Both bones and cartilages are connective tissues. But they vary in their structures and functions.
Bones on one hand are harder, solid and rigid structures. Their primary function is to provide structure and stability to the body. They also protect the internal organs from getting injured.
While the cartilages are soft and flexible tissues. They are present between two bones to support joints. Also, they reduce the impact of friction while moving.
The cells of bones are osteocytes and their growth occurs in a bidirectional manner. They have an active supply of nutrients through proper blood vessels.
On the other side, the cells of cartilages are chondrocytes that grow in a unidirectional fashion. Whereas the cartilages lack blood vessels.
In this context, we will learn the key differences between bones and cartilages.
Content: Bones Vs Cartilage
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Bone | Cartilage |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Bones are the complex structure, made up of connective tissues which are hard and are helpful in providing protection, shape to the body. | Cartilage is the simple structure, made up of connective tissue which is soft and are useful in providing flexibility to the joints and also protect from the external and internal shocks. |
| Features | They are rigid, non-flexible, and tough. | They are flexible and are soft-elastic. |
| Bones grow in both directions (bidirectional). | Cartilage grows in single direction (unidirectional). | |
| Haversian system and Volkmann's canals are present. | Haversian system and Volkmann's canals are absent. | |
| Bone marrow is present (it is a kind of haematopoietic tissue from which all blood cells are made). | Bone marrow is absent. | |
| Lacunae possess canaliculi where each lacuna consist of only one cell (osteocyte). | Lacunae do not possess canaliculi, and each lacuna has two-three chondrocytes. | |
| These are active participants of blood supply. | They are not the participants in blood supply, except in perichondrium. | |
| Matrix consist of the protein called ossein and can be both organic and inorganic. They occur in lamellae and are vascular. They have the deposit of calcium salts largely of calcium phosphate. | The matrix consists of the protein called chondrin, and they are organic. In cartilage, a matrix is said to be as homogenous mass without lamellae. They do not possess calcium salts. | |
| Bones cells are also known as Osteocytes. | Cartilage cells are also known as Chondrocytes. | |
| Bones are hard due to the deposition of phosphates and carbonates of calcium in the matrix. | Cartilage is soft, except the calcified cartilage and matrix is made up of proteins and sugars. |
|
| They are responsible for the formation of the skeletal system, which gives the shape to the body. | Cartilage is found in ear, nose, larynx and trachea. | |
| Types | Two types 1. Compact bone. 2.Spongy bone. | Three types 1. Fibrocartilage. 2. Elastic cartilage. 3. Hyaline cartilage. |
What are Bones?
Bones are a type of connective tissue that is strong, hard, and rigid. They support the structural organization of a vertebral body.
They provide a structural framework to a body. This structural bony framework is called a skeleton or endoskeleton. It protects the delicate and soft internal organs from external factors like a jerk. Without These tissues, our body might not be able to move as they aid the locomotion of a body.
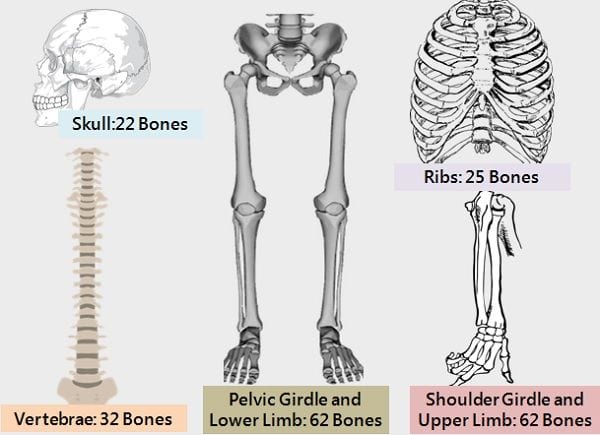
At the time of birth, we have around 300 bones. As our body grows, some of them fuse. Due to this, an adult has only 206 bones.
Definition of Bones
“Bones are living connective tissues that provide structural strength and a proper shape to a body”.
Function of Bones
- Prevents the internal fragile tissues and organs from damage.
- Delivers the necessary mechanical support to the body.
- Gives a proper shape and structure to the body.
- Acts as site (bone barrow) for the formation of blood cells.
- Protects the components of the nervous system i.e., brain and spinal cord from getting hurt.
- Serves as a mineral reservoir that controls the level of calcium and phosphate in the blood flow.
Formation of Bones
Bone formation is a replacement process. As the body continuously grows and develops, the soft tissues are replaced by the hard bonny tissues. This is through the process called ossification or osteogenesis.
Osteogenesis occurs in two ways:
- Intra-membranous ossification: This process leads to the formation of flat bones. For instance, clavicle, mandible, and skull bones are formed with this ossification,
- Endochondral ossification: This generates long bones like the tibia, femur, radius, humerus.
Bone modelling forms the new bones at the time of childhood and adolescence. Whereas bone remodelling is the aggregation of both processes of bone formation and resorption that takes place at the time of bone remodelling.
What are the Bones made of?
The bones comprise collagen proteins as well as an indispensable mineral i.e., Calcium phosphate. So we can say that they are mineralized connective tissues.
Bones have four major components:
- Osteoblast and Osteocytes
- Osteoclasts
- Osteoids (Non-mineral matrix)
- Mineralized calcium deposition
The bonny tissues can be separated into two distinct zones based on the level of mineralization. These two distinctive regions are:
- Hard outer layer: Also referred to as compact or cortical bone.
- Spongy inner layer: Also referred to as trabecular or cancellous bone.
There are several other tissues linked along with the bonny tissues. For example, cartilages, endosteum, periosteum.
These connective tissues have sufficient blood supply through the proper vascular arrangement. The bonny tissues discharge the stored calcium into the bloodstream at regular time intervals.
Types of Bones
a. Based on the arrangement of collagen fibres
On the basis of the arrangement of collagen fibres forming a distinct pattern in osteoid, they are of two types:
- Woven
- These are weak and fragile.
- Contain messy, jumbled, and disorganized arrangement of collagen threads.
- Lamellar
- Have collagen fibres arranged in a parallel manner.
- These are strong and solid.
b. Based on Size, Shape, and Structure
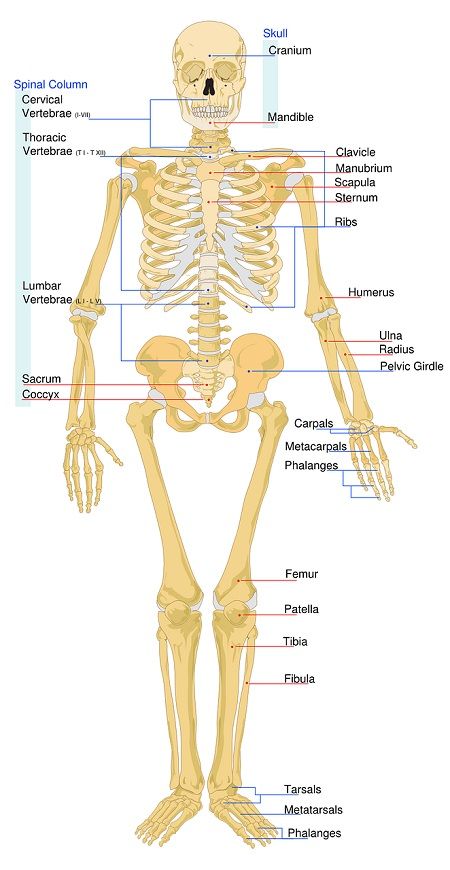
- Long: The bones of limbs are relatively longer. They have a long shaft and curvy ends.
Example: Ulna, femur, humerus, radius, tibia, and fibula. - Short: They are present in the regions like the ankle and wrist.
- Flat: These are thin flat and are slightly curved. Located in sternum and skull portion.
- Irregular: These are present spinal region and hips.
- Sesamoid: They are located at limited places in the body. Significantly present in kneecaps.
- Sutural: These are very small-sized. Mainly found between the cranial region. They vary from one person to another.
Note: The largest bone is the femur or thigh bone, and the smallest bone is the stapes, which is present in the middle ear.
Disorders related to Bones
- Fractures: Is is a simple breaking, cracking, or twisting of bone.
- Osteoporosis: This causes the loss of mineral deposition in the bones making them less dense. It makes the them more vulnerable and increases the chances of fracture.
- Osteosarcoma: It is the cancer of bones.
- Osteomyelitis: This is the infection of bone marrow.
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: It is a hereditary disorder that occurs due to disturbance in the genetic makeup of an individual.
What are Cartilages?
The cartilages are thin and soft connective tissues. They are fibrous and flexible in nature. These tissues are less hard than bones but are harder than muscles. This is because they are not stiff and solid as bones. But, they are less elastic than muscles.
These cartilages cannot be stretched as they are rigid. But are soft enough to get bent.
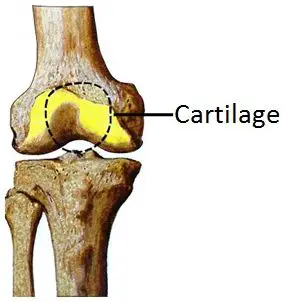
The cartilages are present at different places in our bodies. Like the external ear, larynx, at joint articulates, in the respiratory tract, in-between spinal discs, and the rib region.
Functions of Cartilage
Their primary functions are:
- To connect bones at joints.
- Aid the movement of bones, especially at the joint region.
- Cushioning the bones to prevent the impact of friction while moving.
- To support the tracheal and bronchial pipes while inhalation and exhalation.
- Also, they act as a shock absorber between the subsequent vertebral discs.
Characteristics of Cartilage
- The cartilages deprive blood vessels. Thus, there is no source to supply nutrients to the chondrocytes.
- Thus, the nutrients diffuse through the perichondrium and reach the core of cartilage. This leads to delayed growth and slower repair of the cartilage in comparison to the other tissue.
- The cartilages form the skeleton in the mammalian embryos prior to the formation of bones.
- They are also the essential component of the skeleton of lower vertebrates like smaller fishes.
What are Cartilages made of?
- The cartilages are made up of cells called chondrocytes. These chondrocytes generate an extracellular matrix. The matrix consists of elastin fibres, collagen fibres, and proteoglycan.
- They have a dense framework of collagen threads surrounded by gelatinous substances. This gel-like substance consists of chondroitin sulfate (polysaccharide derivative).
- The gel provides the cartilages with consistency and tensile strength just like plastic. Due to this, these tissues can bear weight and can maintain flexibility. This combined assembly of collagen protein and ground gel is proteoglycan.
- Perichondrium separates the cartilage from its surrounding tissues.
Perichondrium comprises two distinct regions-
- Outer layer: It is a fibrous layer that protects the cartilage. It also gives mechanical support and connects the cartilage to the surrounding structures.
- Inner layer: It aids the proper growth and maintenance of cartilage.
Types of Cartilages
Cartilage is of three types:
- Elastic Cartilage: Found in the ear, as it is the most flexible type.
- Hyaline Cartilage: Present at the end of ribs and in the nose, it is the second most flexible type of cartilage.
- Fibro Cartilage: Present in the knee, as well as between the spinal column.
Key differences between Bones and Cartilage
- Bones are hard and complex connective tissues. They are helpful in providing protection and shape to the body. While cartilages are simple and soft connective tissue. They provide flexibility to the joints, thereby avoiding the damage from shocks.
- Bones are rigid, non-flexible, and tough, whereas cartilage is flexible and are soft-elastic.
- Bones grow in both directions (bidirectional). While cartilage grows in a single direction (unidirectional).
- The bones have an active and properly channelled supply of blood. But the cartilages lack blood vessels.
- The bones comprise osteocyte cells. While the cartilages have chondrocyte cells.
- Bones are hard due to the deposition of phosphates and carbonates of calcium. Cartilages are soft as they constitute simple proteins and sugars. Except for the calcified cartilage.
Conclusion
As from the above article, we come to know the importance of connective tissue in maintaining the rigidity, shapes, safety of the body’s and its essential parts. Apart from muscles, bones and cartilage act as the main structural components of the body.

Leave a Reply