The immunoglobulins are glycoproteins that identify and bind to the specific epitope of an antigen. They aid the clearance of the foreign pathogenic antigen from the human body. Both IgM and IgG are significant immunoglobulins in our healthy immune system.
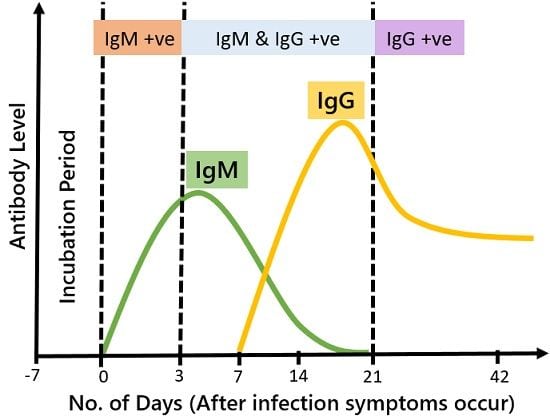
As soon as any foreign antigen encounters the body, the production of IgM immediately starts. It is the first type of immunoglobulin generated after disease exposure. Thus, their presence in the blood confirms the existence of infection in the body.
But they are very short-lived and temporary and get dissolved after some weeks of exposure.
On the other hand, the IgG are generated as a delayed response. The body generates them in later stages of infection after asserting the antigenic properties. It is the most abundantly found antibody in the blood. It acts as an effective fighter that defends the body during the secondary immune response.
They survive in the bloodstream for a longer duration of time, unlike IgM.
In this context, we will study the differences between the structure and functions of IgM and IgG.
Content: Immunoglobulin M (IgM) Vs Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
- Comparison Chart
- What is Immunoglobulin G or IgG?
- What is Immunoglobulin M or IgM?
- Key Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparision | Immunoglobulin (Ig) G | Immunoglobulin (Ig) M |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 150,000MW or 150kDa. | 900,000MW or 900kDa. |
| Presence in serum | 75% of total serum. | 10% of total serum. |
| Percentage of Carbohydrate | 3% | 12% |
| Heavy chain | gamma (γ ). | mu (µ). |
| Light chains | kappa (κ ) and lambda ( λ). | kappa (κ ) and lambda ( λ). |
| Types | Are of four types IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4. | No more types. |
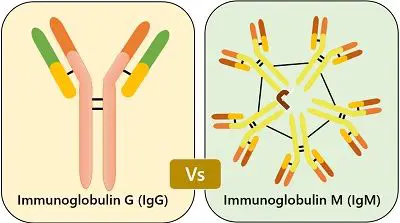
| Size | It is a monomer consisting of the single Y-shaped unit with only two antigen binding sites. | It is pentamer consisting of 5 Y-shaped units together by a polypeptide chain with ten antigen binding sites. |
| Role | IgG is a long term response for any disease and thus protect our body from viral and bacterial attacks. | IgM serves as the first kind of defense, which means it is the first antibody to be immediately developed when any foreign particle is introduced, though its function is temporary. |
| Where it is found | Abundantly found in lymph, blood, and intestine. | IgM is found in lymph fluid and blood and is produced in plasma cells. |
| Effect of high level | High level of IgG in the body means a long-term infection like HIV, multiple sclerosis, multiple myeloma. | High level of IgM may give rise to parasitic infections, kidney damage, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis, mononucleosis. |
| Effect of Low-level | Low level of IgG results in kidney damage and few types of infections. | Low level of IgM results in few types of leukaemia, and some inherited diseases. |
| Sedimentation Co-efficient | 7 | 19 |
| Half-Life (days) | 23 | 5 |
| Daily Production (mg/kg) | 34 | 3.3 |
| Intravascular Distribution (%) | 45 | 80 |
| Placement transport | + | _ |
| Present In Milk | + | _ |
| Heat Stability (56 °C) | + | _ |
What is Immunoglobulin G or IgG?
IgG is the most commonly found immunoglobulin in our body. It constitutes around 80% of the total antibody concentration in blood serum. Our body produces them in the later stages of the infection. And thus, it is a part of the secondary or delayed immune response.
The B-cells also manufacture IgG. Thus, at the time of their production, B-cells have to undergo class switching. For this reason, it takes time for B-cells to generate IgG.
Characteristics of IgG
- Their molecular weight is around 150,000 (7S).
- These are equally dispersed in the intravascular and extravascular sections.
- Their carbohydrate content is comparatively lower than that of other immunoglobulins.
- IgG has a half-life of about 23 days.
- Their average nonpenetration in serum is approx 8-16 mg/ml.
- IgG is the only immunoglobulin that can pass through the placenta, i.e., from mother to baby. This is due to their smaller size.
Thus, it becomes the initial protector of the baby after the first six months after birth. Here, a baby’s immune system is not very developed, making them more susceptible to diseases. IgG gained from the mother offers natural passive immunity to the baby. This immunity helps him to defend against the infection. - As it passes to the baby via the mother, can cause a pathological condition known as erythroblastosis fetalis.
Structure of IgG
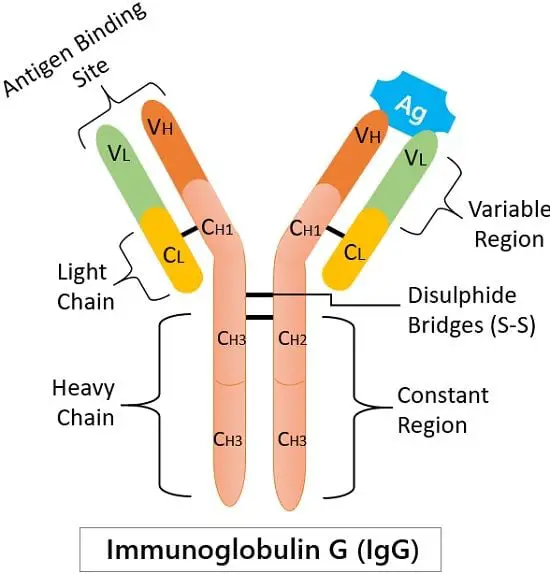
Immunoglobulin G is a giant globular proteinaceous molecule with an average weight of 150 kDa. It has a tetrameric quaternary structure that consists of four peptide chains-
two heavy and two light. Two of the heavy γ (gamma) chains (50 kDa) are identical. And two similar light chains (25 kDa).
Heavy and light chains link with the disulphide bridging. Due to this, the resulting tetramer generates a Y-shaped structure having two identical halves.
We can divide the IgG molecule into two central regions based on their functioning:
1. Antigen Binding site or region: It is the place where the antigen comes and binds.
2. Constant region (Fc region): It is the stem portion of a Y-shaped structure. The Fc receptors of macrophages and neutrophils recognise this region.
Although all four classes of IgG are 95% similar, the hinge region in all four subclasses is different. This difference provides them with their distinctive biological properties.
Catabolism of IgG
It is a unique process that varies according to IgG concentration in the serum.
When the IgG level is high, the catabolism reaction will take place more rapidly. This case might result in the deprivation of other antibodies. Whereas, in the situation of hypogammaglobulinemia, the catabolism reaction occurs quite slowly.
Functioning of IgG
IgG plays a most significant role in almost every kind of immune response produced by our body. It actively performs its role in reactions like neutralisation, complement fixation and opsonisation.
· Opsonisation
IgG coats the pathogenic antigens to make them look more appetising for phagocytic cells. This process is referred to as opsonisation. This process attracts the macrophages and neutrophils to eat the foreign antigen.
Generally, the pathogen freely floats and circulates around the body. At that time, they remain unnoticeable to the phagocytic cells. Thus, the IgG gets attached to these antigens and thoroughly coats them. This accumulation of IgG signals the phagocytes to reach and eat the antigen.
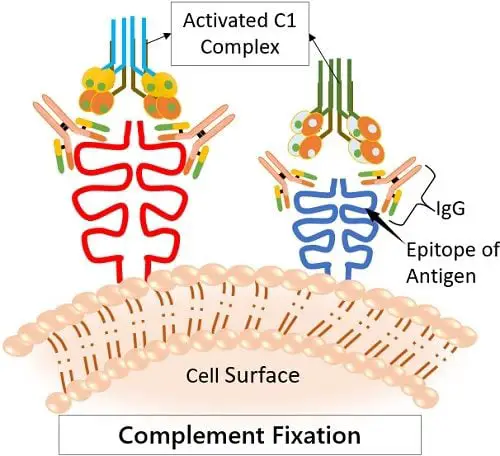
· Complement Fixation
One of the major roles of IgG is to fix complement. This means to attract the complement proteins to come and bind to it. This induces the classical complement pathways.
The complement system is essential as it is one of the prominent ways by which our body kills pathogens. Here, the IgG marks the foreign antigens that culminate its killing by pocking holes in their membrane.
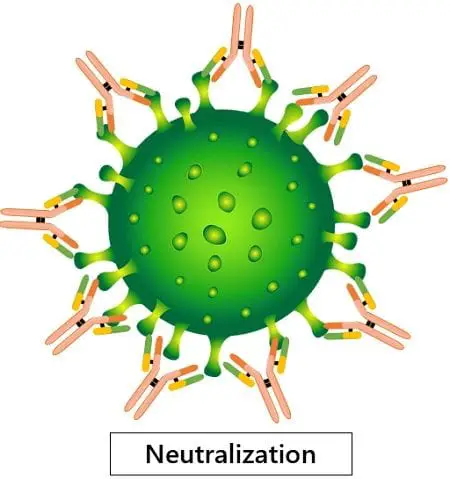
· Neutralisation of toxins and viruses
IgG directly neutralises the antigens on the pathogenic surface. IgG binds to the active site of the pathogen and covers it completely. This makes it harder for them to infect cells or cause any harm.
This process is different from simply flagging the pathogens like in opsonisation. Here, the IgG antibodies directly tackle the pathogens without seeking help.
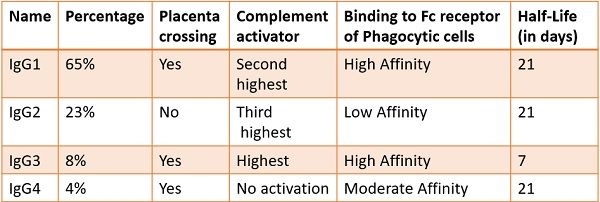
Sub Classes of IgG
The IgG has four major classes based on their γ chains. The subclasses are as follows:
- IgG1 – γ1
- IgG2 – γ2
- IgG3 – γ3
- IgG4 – γ4
All of them are dispersed in the serum with concentrations of 65%, 23%, 8%, and 4%, respectively.
These four classes are 95% similar to each other. Minor differences are present in the constant Fc regions at the stem. They subtly vary due to the size of the hinge section and by the number of disulphide linkages among the heavy chains.
What is Immunoglobulin M or IgM?
Immunoglobulin M or IgM is the largest antibody produced by our body. As the pathogenic antigen gets introduced inside the body, the production of these antibodies instantly begins. Thus, IgM plays a significant part during the initial stage of encounter and infection. Their generation through plasma B cells is considered the first-line immune response of the body.
The IgM manufactured as an outcome of infection are immune IgM antibodies. But we also have natural antibodies that keep on circulation in the blood flow. These antibodies decrease inflammatory reactions and prevent autoimmunity.
As the infection begins and pathogenesis rises, the level of IgM is increased too. It keeps on increasing until the secondary immune response is generated in the form of IgG. During the later phase of infection, as the concentration of IgG increases, the level of IgM automatically start to decrease.
Characteristics of IgM
- Based on the phylogenetic studies, IgM are the most ancient type of immunoglobulin. Its synthesis begins at a very early stage of foetus development, i.e., around 20- weeks of conception.
- They make around 5-8% of the total antibody concentration in the blood serum.
- On average, their normal level in the body is estimated as 0.5-2.0 mg/ml.
- IgM antibody is quite heavy, with molecular weight ranging between 900,000-1,000,000 (19 S). For this reason, it is often referred to as ‘the millionaire molecule’.
- Because of its heavyweight and giant size, it cannot cross the placenta.
- The half-life of IgM molecules is about five days.
- Mostly IgM (around 80-85%) are present in the intravascular compartments.
- These immunoglobulins have a shorter life span. And they start getting dissolved with a gradual rise in IgG levels.
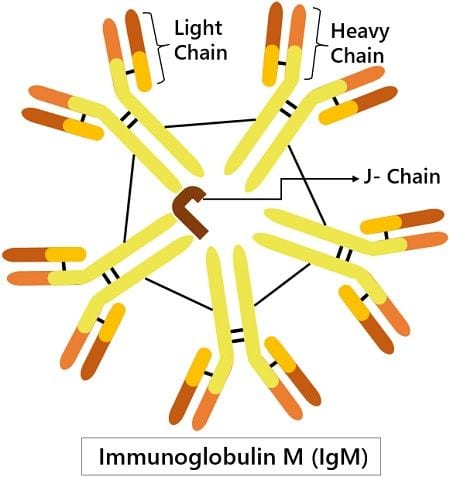
Structure of IgM
Based on the sedimentation velocity and electron micrographs, IgM antibody is inferred as a polymer of five; four-peptide subunits. That means it forms a pentameric structure having five monomers. The disulphide bonding links these monomers together at the C-terminal of the heavy chain.
Each monomer comprises a light and heavy chain. The light chain has around 220 amino acids. And is divided into two domains- variable or VL domain (110 amino acids) and constant or CL domain (100 amino acids).
Whereas, the heavy chain has around 576 amino acids. It is also divided into variable or VL domains (~110 amino acids) and constant or CL domains (~110 amino acids). There are four constant regions, Cµ1, Cµ2, Cµ3, Cµ4, each with 110 amino acids. Also, it has a tailpiece of around 20 amino acids.
The polymerisation of the monomeric subunit depends on the presence of the J chain. This short-chain (~137 amino acids) couples two heavy chains with disulphide bridging.
Functions of IgM
- It is the most successful immunoglobulin in fixing the complement system. It efficiently binds with the C1 component and initiates the processing of the complement system.
- It’s the first antibody that our body produces after encountering the pathogen. Thus, it’s an essential part of the primary immune response.
- While diagnosis, they are the best indicators to determine whether a person is suffering from a disease or not.
- They fight with the foreign antigen until our body generates a more specific immune response in the form of IgG.
- They also in carrying out the immune reaction like agglutination, neutralisation etc.
- Although it has lower affinity binding sites, but have more avidity towards the antigens. They possess ten combining sites that collaborate at the time of antigen encounter.
- They also serve their role during autoimmune disorders.
What does a low level of IgM indicate?
The IgM antibodies freely circulate even in the absence of infection. And as the pathogen encounters, their concentration exponentially rises. But if the IgG level is lower than the average count in our body, this indicates the dysfunctioning of our immune system. This makes our body more susceptible to diseases.
Causes of low IgM levels
- The lifestyle habits like smoking, alcohol intake, excessive strain, over endurance exercises.
- Diseases like arthritis, thyroid, celiac disease, lupus, thrombocytopaenia etc.
- Other health disorders like diabetes, leukaemia, lymphoid nodular hyperplasia etc.
What does High-level of IgM indicate?
There are two types of IgM produced by our body- natural and immune. The natural exist in the blood serum defending the body against infections. But the immune IgM are generated only after the intrusion of any foreign antigen.
Thus, if the doctors certainly diagnose the level of IgM, he thereby confirms the presence of disease in the body. During the initial stages of infection, the concentration of IgM exponentially rises. This acts as an indicator to know the presence of disease.
Causes of High-level IgM
- Bacterial or viral invasion and infection.
- Autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes etc.
- Hyper IgM syndromes
- In kidney damages
- Cancers such as myeloma and Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia.
Key Differences Between IgM and IgG
Following are the key differences between IgM and IgG:
- Though both the antibodies (IgM and IgG) are proteins, made for fighting against antigens or foreign particles, IgM provides immediate response when an antigen enters the body while IgG responds later with the permanent eradication of antigen and its effect is lasting. Also, IgG helps in developing a secondary immune response against any particular antigen.
- The molecular weight of IgM is 900kDa and that of IgG is 150kDa.
- IgM account for only 10% of the total volume of the serum and IgG occupies 75% of the total volume of the serum.
- IgM has the heavy chain as mu (µ) and IgG has the gamma (γ ), though both have the light chain as kappa (κ ) and lambda ( λ).
- IgG is of four types which are – IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4. IgM has no such types.
- IgM is produced in plasma cells and is found in lymph fluid and blood, whereas IgG is abundantly found in the intestine, lymph, blood.
- Due to the larger size, IgM is unable to cross the placenta, though it’s the first antibody produced in the human fetus while IgG is smaller in size and can cross the placenta and provides the mother’s immunity to developing the embryo.
- IgM is a pentamer unit with ten antigen-binding sites, but out of it, only five are functional due to many monomers bonding among themselves resulting in a restriction to binding sites. Whereas IgG is a monomer with two antigen-binding sites.
Conclusion
Immunoglobulin (Ig) or Antibodies are the proteins produced in B-lymphocytes, to fight against any infections, there is five kind of antibodies, and all plays a vital role in fighting diseases and are very specific to these antigens, these antibodies are of different size, having light and heavy chains.
IgM is the first antibody to fight against, and attack of viruses or bacteria whereas IgG reacts later but help in the permanent eradication of antigens by enhancing phagocytosis or opsonization.


abdulhalim khan says
nice topic for understanding immunity for infection.
Anthony C Capasso says
Trying to find IGM positive abnormal what it means and IGG positive abnormal what does the two mean. You excellent explanations on everything I enjoyed reading
Sandra Shipley NP says
Loved the information!
I have questions regarding a specific Antigen. Varicella or covid. Some people have a documented of covid or varicella, but a year later are IgG antibody negative. The B cells and T cells will again attacked and produced antibodies again if re-exposed to the virus, right?
Also, if the IgG fall to undetectable levels, how do you prove immunity?