individual atoms or nearby electronegative values.
The covalent bonds are also known as molecular bonds. Nitrogen (N2), hydrogen (H2), water (H2O), ammonia (NH3), chlorine (Cl2), fluorine (F2) are some of the examples of the compounds having covalent bonds. Sharing of electrons allows the atoms to obtain the stable outer electron shell configuration.
There are two types of covalent bonds, polar and nonpolar. This division is on the basis of electronegativity, as in case of non-polar bonds the atoms share the equal number of electrons as the atoms are identical and have the electronegativity difference less than 0.4.
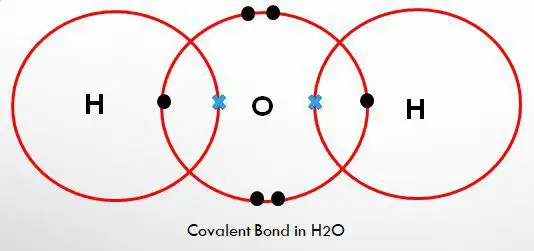
For example, water having the formula as H2O, in this the covalent bond is between each hydrogen and oxygen molecules, where two electrons are shared between hydrogen and oxygen, one from each.
As a hydrogen molecule, H2 contains two hydrogen atom which is linked by the covalent bond with oxygen. These are the attractive forces between the atoms occurring in the outer most orbit of the electrons.
Definition of Metallic Bonds
The type of chemical bond which is formed between the metals, metalloids, and alloys. The bond is formed between the positively charged atoms, where the sharing of electrons takes place in the structures of cations. These are considered good conductors of heat and electricity.
In this type, the valence electrons continuously move from one atom to other as the outermost shell of electrons of each metal atoms overlaps the neighboring atoms. So we can say that the in metal the valence electrons continuously moves independently from one place to another throughout the entire space.
Due to the presence of the delocalized or free-electrons of the valence electrons, Paul Drude came up with the name “sea of electrons” in 1900. The various characteristics properties of the metals are; they have high melting and boiling points, they are malleable and ductile, good conductors of the electricity, strong metallic bonds, and low volatility.
Definition of Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are defined as the bonds between the positive ion and the negative ion, having the strong electrostatic force of attraction. Ionic bonds are also called as electrovalent bond. The atom that gains or loses one or more electrons is called an ion. The atom that loses the electrons attains the positive charge and is known as the positive ion, while the atom that gains the electrons attains the negative charge and called as the negative ion.
In this type of bonding, the positive ions are attracted towards the negative ions, and the negative ions are attracted towards the positive ions. So we can say that opposite ions attract each other and like ions repel. So the opposite ions attract each other and make the ionic bond due to the presence of an electrostatic force of attraction between the ions.
The metals in the outer most orbit have only a few electrons, therefore by losing such electrons the metal achieve the noble gas configuration and thus satisfy the octet rule. But on the other hand, the valence shell of non-metals have only 8 electrons and therefore by accepting the electrons they attain noble gas configuration. The total net charge in the ionic bond must be zero. The acceptance or donation of the electrons can be of more than 1, in order to satisfy the octet rule.
Let’s take the prevalent example of the Sodium Chloride (NaCl), where the outermost orbit of the sodium has one electron, while chlorine has seven electrons in the outermost shell.
So, Chlorine needs only one electron to complete its octet. When the two atoms (Na and Cl) are put close to each other, the sodium donates its electron to chlorine. Thus by losing one electron sodium becomes positively charged and by accepting one electron chlorine becomes negatively charged and becomes chloride ion.
Key Differences Between Covalent, Metallic and Ionic Bonds
Given below are the points which differentiate among the three types of strong or primary bonds:
- Covalent bonds can be said when there is the strong electrostatic force of attractions between two positively charged nuclei and the shared pair of electrons. While metallic bonds have the strong electrostatic force of attractions between the cation or atoms and the delocalized electrons in the geometrical arrangement of the two metals. When there is the strong electrostatic force of attraction between a cation and an anion (two oppositely charged ions) of elements is called ionic bond and is formed between a metal and a non-metal.
- Covalent bond exists as solids, liquids and gasses, metallic bonds and ionic bonds exist in the solid state only.
- Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals, metallic bonds is between two metals, while ionic is observed between non-metal and metal.
- Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons in the valence shell, metallic bonds are the attraction between the delocalized electrons present in the lattice of the metals, and ionic bonds are referred as the transferring and accepting of electrons from the valence shell.
- Conductivity is low in covalent and ionic bonds, though high in metallic bonds.
- Covalent bonds are not very hard, though exceptions are silicon, diamond, and carbon, even the metallic bonds are not hard, but ionic bonds are hard, because of the crystalline nature.
- Melting and boiling points of the covalent bond are low unlike the metallic bonds and ionic bonds which have higher.
- Metallic bonds are malleable and ductile, while covalent bonds and ionic bonds non-malleable and non-ductile.
- Bond energy is higher in covalent and ionic bonds than the metallic bonds.
- Examples of covalent bonds are diamond, carbon, silica, hydrogen gas, water, nitrogen gas, etc., whereas Silver, gold, nickel, copper, iron, etc. are examples of the metallic bonds and NaCl, BeO, LiF, etc. are the examples of the ionic bonds.
Similarities
- They all have the electrostatic force of attractions which makes the bonds stronger.
- They connect one atom to another.
- The bonding between the atoms results to form a stable compound.
- All three types of bonding yield different properties, then the original elements.
Conclusion
In this content, we studied the different types of strong bonds and their various properties by which they vary from one another. Though they have certain similarities too. The study of these bonds is essential to identify them and can use them carefully and wherever needed.



Asif Khan says
Thank you.now I am crystal clear about the different types of bonds and their key difference
teter jjkjk says
Thanks For This Covalent, Metallic and Ionic Bonds Chart
Berns says
Thank you for this info, really good