Both the xylem and phloem are complex permanent tissues. But they perform different roles in plants. The xylem facilitates the transportation of water from roots to the other part of the plant. Whereas the phloem aids the translocation of photosynthesized food material from the source to the other part.
Content: Xylem Vs Phloem
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Xylem is the complex tissue of plants, responsible for transporting water and other nutrients to the plants. | Phloem is living tissue, responsible for transporting food and other organic materials. |
| Contains | Dead cells (parenchyma is the only living cells present in the xylem). | Mainly contains living cells (fibers are the only dead cells in the phloem). |
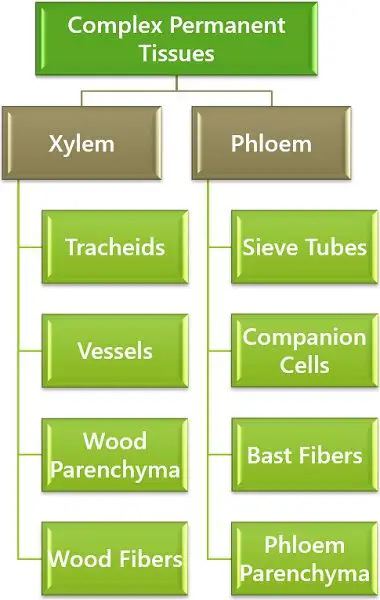
| Comprises of | Xylem vessels, fibre and tracheids. | Phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells, phloem parenchyma and companion cells. |
| Found | Xylem is located in the centre of the vascular bundle, deep in the plant. | Phloem is located on the outer side of the vascular bundle. |
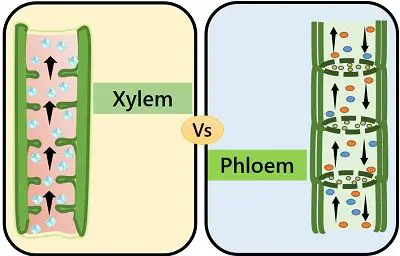
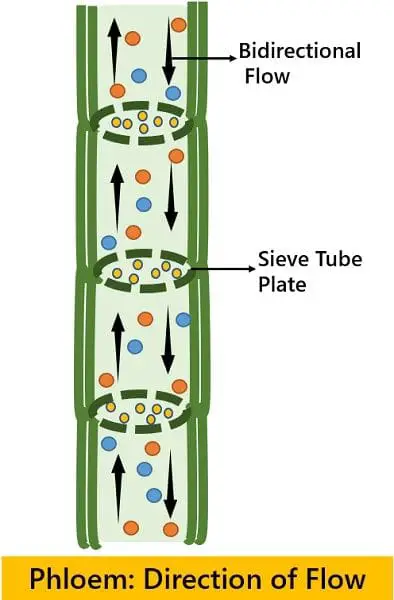
| Kind of movement | Unidirectional. | Bidirectional. |
| Role | Xylem transports only minerals and waters from the roots. | Phloem transports food materials that are prepared by the green parts of the plants to other parts of the plant. |
| Provide mechanical support. | Does not provide mechanical support. | |
| Other features | Xylem is the dead tissues at maturity, but no cell contents. | Phloem is the living tissue, but not with the nucleus. |
| Xylem often constitutes the bulk of the plant body. | Phloem forms a small part of the plant body. | |
| In xylem, the conducting cells or tracheary cells are dead. | In phloem, the conducting cells are living. |
What is Xylem?
The word xylem has its origin from the ancient Greek term xylon, which means wood. This term was first given in the year 1858 by Carl Nageli. Xylem is a permanent, complex vascular bundle required to transport sap and water. They become hard with the gradual growth of a plant and transform into the wood.
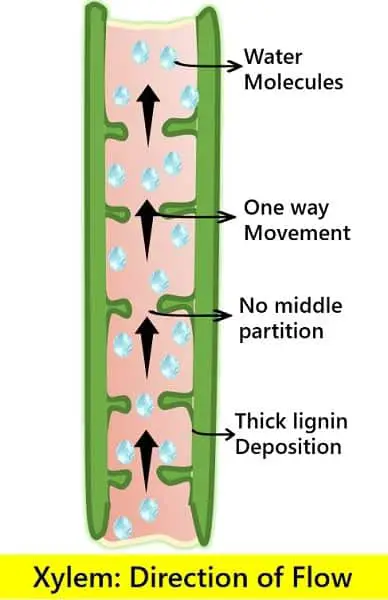
The xylem tissues carry water, salt and minerals only from the root region to the upper plant organs. Thus, this flow is unidirectional only. These tissues have to carry the materials against the gravitational pull.
Importance of Xylem
The major function of the xylem is to carry and supply the water from roots to the other plant parts. The water can act as a limiting agent in the plant’s growth, development, and productivity. It also determines the vegetation of a particular area. Thus, we can guess the importance of water transport in the plant from this.
Xylem Functioning
Xylem tissues transport the water, minerals, salts and other inorganic material from roots to the different plant parts. This material flowing through the xylem is referred to as xylem sap. The system which enables this transport in the upward direction, i.e., against gravitational force, is known as capillary action. This mechanism of capillary action relies on the surface tension of the liquid.
Note: This movement of xylem sap doesn’t require any external energy, and thus, it is a type of passive transport.
Types of Xylem
All types of xylem perform the same function. But we can classify the xylem based on the type of growth- Primary and Secondary.
- Primary Xylem
They are generated during the primary growth of the plant. Mainly present in the rapid growth regions like- tips of roots and shoots, flowering bud, etc. . Their function remains the same of transporting the water and sap. Along with this, they elongate the roots and shoots to make the plant longer.
- Secondary Xylem
They grow during the secondary growth of a plant. These xylems thereby increase the girth of the plant body that widens the tree trunks. The dark rings that determine the age of the plant are due to these secondary meristems only. They are very prevalent in two plant groups- angiosperms and gymnosperms.
Example: Conifers, mango tree, pines etc.
Development of Xylem
- Protoxylem: At the time of primary plant growth, the first xylem develops, i.e., the protoxylem. The protoxylems comprise smaller cells with thin and narrow vessels. Some of their cells have thick walls that produce rings and helices. They can grow in size with gradual shoot and root elongation.
- Metaxylem: The metaxylem during the later stages of plant growth. They are larger cells. They are thickened from outside by scalariform (ladderlike transverse bands) or by continuous sheets (pitted).
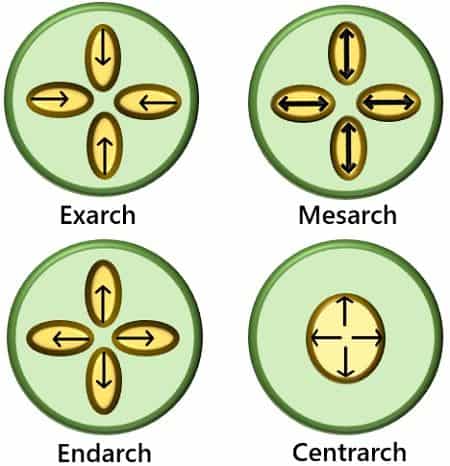
The arrangement of protoxylem and metaxylem in the plant is in four patterns:
- Endarch
- Exarch
- Mesarch
- Centrarch
What are the Components of the Xylem?
Xylem comprises four types of cells in which, some of which are living and some of them are dead.
The xylem tissue constitutes four primary components:
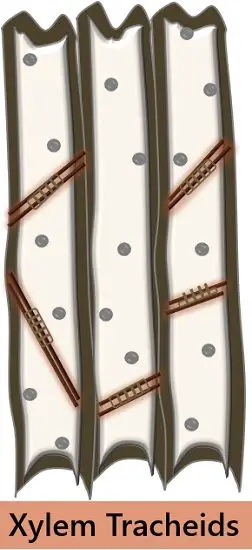
- Tracheids: Tracheids are the fundamental cells of xylem tissue. These are elongated tubular cells with tapering chisel-like ends. They possess lignified cell walls and are devoid of cytoplasm. On the basis of the thickening of the lignin layer, the tracheids are of the following types:
- Pitted
- Reticulate
- Spiral
- Annular
- Scalariform
2. Vessels: Also known as Tracheae. These ar4e long cylindrical tube-like cells. They gradually lose their protoplasm thereby are dead at maturity. These cells are interconnected with the small holes in the common walls for the passage of material. The walls of these vessels are hard due to lignin deposition but are not very thick. The cellular ends are generally round.
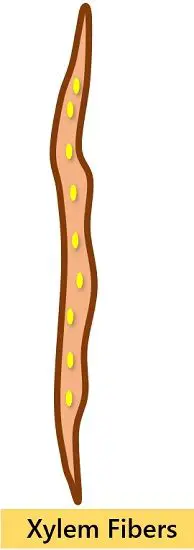
3. Xylem Fibers: Also known as wood fibres. Made up of dead sclerenchymatous tissues produce long, narrow fibres with tapering ends. Their major function is to provide mechanical support.
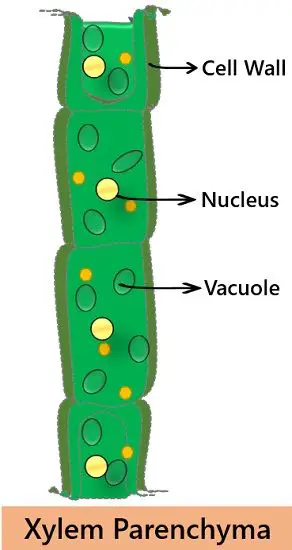
4. Xylem Parenchyma: These are the only living component in the xylem tissue. Their primary purpose is storing starch and food. They help in the conduction of water over shorter distances.
What is Phloem?
Like xylem, the term phloem also originates from the ancient Greek language. It comes from the pholoios, which refers to ‘bark’. Carl Nageli introduced it in 1858.
Phloem is the complex permanent tissue responsible for the conduction of food material in plants. Green plant parts produce organic food with naturally available inorganic matter during photosynthesis. Phloem plays the role of the conductor to transport this food material to the different plant parts for uniform growth.
Note: The process of food transportation in plants via Phloem is called translocation.
Importance of Phloem
For long-distance transport of food material, the Phloem is the only tissue. The food generated in the source organs is efficiently carried to the sink organs for their sustainable growth. The translocation mechanism relies on different hydrostatic forces between the source and sink organ. Mainly the turgor pressure translocates the food assimilates.
Working of Phloem
The translocation process is an active type of transport that demands energy in the form of ATP. The Phloem utilizes the turgor pressure for transportation purposes. The higher solute concentration inside the cell will create an osmotic gradient. This will draw the water from the nearby xylem to establish the equilibrium. The now generated sugar solution will exert a high turgor pressure over the walls of Phloem. The turgor pressure pushes the soluble sugar molecules to move the phloem tube, further moving to the sink organ.
As soon as the sink gets the soluble sugar, it gets accumulated by the part where it is required. With the gradual reduction in the sugar concentration, the amount of water influx from the xylem also falls. Thus, the sink tissues experience low pressure. In this way, the food material gets transported constantly around the plant sink organs, i.e., between higher and lower pressure areas.
Bidirectional flow in Phloem
As we all know, the green plant part synthesizes the food and thus are the sources. While the other non-green plant parts like roots are sink as they utilize the food translocated through Phloem. Since the green leaves are part of the shoot system, the movement is from up to down.
But during early springs or autumn, the plant’s significant food sources shed off. In this scenario, the soluble sugars present in the roots move upward to nurture the growing buds and leaflets. Thereby, it is very evident that the flow of phloem transport is bidirectional, i.e., from upward to downward and vice versa.
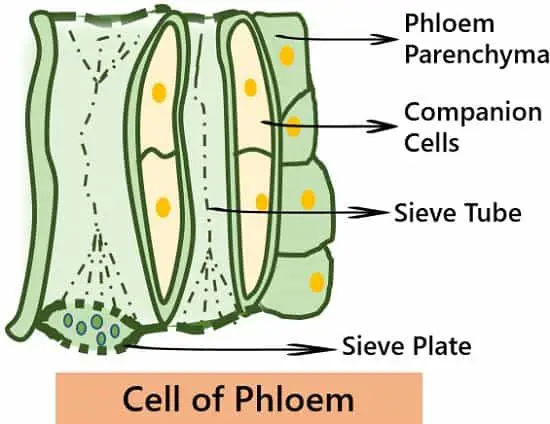
Components of Phloem
The Phloem has its prime components:
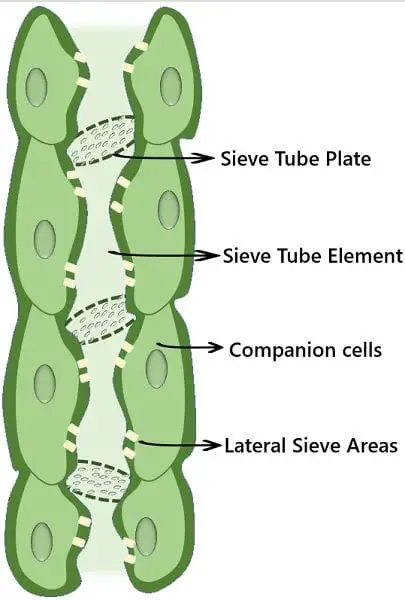
- Sieve tubes
- Sieve tubes are living anucleated cells with a thin layer of cytoplasm.
- The cytoplasm of two adjoining sieve tubes is continuous due to the pores present in the sieve plate.
- They have sieve plates that are either oblique or transverse perforated septa.
- They form the elongated conducting channels of Phloem that lie one on the other in a linear pattern.
- Companion cells
- Companion cells are thin-walled, elongated living cells.
- They possess protoplasm with a big sized nucleus.
- Found usually anchored to the sieve tubes at the lateral side.
- They are connected to the sieve tubes through simple pits on the outer surface.
- They are prevalent in angiosperms but absent in lower plants like pteridophytes and gymnosperms.
- Their primary purpose is to aid the translocation with the sieve tubes.
- Phloem Parenchyma
- These are fundamental parenchymatous cells.
- They develop in association with companion cells and sieve tubes.
- They are absent in monocot plants as well as in some dicots.
- A major role is to store food and later translocate the same food.
- Phloem Fibres
- Also called Bast cells.
- They are dead sclerenchymatous cells that have a fibrous appearance in the Phloem.
- They have lignified cell walls along with simple pits.
- Their primary role is to strengthen the phloem tissue and support translocation.
- These fibres on drying are utilized for making ropes and rugs.
Types of Phloem
We can differentiate Phloem as protophloem and metaphlem.
- Protophloem
- They grow in the initial growth phase of the plant during the process of enlargement.
- They constitute thin enucleate sieve elements present either singly or in groups.
- Companion cells may or may not be present.
- Metaphloem
- They are the primary Phloem that grows when the enlargement is stopped.
- The sieve components are broader and elongated.
- Companion cells are surely present.
- The phloem fibres are absent.
- And the parenchymatous cells become sclerides.
Key Differences Between Xylem and Phloem
- The xylem handles the transportation of water and sap material. While the phloem tissues translocate the soluble organic material.
- Xylem tissues also provide some mechanical strength and support to the plant body. Whereas the phloem doesn’t give any strength to the plant’s framework.
- The conduction of water by the xylem is a unidirectional flow. This takes place from roots to the upper parts of the plant. On the other side, phloem translocates the food material bidirectional manner. This type of flow carries from shoot to root and vice versa.
- Conducting elements in the xylem are tracheids and vessels. While phloem has only one conducting element i.e., sieve tube.
- Xylem vessels are deprive of septa. In contrast, the sieve tubes possess thick, bulged and porous septa.
- The conducting cells of xylem tissue have a lignin coating. Whereas the conducting cells of phloem are not lignified.
- Xylem has three kinds of dead cells- vessels, fibres and tracheids. While the phloem has only one type of dead cell- phloem fibres.
Similarities
- The cell wall is made up of cellulose in both the xylem and phloem.
- Xylem and phloem both contain chloroplast.
- Both of them contain vascular tissue, which helps in the transportation of material throughout the plant.
- Parenchymatous cells are present in both of them.
Conclusion
The two most important complex kind of tissue, constituting vascular bundles is the xylem and phloem. We discuss the role that the xylem is responsible for transporting water and other soluble materials in the plant unidirectionally.
On the contrary, the role of phloem is to transport the food and other organic material produced by leaves (through the process of photosynthesis). Hence both the vascular tissues have their equal importance, which is necessary for the growth of the plants.


Arundeep says
it is a very important difference, I like it. Thanks
Aditya varshney says
It is very useful website……..
A Supertramp says
Thank
Laibah Shahid says
It clears all the doubts and confusion and it’s proper presentation
kaira says
Thanks. It clears all my doubts…