Hibernation and aestivation are the forms of sleeping states which occurs under two different climate conditions. Both of them are extended forms of torpor.
Sometimes, the animals fall asleep to survive in harsh and extreme environments. This sleeping pattern may vary as per the climate and the growth phases of the organism.
The primary difference between hibernation and aestivation is that the former is winter sleep while the latter is summer sleep.
During extremely low temperatures, animals like bears, crocodiles etc., sleep for a prolonged period. They deliberately slow down their metabolic rate, heart beating, and breathing to stay alive and conserve energy.
The counterpart of hibernation is aestivation which occurs in the summers. The animals undergo aestivation to protect themselves from burning hot and dry conditions, mainly in desert regions. Here also, the organisms undergo dormancy by hiding in the moist and marshy areas to keep their bodies cool and wet.
With the help of these two sleeping mechanisms, the animals can live out in harsh climates. By this, they reduce energy use by 70-100 %, which is lesser than the usual time, i.e., in the active state.
We will discuss the primary differences between hibernation and aestivation with a comparison chart and related examples in this context.
Content: Hibernation Vs Aestivation (Estivation)
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Hibernation | Aestivation (Estivation) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Hibernation is the type of winter sleep, performed by the warm and cold-blooded animals. | Aestivation is the type of summer sleep, performed by cold-blooded animals. |
| Duration | It is for the whole winter. | It is of short duration. |
| Process | As hibernation is the sleep during the winter, the animals look out for the warmer place, their metabolic activities slow down, and it is the dormant stage. | Aestivation is a summer sleep, so animals search for the moist, shady and cool place to sleep. |
| Examples | Bats, birds, mammals, insects, etc. | Bees, snails, earthworms, salamanders, frogs, earthworms, crocodiles, tortoise, etc. |
| Importance | Hibernation helps in maintaining the body temperature and thus avoids from any internal body damage due to low temperatures. | Aestivation also helps in maintaining the body temperature by avoiding the excessive water loss and any internal body damaged due to high temperatures. |
What is Hibernation?
Certain places on the earth experience freezing climates during the winter season. This may include areas like the northern and southern poles, Arctic and Antarctic regions etc.
During this time of dramatically cold ambience, the flora and fauna of that particular region get impacted the most. Thus, in order to survive in such harsh conditions, they enter the state of dormancy or inactivity, i.e., hibernation.
In layman terminology, you can understand it as a power-saving mode of your laptop. Imagine your laptop is neither working nor turned off; it is just resting. It saves the data of whatever work you were up to and enters the power-saving mode. Later, when you turn it on, it resumes back with your data.
Similarly, hibernation is a power-saving mode that conserves energy and protects the organism from a harsh environment.
Why does hibernation occur?
After knowing what hibernation is, you must wonder what hibernation does that protects the organism from extreme cold. So, let us know more about it!
The reason behind hibernation is self-explanatory. Let’s discuss some of them.
1. Availability of Food
The animals either rely on plants or other fauna to meet their need for food. The natural vegetation gets ruined completely during extreme colds because of snow and moisture.
Only some exceptional plants that have adapted to survive can tolerate and grow there.
This hampers the animals which were dependent on the plants for food. On the other hand, the smaller preys also hide or sometimes die in the cold climate. Thus, the number of prey for the predating animals also reduces.
So, in order to curb this food requirement, the hibernators undergo a hyperphagic state. By this, they multiply their appetite by eating as much food as possible to stock the energy for the entire season.
2. To maintain the internal heat
The internal body temperature of the ectothermic organism relies on external climatic conditions. Thus, their internal temperature dramatically fluctuates with changes in the climate.
Thus, some ectothermic organisms hibernate by which they settle their body temperature in a particular range. Thereby, they don’t get affected by the environmental changes happening around them.
3. To conserve the energy
Organisms living in cold areas are fully aware of the scarcity of food during winters. Even though they are in a hyperphagic state to eat more and more, still the food will be exhausted if the body consumes energy very fast.
During hibernation, the hibernator aims to lower down the body activity so as to reduce the energy consumption. The metabolic functioning is nearly halted. The breathing and heart rate decrease, no physical movement, etc., are some of the activities that occur during hibernation. They tend to conserve the excess use of energy.
Process of Hibernation
There are three phases of hibernation: preparation, actual hibernation, and arousal from hibernation.
Preparing for Hibernation
Organisms start preparing themselves for hibernation by the time of the fall season so as to gather sufficient energy to last up till spring. Mostly the animals store this energy in the form of internal fat. For instance, woodchucks have only 5% of the body fat during early summers, which increases upto 15% as the fall comes. It does it by manipulating its brain chemistry which makes him hungry all the time.
Some hibernators have a specialized mechanism of generating a thick fat layer consisting of the adipose tissues in bulk. This fat layer is also referred to as the brown fat layer or brown adipose layer, mainly located in the shoulder blades of the animal.
The primary function of this fat layer is to insulate the inner organs from the external cold and rapidly produce heat when metabolized at particular intervals.
Some of the animals store their food externally also. Such as chipmunks collect plenty of food and fill it in their burrows. They consume this food at periodic arousals from their state of torpor throughout the whole winter season.
Going into the Hibernation
Entering into the hibernation is a gradual process that slowly lowers down all the physical and mental activities occurring inside the body. The heartbeat and respiration rate falls down to a few times a minute. Also, the body temperature reduces from 37± 2°C (101.5 to 103.5°F) to 10-20°C (50 to 68°F). This reduced body temperature favours only a few demands and metabolic actions, thereby helping to preserve the energy
The brain’s activity also ceases completely as the electrical impulses are turned off. Only a few of the areas related to the response of external stimulus, including light, temperature, noise etc.
Arousal Period
Hibernation might be continuous or discontinuous. Large organisms can gather lots of nutrients and stay hibernated for the entire season. But smaller animals like rodents cannot store very much food during their torpor.
Thus, they arise at regular intervals in order to eat, urinate and defecate. Such animals are shallow hibernators. Chipmunks, skunks, squirrels, and raccoons are some examples of shallow hibernators.
The arousal process initiates by gradually increasing the heart beating and blood flow and dilating the contracted vesicles. Also, the rate of breathing increases. The blood starts to circulate all around the body parts, particularly around the heart, lungs and brain. These all metabolic activities stimulate the organs. This process might take several hours to activate the entire body.
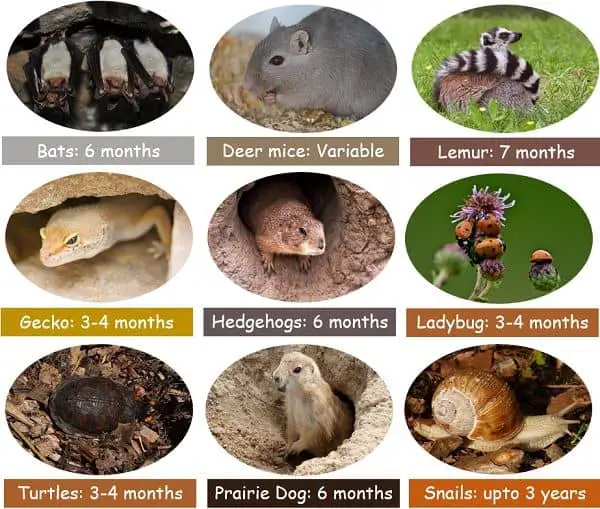
Understanding Hibernation with Examples
- Bats: The bats living in the cold environment tend to hibernate in the caves, crevices of rocks, and wall spaces that are dark and quiet. While hibernating, they can drop their heart rate extremely low, which may not require to breath for an hour or more.
- Bears: Mostly, the brown grizzly bears need to hibernate for about 5-7 months during the winter season. They hibernate in remote areas like caves, dens, tree crevices, hollow passages under mountains etc.
- Bumblebees: As the winter starts, all the bees except for the queen bee die. The queen searches for a safe place to hibernate for 4-6 months. As the season becomes favourable, she gives rise to a new generation.
- Box turtles: Their hibernation period is around 3-4 months. They don’t require a perfect spot to hibernate. Instead, they just find a quiet place and go inside their shells which safeguards them during hibernation.
- Chipmunks: They hibernate by digging a burrow upto 3 feet for around four months. Since they can’t store enough fat in their body, they wake at regular intervals during their torpor to eat.
What is Aestivation?
The aestivation also referred to as estivation, is equivalent to hibernation but occurs in summers. We refer to hibernation as winter sleep, just like that aestivation is the summer sleep. It is a very smart trick that the animals living in hot and dry climates use to deal with the extreme heat.
The term aestivation comes from the Latin word aestīvāre, which means “to spend summers“. Thus, we can say that aestivation refers to a specialized method to evacuate the heat and survive easily during summers.
In zoology, aestivation is an extended and deep torpor period that maintains the internal body temperature of the ectotherms during summers. Thereby often referred to as summer dormancy.
Like hibernation, the aestivation is also characterized by slow metabolic functioning of the body. This may involve low heart rate, decreased respiratory rate, ceasing of the brain impulses (except some mandatory ones) etc.
Why do the animals undergo aestivation?
During the summers, ectothermic organisms face lots of issues related to the regulation of body temperature. They are cold-blooded, thereby unable to manage their body’s constant temperature. Instead, their internal temperature fluctuates as per the temperature changes in the surrounding.
In summers, when the external heat goes high above 40-45°C, their body temperature will eventually rise upto the same limit. Therefore, in order to prevent them from getting so heated, they undergo aestivation. It not only prevents their body from extreme heat but also protects them from the other environmental stresses during the summers. Such as drought, famine, water scarcity etc.
Role of Aestivation
The fundamental purpose of aestivation is the same as that of hibernation, i.e., survival during extreme environmental conditions.
The hot and dry climate supports very few floras and faunas to grow. This creates a scarcity of food during the summer season. The animals try to get the maximum amount of nutrition in the rainy and winter seasons and use this stored energy while aestivating.
Also, the dry and arid regions are devoid of the proper water supply. The aestivation also helps the animals to deal with the water scarcity as they don’t need water during summer sleep.
Besides the above, aestivation plays a part in stabilizing the internal body organs by protecting them from getting heated and desiccated.
What triggers Aestivation?
The hot, dry and arid climatic conditions prompt the animals to undergo summer dormancy. Both the terrestrial as well as aquatic ectothermic organisms may undergo aestivation as per the temperature fluctuation taking place.
Researchers suggest that this mechanism has taken several million years of evolution to successfully record and react according to extreme temperature conditions. The dryness and heat automatically trigger the process of aestivation as soon as the summer season is about to start.
Understanding Aestivation with Examples
- Crocodile: Mostly, the crocodiles are able to thrive nicely in summers. But sometimes, the condition becomes too hot to handle. In such a situation, crocodiles tend to dig down into the burrows or submerge in the mud of marshy areas. There they enter into a deep torpor state and wait for the rain to arrive.
- Lungfish: These fishes have a special mechanism of keeping themselves moist by secreting the mucous layer surrounding them. This layer holds moisture and protects them from getting desiccated. For aestivation, these fishes go deep in mud at the bottom of the water body.
- Desert Tortoise: The tortoise living in the desert regions also aestivate. They can easily tolerate the hot climate because of their shell, but they aestivate when the temperature exceeds a certain limit. They simply cover themselves from mud and get settled for the summer sleep.
- Water-holding Frog: These amphibians have built the same mechanisms as lungfish. Thus, when the climate becomes insufferable, these frogs bury themselves deep underground and release mucus. This mucus hardens from the outside, making a cyst-like protective structure. This internal space remains filled with mucous, which prevents further dehydration.
Key Differences Between Hibernation and Aestivation
- A state of sleep during the winter season to survive in the extreme cold is Hibernation. On the other hand, aestivation is summer sleep or a state of inactivity during the summer season.
- Both the warm and cold-blooded animals undergo hibernation. Mostly the cold-blooded animals perform aestivation.
- Hibernation is for the entire winter season when the animals enter a dormant state in warmer places. While the Aestivation is of short duration, where the animals search for a moist, shady and cool place to sleep.
- Hibernation occurs to protect the animals from extreme cold environments. While the aestivation protects the organism from insufferable heat.
- Bats, insects, birds, mammals, etc. are examples of hibernating animals. Whereas Bees, snails, earthworms, salamanders, frogs, earthworms, crocodiles, tortoises, etc. are examples of aestivating animals.
Conclusion
In this article, we studied hibernating animals as well as the animals who performed aestivation. We came across the importance of these activities. We also came to know the reason for such periods of sleep and why it becomes necessary for the animals living in such areas.











Leave a Reply