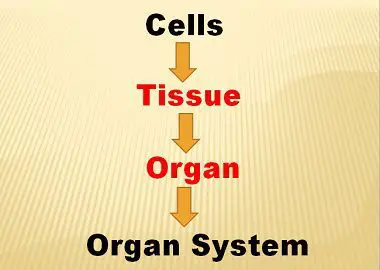
Cells make tissues and tissues make an organ, and different organs present in the body make an organ system. The tissue is capable of performing the simple task while organs are known for operating the complex one. Though the size of the organ is greater than the tissue and requires more energy to perform any function.
Living organisms have great diversity, whether living in water or land, but shares the essential component in common that is ‘the cell‘. Being the primary part of every life, the cell varies in their complexities from one organism to other, and this makes every species diverge. The whole biology is studied under two important categories, which are unicellular and multicellular.
Unicellular are the single-celled organisms like protozoans, while multicellular is the organisms having two or numerous cells. We humans and other mammals having the complexed cellular structure with the higher level of multicellularity. Due to which we need a proper organization of the cells to get our body and its internal part work accordingly. So our body also has some levels of systems or configuration according to which it works.
Cells, tissues, organs, and organs systems are part of this system only; these systems work for the body just to maintain the legitimate health. In this article, we will be going through the differences between two of the levels of the human body which are tissue and organs with a brief description.
Content: Tissue Vs Organs
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Tissue | Organ |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Tissues are evenly distributed structures in the body, performing the specific function. These are found in plants and animals, made up of similar cells and function specifically. | Organs are the hollow structure, made up of tissues, and organised to work precisely for the body in animals as well as in plants. |
| Made up of | The same type of cells. | The same type of tissues. |
| Repairing process | If there is some damage in tissue, they can be repaired by regeneration and fibrosis. | As tissues make organs, so repair in tissue, will result in repair of the organ. |
| Function | Numerous and similar cells make tissue, and this tissue forms organs. They have the certain unique function in the body. | Different organs work for different purpose like breathing, pumping blood, digestion, etc., and these organs together form an organ system. |
| Examples | Nerve tissue, muscles tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue. | Stomach, lungs, heart, intestine, bladder, brain, kidney, etc. |
Definition of Tissue
When the specific and similar type of cells are grouped or organized together constitute the tissue. These tissues are assigned to perform the specific function. The ‘histology‘ is the term used for the study of animal and human body tissue while for the study of plant tissue the term is known as ‘plant anatomy‘.
With the invention of the electron microscope, it is observed that the cells present within the tissues shows the morphological similarities and so can be said that they have the common embryonic origin too. It is also found that the cells are properly arranged and thus helps tissue to work in the formation of the organ. Animal tissues are categorized into four types, like connective tissue, nervous tissue, epithelial tissue, and muscles tissue.
Connective tissue – It connects with the group of other tissue and is found between the organs and other tissue. These are the most abundantly and most widely distributed of all the tissue. Connective tissues play many important roles like it support and protect the organs. Dense fibrous tissue, cartilage, bone, lymph, fat tissue, loose connective tissue are some of the following connective tissue in the human body.
Some of the disorder occurs in connective tissue like sarcomas, lupus, scurvy, Marfan syndrome.
Nervous tissue – These tissues are present in the nervous system especially in the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and brain. Neuron or nerve cell is the string and long like structure. The function of nerve tissue and cell (neuron) is different, as it receives stimuli and conduct impulses from all parts of the body.
Alzheimer’s disease – like memory loss, confusion, and mood swings occur due to the problems of nervous tissue. Sclerosis is also one of the diseases due to degeneration of nervous tissue and leads to high brain loss. Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease are also the problems due to the nerve impairment.
Epithelial tissue – These tissue covers the lining the of the most internal cavities. It performs the function of secretion, absorption, protection, and filtration in the body. Skin is one of the organs made up of epithelial tissue and thus protect from dust, dirt and other microorganisms. Epithelial tissue is different types simple epithelium, squamous epithelium, columnar epithelium, etc.
Muscular tissue – This tissue makes muscles of the body. It is of three types skeletal muscles tissues, cardiac tissue, and smooth muscles tissue. It responds to stimulation and supports the movement.
Definition of Organs
The organ is the group of tissues present in a living organism and is assigned to perform the specific task. The stomach, the heart, the kidneys, the skin, and the liver are composed of tissue and together forms an organ system. Various organs perform the various function like pumping of the heart, breathing, reproduction, excretion, protection (skin), etc.
All types of organs are made up of four types tissue. In human anatomy, the variety of organs and organ system studied are:
Endocrine system – This system deals with hormones produced by endocrine glands like pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pineal gland, parathyroid, thyroid and adrenal gland.
Cardiovascular system – This system deals with the pumping of blood from the body, lungs with heart.
Excretory system – Bladder, urethra, kidneys, and urethra are the parts involved in the excretory system.
Muscular system – Involves the movement of muscles.
Respiratory system – Pharynx, larynx, bronchi, lungs, diaphragm, trachea are the parts of used in breathing.
Reproductive system – Testes, vas defrens, vulva, vagina, seminal vesicles, prostate, penis, ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus are the parts of the reproductive system.
Nervous system – Brain, spinal cord, and nerves are used to transfers and process information in the body.
Lymphatic system – It connects tissue and bloodstream and thus supports the immune system and provide protection against the disease.
Digestive system – This system helps in digestion and includes parts like pancreas, gallbladder, colon, rectum, stomach, esophagus, salivary glands and anus are involved.
Skeletal system – It supports and provide shape to the body; it includes parts like tendons, ligaments, bone, and cartilage.
Key Differences Between Tissues and Organs
Following are the few though important points to discriminate between tissue and organs:
- Tissues are the assembly between cells and organs and are evenly distributed structures in the body. They are assigned to perform the fixed task. Tissues and organs are found in plants and animals, made up of similar cells which function in a precise manner. Organs are the hollow structure comprise of tissues and organized to work precisely for the body in animals as well as in plants.
- The tissue is made up of the same type of cells while organs are the outcome of the same type of tissues.
- Tissue play limited though important role in the body and the prior one is to make organs. While breathing, digestion, excretion of body waste, blood circulation are the different function performed by the different organs present in the body.
- Tissues can be repaired by regeneration and fibrosis but as tissues make organs, so repair in tissue, will result in repair of the organ.
- Nerve tissue, muscles tissue, connective tissue, epithelial tissue are the examples of the tissues, while stomach, lungs, heart, intestine, bladder, brain, kidney, etc., are the name of few of the organs.
Similarities
- Tissues and organs are made up of cells.
- The functions of each tissue and organs are particular.
- Both are found in multicellular organisms.
Conclusion
In the above content, we studied the tissue and organs, as well their precise function. We also came to know the critical point on which these two differentiate. Even the cells, tissue and organs are specialized to play different roles. So it’s worthful and correct to say that cells are the fundamental unit of life, from which these are made.

Leave a Reply