Leaves perform crucial functions like photosynthesis, storing food and water etc. But they can vary in their shapes, sizes, colours, arrangements, and patterns based on different environmental conditions. On the basis of these differences, we can broadly classify the leaves as-Simple and Compound.
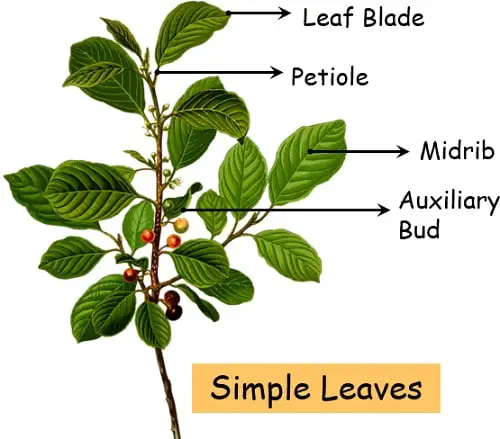
The simple leaves are the one which bears a single leaf blade or lamina that remains undivided. The lamina consists of margins, but they are not deeply incised upto the midrib.
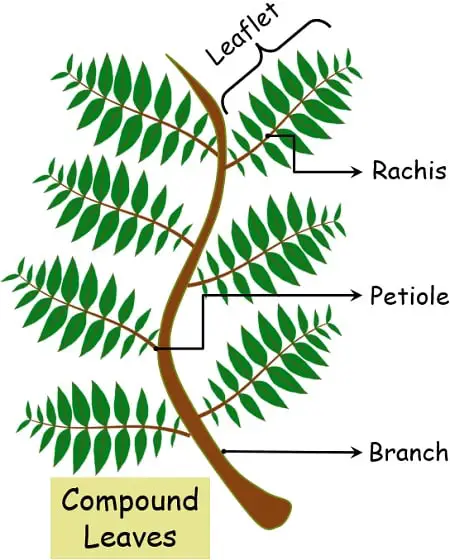
On the other hand, the compound leaves consist of segmented leaf blades, i.e., the lamina remains divided into small leaf-like projections called leaflets or pinna.
The simple leaves remain aligned in acropetal succession. In comparison, acropetal succession is not present in compound leaves.
Stipules are present at the base of the simple leaf. In contrast, they are not present near the basal end of each compound leaf.
Every simple leaf comprises of an axillary bud at the axis. In contrast, the compound leaf has no axillary bud.
Here, we will discuss the key differences between the simple and compound leaves with a comparison chart, characteristics and structure.
Content: Simple Vs Compound Leaves
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Simple Leaves | Compound Leaves |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Such leaf in which the leaf blade or lamina is undivided into lobes is called simple leaf, and the arrangement of such leaves are in acropetal succession. | The leaf which properly shows the division of leaf blade or lamina into leaflets is called as compound leaves. These leaves do not make acropetal succession arrangments of the leaflets. |
| Leaf blades | They have single blades. | They have smaller and separate leaf blades called leaflets. |
| Axillary bud | Bud is placed in the axil (near the petiole and stem). | Each leaflet does not have axil, though buds are placed in the axil of the leaf. |
| Division in lamina | There is no division of lamina. | The lamina is divided into more than two leaflets, arising on the side of a rachis or at the tip of the petiole. |
| Stipules | The base of a leaf contains stipules. | The stipules are found at the base of the leaf, but other additional structures are absent. |
| Examples | Black gum trees, Black cherry trees, Guava, Mangoes, various types of Oaks. | Rose, Neem, Shame plant, Buckeye. |
What are Simple Leaves?
A simple leaf is basically a single unit that consists of no division or segmentation of the leaf blade. It is one flat undivided structure that remains attached directly to the stem via petiole. And since it forms no further sub-division of itself and remains simple in structure, thus we refer to it as a simple leaf.
Generally, the simple leaves are visibly distinct from compound leaves because of their size, arrangement and segmentation. But there are certain exceptions where it becomes difficult to distinguish between simple and compound leaves. Thus, the ideal way to identify whether the leaf is simple or compound is by the presence of an axillary bud.
Examples of the plants having Simple Leaves
There are many examples which will explain the pattern the simple leaves have. Some of the common examples are:
- Pear
- Oregano
- Hibiscus
- Maples
- Black oak
- Scarlet oak
- Sycamore
- Elm
- Oak
- Cherry
- Birch
- Guavas
- Mangoes
Characteristics of Simple Leaves
- The leaf blade or lamina is completely undivided.
- Axillary bud in the axis of each leaf.
- The marginal edges of these leaves may be smooth, jagged or lobbed.
- The margins are deeply incised but don’t reach upto the midrib.
- The leaflets are absent here.
- The leaves remain aligned in acropetal succession.
- The stipules are present at the base of the leaf.
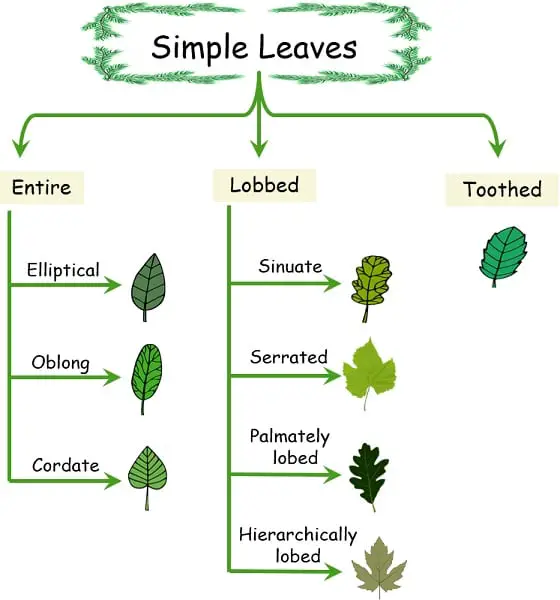
Types of Simple Leaves
Based on the edges of a simple leaf, it can be of three prominent types:
- Smooth or entire
- Lobed
- Parted, toothed or jagged
What are Compound Leaves?
The compound leaves are those where the lamina or the leaf blade remains divided into small leave like structures named leaflets.
Multiple leaflets remain attached to the main stem via a modified midvein called the rachis.
The compound leaves are easy to identify, but the best way of identification is the absence of axillary buds at the end of each leaf.
Some advantageous properties of compound leaves are:
- These leaves reduce the rate of water loss from the plant.
- Help the plant grow rapidly by utilizing them as branches. Thereby they are present in early tropical and early succession species.
Examples of plants having Compound Leaves
- Clover
- Lemon
- Bombax
- Munaga
- Rose
- Neem
- Bauhinia
- Chestnut
- Bell
- Cassia
Characteristics of Compound Leaves
- The leaf blade remains segregated into many small leaf-like parts known as leaflets.
- Leaflets of a leaf will always be present on the same plane.
- The axillary buds are not present at the basal end of the leaf.
- The bud may lie on the axil of the full leaf, but they are not present in every leaflet.
- The incision of the leaf blade extends up to the midrib that divides the lamina into several segments or leaflets.
- The size of the leaflet is much smaller than that of a single simple leaf.
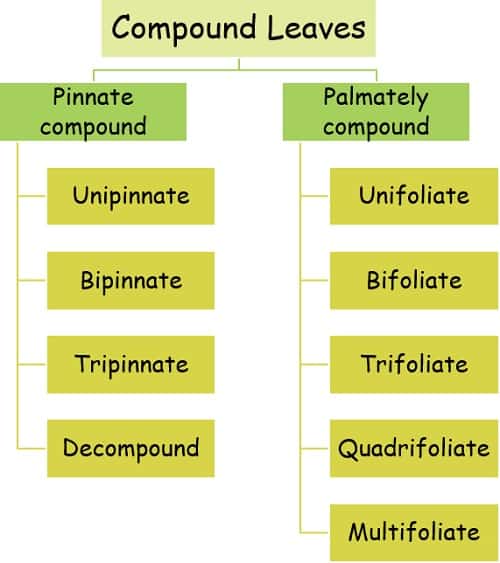
Types of Compound Leaves
Compound leaves are of different forms but are broadly classified as Pinnately Compound leaves and Palmately Compound leaves.
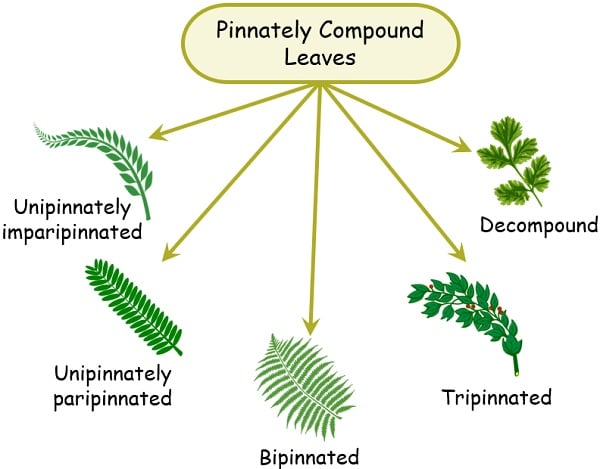
1. Pinnately Compound Leaves
The term ‘pinnation’ refers to the sub-division of a leaf into leaflets. The pinnate leaflet arrangement can be either evenly paired or oddly paired.
In the pinnate leaves, the arrangement of the leaflet is opposite and even are paripinnate leaves. The rachis at the ends (termination point) is sprout with two leaflets. For example, Mahogany, Tamarind, and Candle bush are a few examples.
In pinnate leaves where the leaflets are opposite and oddly arranged are imparipinnate leaves. Here, the rachis at the end sprouts with the single leaflet.
Example: Pecans, Roses, Acacia are some examples.
Based on the pinnation arrangement, pinnately compound leaves are of three types: Unippinate, Bipinnate, and Tripinnate.
- Unipinnate: When there is a regular arrangement of leaflets on the rachis, these are unipinnate leaves.
An example is Azadirachta Indica. - Bipinnate: It is also called twice-pinnate or double pinnate. There is a secondary rachis on which the leaflets are present, apart from the central rachis or axis.
An example is Mimosa pudica, a Honey locust. - Tripinnate: The leaf is thrice pinnate. Here, the secondary axis generates a tertiary axis that again bears a leaflet.
An example is Moringa oleifera. - Decompound: The leaf which consists of more than three pinnae are decompound leaves.
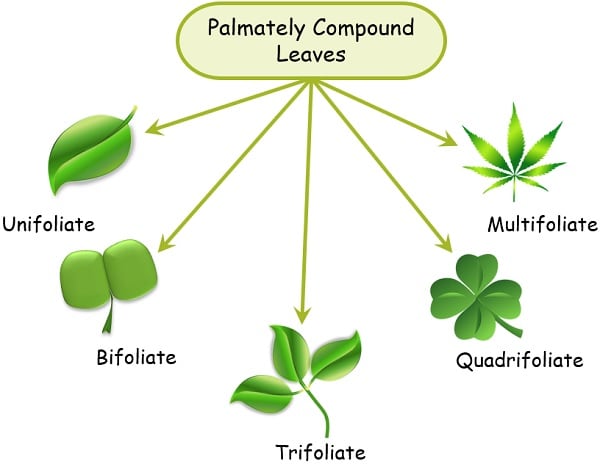
2. Palmately Compound Leaves
The leaves where leaflets arise from the single point of the petiole are Palmately Compound leaves. Here, the arrangement of the leaflets is similar to the fingers of the palm, thus they got the name “palmate”.
We can further divide them as Unifoliate, Bifoliate, Trifoliate, and Quadrifoliate.
Some of the common examples are Citrus maxima, Citrus Limon, Bauhinia, Clover, Oxalis, Marsilea, Buckeye, and Chestnut.
Key Differences Between Simple and Compound Leaves
- In a simple leaf, the lamina remains undivided and remains directly attached to the stem. On the other hand, we can see the proper division of lamina into small leaflets in a compound leaf.
- The arrangement of simple leaves is in acropetal succession. In comparison, compound leaves do not show the acropetal succession of the leaflets.
- Simple leaves have a single leaf blade or lamina, while compound leaves have smaller and separate leaflets, each with a distinct leaf blade.
- The base of a simple leaf contains stipules. But in a compound leaf, the stipules are not present at the base of the leaf.
- Each simple leaf possesses the axillary bud at its base. In contrast, these buds are strictly absent in compound leaves.
- Examples of simple leaves are Black gum trees, Black cherry trees, Guava, Mangoes, and various types of Oaks. While Rose, Neem, Shame plants, and Buckeye are a few examples of compound leaves.
Conclusion
We can easily distinguish between simple and compound based on the structure of leaf blades or lamina. The above context is the overview of the identification of the leaves and how they can be classified by the arrangement of the leaflets. This will help you identify the plant species just by the structure and orientation of its leaf.

TEJARAJ PATIL says
Great work it helped me to understand simple and compound leaves easily…. THANK YOU ✋✋✋✋
Sarah says
Thanks for this. I understand leaves better, now.