All the animals present on earth are either Invertebrates or Vertebrates. Invertebrates make up the larger proportion i.e. approx 98% of the total animal kingdom whereas vertebrates are only 2%.
The invertebrates are organisms with simple structures and uncomplicated living mechanisms. They are known as invertebrates as they lack the vertebral column or vertebrae to support their body. Invertebrates lack a proper endoskeleton and also a developed nervous system.
Contrarily the vertebrates are complex organisms with well-defined structures with intricate life processes. They bear vertebrae for either some period or the whole of their lifetime. The vertebrates possess bony and cartilaginous endoskeletons to support their body organization. They also have developed organ system machinery like the nervous system, respiratory system, digestive system etc.
It is assumed that all the vertebrates have evolved from invertebrates during the process of evolution. Due to which the vertebrates have modified and adapted their bodies as per the changes in the environment. In this section, we will try to know more about vertebrates and invertebrates with a comparison chart, classification and examples.
Content: Invertebrates Vs Vertebrates
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparision | Invertebrates | Vertebrates |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Animals without the backbone. | Animals with the backbone are called Vertebrates, their internal structure is made up of numerous bone. |
| Examples | Insects, roundworms, tapeworms, Sponges, Annelids. | Humans, elephant, birds, snakes, etc. |
| Characteristics | 1.No cell walls. 2.Reproduce sexually. 3. Multicellular. 4.No backbone. 5. Heterotrophic (which depends on other for food) or Parasitic. | 1.Presence of backbone. 2.Cell walls present. 3.Multicellular. 4.Advanced nervous system. 5.Well-developed internal skeleton. 6.The outer covering of protective skin. |
| Size | Small and slow moving. | Vary in size from big to small. |
| Body Symmetry | Radial or bilateral. | Only bilateral. |
| Body structure. | Simple and unorganised nervous system. | Complexed and highly specified organs and their functions. |
| Layers of skin | They have only one layer of skin. | Two layers of skin, outer one in known is epidermis and beneath is dermis. |
| Type of Eyes | Usually, compound eyes are present and which are not outgrowth of the brain. | No compound eyes found and eyes are the outgrowth of the brain. |
| Their presence | 98% of animal species are invertebrates, which identified and counted around 2 millions and much more are yet to be identified. | 2% of the animal species are vertebrates, which are around 57,739 only. |
| Kingdom | Animalia. | Animalia. |
| Phylum | Chordata. | Chordata. |
What are Vertebrae?
Vertebrae are a series of small interlocking bones that combine to produce a long spinal column in which the spinal cord is situated. These tiny bones are interconnected through facet joints that aid the mobility of the spine. This vertebral column thus provides mechanical support and protection to the sensitive spinal cord.
What are Invertebrates?
The living entities that lack the vertebral column or backbone are categorised as invertebrates. They are found in almost all kinds of habitats because of their ability to survive in a variety of environments. Thus, they are highly diversified and are easily found in fresh or marine waters, on lands, desserts, as well as inside another living body as parasites.
Characteristics of Invertebrates
- Among 35 estimated phyla of kingdom Animalia, only one of them possesses the vertebrae(chordates). This manifests that 98 % of the animal kingdom comprises only invertebrates.
- They lack the internal body skeleton, i.e. endoskeleton, to support the inside body organs. They are also deprived of the organised nervous system. For these reasons, they are often referred to as lower organisms.
- Instead, these organisms might have an outer skeleton, i.e. exoskeleton, for protection and support.
- They can have either heterotrophic or parasitic modes of nutrition.
- Have an open circulation system for the transportation of materials.
- The respiration system can be complex or can be simple as diffusion.
- Their body symmetry may be bilateral or radial based on the intricacy of the organisation.
- They are generally poikilothermal, which means they can’t regulate the temperature of their body. Thus, their body temperature keeps on fluctuating as the changes in environment.
- They widely vary in their sizes as they can be as small as microscopic creatures or can be as big as giant squids.
- The prominent reason behind their successful survival is their reproductive ability and their adaptability.
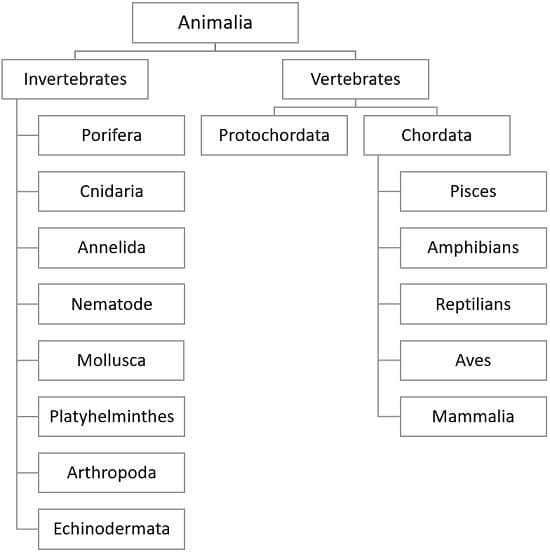
Porifera
- Organisms under the phylum Porifera are generally sponges with large size pores.
- Found in deep seas and oceans. Some of the species are also found in freshwater bodies like lakes and ponds.
- Sessile means they do not move on their own and remain anchored on a rock or corals.
- Often, they grow branches like trees that are tubular vase-like in structure.
- Some sponges are even giant barrel-like structures spreading in several diameters.
- These poriferans are of numerous colours like blue, ultramarine, crimson, purple, red, yellow etc. These colours make them look more attractive.
Cnidaria
- Phylum cnidaria comprises soft-structured stinging organisms.
- The word Cnidaria has its origin from the Greek word Cnid– which refers to nettle, a stinging plant.
- They have a tentacle over their entire body. These tentacles have poison in them, which protects the organism from danger.
- Found in both freshwater and marine habitats.
- Cnidarians are average size animals but have several metre-long tentacles.
- Use summer salting for locomotion.
- Examples: Sea anemone, hydra, jellyfish etc.
Platyhelminthes
- They are flatworms, found on a wide range of habitats including land, water as well as inside the other living bodies as a parasite.
- The phylum’s name comes from the Greek word Platy meaning flat, while helminth means worm.
- They can be free-living (non-parasitic) or parasitic.
- Parasitic ones like tapeworms can severely injure the body and sometimes be lethal.
- The free-living ones are active predators that hunt for food.
Nematoda
- The Greek word Nema means thread.
- Nematoda includes roundworms.
- Approximately 25,000 species of nematodes have been discovered yet.
- Found abundantly in marine and freshwater sediments.
- They play a significant role as predators and decomposers. Also, they are prominent prey for animals like snails and crabs.
- They can be parasitic and free-living, just like platyhelminths.
- Parasitic nematodes like heartworms infect domestic pets, while pinworms and hookworms attack small kids.
Annelida
- The phylum Annelida got its name from the Latin word Annulus that depicts rings.
- These organisms have complex and segmented bodies. Their body is divided into repeating portions known as segments. All the internal organs are present repeatedly in each segment.
- The most familiar members of this phylum are earthworm and Hirudinea.
- Generally found in brackish and marine water bodies.
Mollusca
- It is the second-largest phylum of the Animalia kingdom, which constitutes more than 100,000 species.
- Molluscs are recognised by the presence of an exoskeleton over their body in the form of a shell.
- Slugs, snails, squids, clams, tusk shells, chitons etc., are placed under phylum Mollusca.
- They are aquatic, both fresh and marine water as well as terrestrial organisms.
- The animal under this phylum has an excellent economic value.
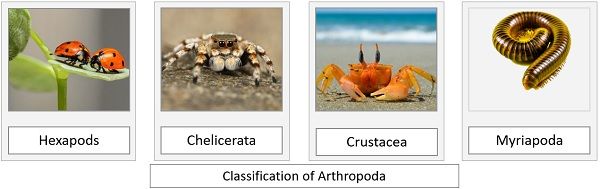
Arthropoda
- The animals under Arthropoda are considered the most successfully evolved creatures on the planet as they make the largest phylum of Animalia kingdom.
- About 85% of the total animal population are arthropods.
- These are characterised by the presence of hard chitinaceous exoskeleton and jointed appendages.
- They habitat in almost all environments as they can survive over a variety of foods.
- Example: insects like grasshoppers, butterflies, fireflies, ladybugs; arachnids like spiders; crustaceans like crabs, shrimps; myriapods like centipedes, millipedes etc. are all arthropods.
Echinodermata
- The Greek word Echino refers to spiny, while the Latin phrase derm refers to skin.
- They are named so as they possess tiny bumps and spines over the outer surface of the body.
- The property that differentiates them from the rest is the presence of a water vascular system. This is a hydraulic pressure system that facilitates their movement.
- Another property that outshines them is their five-sided radial symmetry.
- Examples: Starfish, sea star, star cushion etc.
What are Vertebrates?
The organisms with a backbone or vertebral column are known as Vertebrates. These are comparatively higher animals with developed internal skeleton and muscular system that aids their easy movement. The presences of the vertebral column provide a definite structure, rigidity as well as flexibility to the body.
The small vertebral bones are interconnected and are segregated by soft cushion-like tissues termed discs. The vertebral column is hollow inside through which the spinal cord runs. These hard, bonny but flexible vertebrae thus protect the sensitive spine from damage.
Characteristics of Vertebrates
- These can be homeothermal or poikilothermal organisms.
- They have advanced body organisation, due to which they survive in different habitats.
- These organisms are all bilaterally symmetrical.
- Have well developed sensory, respiratory and nervous systems.
- Most vertebrates possess a skull as a hard covering over their brain.
- The circulatory system is closed, and the heart is located ventrally.
- These organisms have systematic digestive organs starting from the mouth and ending with the rectum.
- The mouth is present on the anterior position for the feeding purpose anus for defecation is located on the posterior end.
- Almost all the vertebrates have a heterotrophic mode of nutrition, i.e. they are dependent on others to suffice the food requirements.
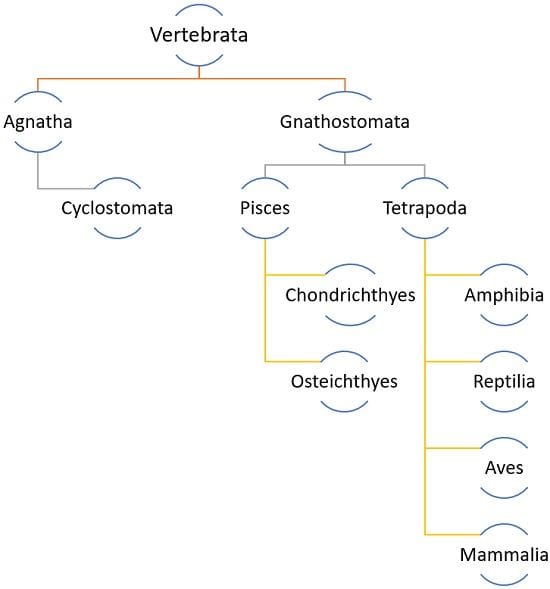
Classification of Vertebrata
The Vertebrata can be divided into two major divisions:
1. Agnatha: These organisms are deprived of jaws thus are often referred to as jaw-less animals.
The major class of Agnatha is Cyclostomata. Cyclostomata includes ectoparasites that live on certain fishes.
- Have a sucking mouth that is devoid of jaws.
- The body lacks paired fins and scales.
- They are marine animals but move to freshwater bodies at the time of spawning.Examples: Hagfish (Myxine), Lamprey (Petromyzon).
2. Gnathostomata: They are jaw bearing organisms.
They are divided into two superclasses:
a. Pisces: This superclass includes fins bearing organisms.
It is again divided into two classes:
-
- Chondrichthyes
- Have a streamlined body.
- Strictly marine.
- Have cartilaginous endoskeleton.
- The notochord is persistent during their whole life.
- Some of them possess electric organs or poison stings like Torpedo and Trygon.Examples: Sting ray (Trygon), Scoliodon (Dogfish), Sawfish (Pristin).
- Osteichthyes
- Found in both freshwater and marine habitats.
- Body is streamlined for easy swimming.
- Have four pairs of gills that are covered by the operculum.
- Cycloid/ctenoid scales cover their body surface.
- Two-chambered heart.
- Air bladder is present to maintain buoyancy.
- External fertilisation.Example: Sea horse (Hippocampus), Katla (Catla), Flying fish (Exocoetus).
- Chondrichthyes
b. Tetrapoda: These organisms are the ones that bear limbs.
They are divided into four classes:
-
- Amphibia
- The word Amphi means dual, and bios mean living.
They are the vertebrates that are capable of surviving in both terrestrial and aquatic habitats. - Mainly possess two pairs of limbs.
- Body can be divided into two prominent zones- head and trunk.
- Has a common exterior opening called cloaca for the urinary, reproductive as well as alimentary tract.
- Three chambered hearts.
- Poikilothermal or Cold-blooded.
- Separate sexes with external fertilisation.
- OviparousExamples: Frog (Rana), Limbless amphibia (Ichthyophis), Salamander (Salamander).
- The word Amphi means dual, and bios mean living.
- Reptilia
(Latin, repere or reptum means to creep or crawl).- This class constitutes crawling and creeping animals.
- Mostly terrestrial.
- Scales or scutes are present on the entire body surface.
- The external ear is absent.
- Three chambered heart (except for crocodile, which has 4 chambered heart).
- Separate sexes.
- Internal Fertilisation.Examples: Turtle (Chelone), snakes like Cobra (Naja), Viper (Vipera), Alligator.
- Aves
- This class comprises birds that are characterised by the presence of feathers.
- Almost all of them can fly except the flightless bird Ostrich.
- They have a beak for food intake.
- Their forelimbs are modified into wings to ease the flight process and reduce body weight.
- Hind limbs possess scales for grabbing, walking or for swimming.
- Their endoskeleton is completely ossified, i.e. bony.
- The bones here are pneumatic bones that are hollow from inside and possess air cavities.
- The heart is four-chambered.
- Homeothermal or warm-blooded animals.Examples: Crow (Corvus), Pigeon (Columba), Vulture (Neophron), Ostrich (Struthio), Peacock (Pavo).
- Mammalia
- Most developed animals on the planet.
- Found in a wide range of habitats– lands like forests, deserts, grasslands, icy polar regions, mountains, etc.
- Most importantly, they possess mammary glands to produce milk for their offspring.
- Have two pairs of limbs that are used for climbing, burrowing, walking, swimming etc.
- The outer skin has hair.
- External ears are found.
- Various types of teeth are found in the jaw.
- The heart is four-chambered.
- Respiration by lungs.
- Sexes are separate.
- Internal fertilisation.
- Viviparous (Except Platypus and Echidna)Examples: Camel (Camelus), Flying-fox (Pteropus), Elephants (Elephas), Dog (Canis), Monkey (Macaca), Cat (Felis), Dolphin (Delphinus), Blue whale (Balaenoptera), Humans (Homosapiens).
- Amphibia
Key Differences Between Invertebrates and Vertebrates
Following are the key differences between Invertebrates and Vertebrates, which may be helpful to some extent in understanding them:
- The most remarkable difference between Invertebrates and Vertebrates is the presence of backbone, skull (outer covering of a brain) which is completely absent in Invertebrates and is well developed and proper functional in Vertebrates.
- Other features like the Nervous system, Respiratory system, Digestive system, Gastrointestinal tract and Circulatory system is not so well developed and organized in Invertebrates as compared to Vertebrates.
- The body structure of Invertebrates is simple, with symmetry like radial or bilateral; Vertebrates have complex and organized body structures with only bilateral body symmetry.
- Above all still, Invertebrates register their presence up to 98% of the total Animalia kingdom and much more to be identified, whereas Vertebrates occupies only 2% of the total Animalia kingdom.
Summary
The animal kingdom is vast and highly diversified containing numerous species with distinct appearances and characteristic properties. Based on the similarities and differences the animal kingdom is classed as vertebrates and invertebrates.
The invertebrates are the lower animals that have less developed structural organization due to the absence of vertebral cord, gill slits, endoskeleton for internal support and a well organized nervous system.
Contrarily the vertebrates being more developed possess all these characters like notochord, pharyngeal gill slits, bony skeleton, and a developed nervous system.
Both the categories include the organisms that are important to the environment in one or the other way, thus it becomes important to have thorough knowledge about their classification.








Leave a Reply