We classify the chemical reactions as endothermic or exothermic, depending on whether it is giving energy or taking energy. The endothermic reactions are when the system takes up the energy in the form of light or heat. In contrast, exothermic systems give up heat or light energy as the reaction proceeds.
In endothermic processes, reactants possess lower potential energy than the product. Thus, in order to react, they absorb the energy from the environment. Due to this, the change in the enthalpy is positive. And therefore the reaction is non-spontaneous in nature.
Oppositely, the reactants of the exothermic system have a higher amount of stored energy than products. Thereby, they release the energy into the environment. For this reason, the change in the enthalpy is negative, and thus, this is a spontaneous reaction.
This section will brief the differences between endothermic and exothermic reactions.
Content: Endothermic Vs Exothermic Reaction
- Comparison Chart
- Enthalpy change of the reaction
- What is an Endothermic Reaction?
- What is an Exothermic Reaction?
- Key Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Endothermic Reactions | Exothermic Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Chemical reactions involving the use of energy at the time of dissociation to form a new chemical bond is known as the endothermic reaction. | Chemical reactions where the energy is released or evolved in the form of heat is known as the exothermic reaction. |
| Energy | The endothermic process requires energy in the form of heat. | The exothermic process evolves or releases in the form of heat. |
| Enthalpy (ΔH) | ΔH is positive, as heat is absorbed. | ΔH is negative, as heat is evolved. |
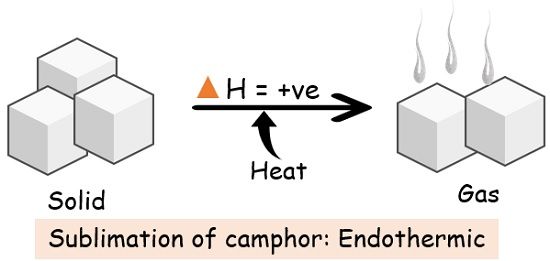
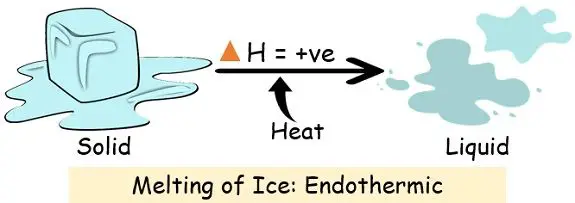
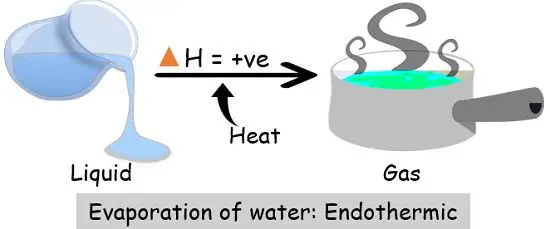
| Examples | 1. Conversion of ice into water vapour through boiling, melting or evaporation. 2. Breaking of the gas molecules. 3. Production of anhydrous salt from hydrate. | 1. Formation of ice from water. 2. Burning of coal (combustion). 3. The reaction between water and the strong acid. |
Enthalpy change of the reaction
We can define the enthalpy of the reaction (∆ H) as:
The heat that is transferred between the system and surrounding at constant pressure and temperature.
∆H = H final – H initial
Or
∆H = H Product – H Reactant
Exothermic Reaction: Heat released: 0 > ∆H, i.e., Negative
Endothermic Reaction: Heat Absorbed: 0 < ∆H, i.e., Positive
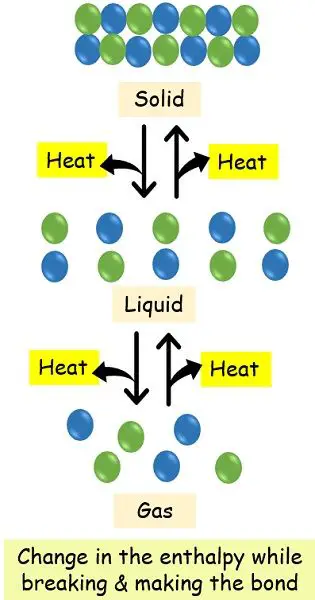
Why does a system release or absorb the energy?
For any reaction to occur, there is a need for continuous breaking and forming of bonds. Different chemical compounds have a different amount of stored energy. During the time of reaction, the breakdown of chemical bonds requires the absorption of energy. Whereas the formation of chemical bonds releases the energy.
It occurs because the molecules have an inherent tendency to stay together. Thereby less energy is needed to gather them and make bonds. Contrastingly, more energy is needed to separate the already existing forces while breaking the bonds.
Since in the endothermic system there is the continuous breaking of bond thus, it absorbs the energy. In contrast, the exothermic system doesn’t need external energy to form chemical bonds.
What is an Endothermic Reaction?
The word endothermic comprises two Greek words, endo and thermic, which mean within and heat, respectively. These reactions intake the energy from the surrounding in the form of heat of light.
The reactants of this system are at lower energy levels than the products. Thus, they require external energy to fill the energy gap. In the endothermic processes, the bonds constantly break, for which the energy is supplied.
As the reaction depends upon energy intake, it is a non-spontaneous process. The average K.E. of the surrounding reduces, which lowers the temperatures of the reaction tube.
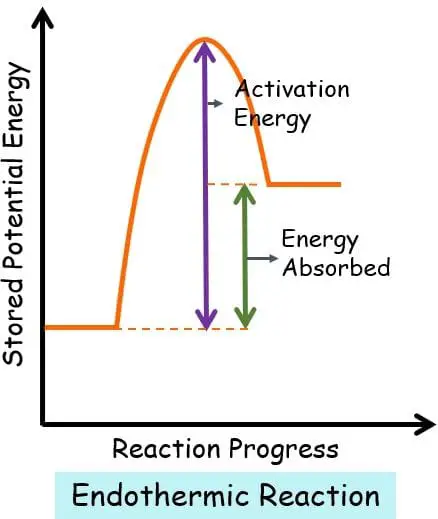
Endothermic Reactions: Energy Diagram
In endothermic system, the graph plotted between stored potential energy and the progress of reaction:
This graph manifests that the reactants are present at a lower energy level than the product. Thus, there is a need for external energy to carry out the reaction. For this reason, the change in the enthalpy is positive.
H reactant < H product
∆H = H product – H reactants = Positive value of ∆H
The activation energy is quite high as the reactants have to cross a long energy barrier.
Note
Activation Energy: It is the minimum amount of energy that is needed by the reactant molecules to collide and bond together. “The greater the activation energy, the more the energy is required to start a reaction”.
Examples of Endothermic Reaction
1. Sublimation
2. Melting
3. Evaporation
What is an Exothermic Reaction?
The term exothermic consists of two Greek words, Exo (out) and therme (heat). As the name suggests, these reactions liberate heat energy outside the system. In such reactions, the reactant bears more potential energy than a product. Thus, they lose energy as the reaction continues in the direction of product formation.
According to the laws of thermodynamics, energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Thus, the extra energy liberated from a system escapes the reaction tube into the surrounding. The most common way of this energy transfer is in the form of heat. The average K.E. of the surrounding elevates, which increases the temperature of the reaction tube.
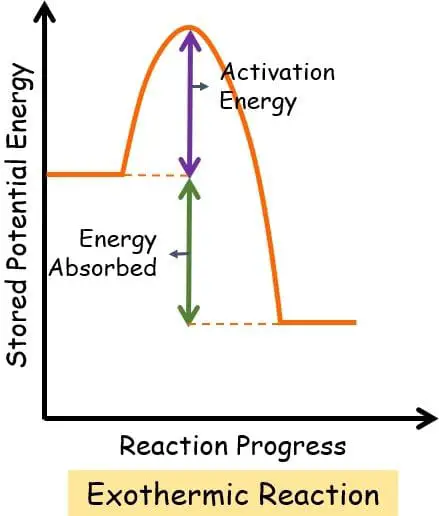
Exothermic Reaction: Energy Diagram
In an exothermic system, the graph plotted between stored potential energy and the progress of reaction:
This graph clearly displays that the reactants lie at a higher energy point in comparison to the product. It indicates that the products are relatively more stable than the reactants. And thus, the change in the enthalpy is negative.
H reactant > H product
∆H = H product – H reactants = Negative value of ∆H
The activation energy of the reaction is low. Instead, the system liberates more energy in the surroundings than needed to start and proceed with the entire reaction.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions
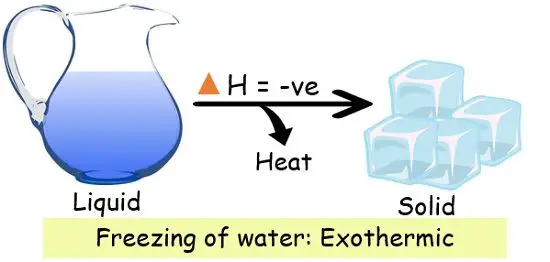
1. Freezing
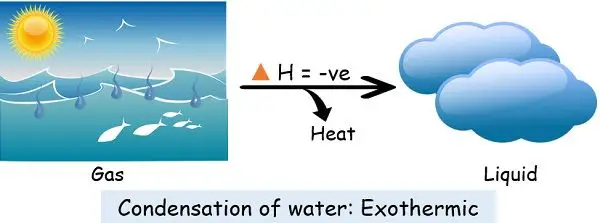
2. Condensation
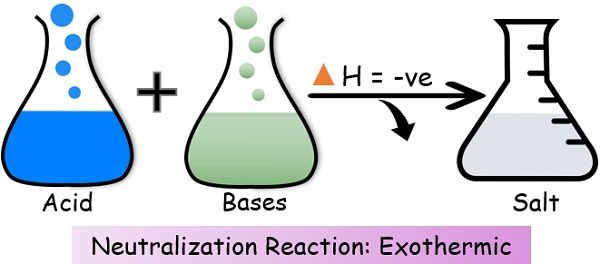
3. Neutralization
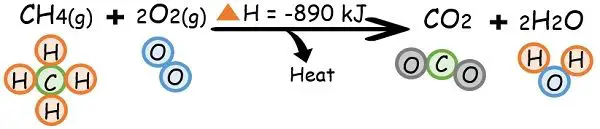
4. Combustion
Key Differences Between Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction
Given below are the substantial points to differentiate between the endothermic and exothermic reactions:
- Chemical reactions involving the use of energy at the time of dissociation to form a new chemical bond is known as the endothermic reaction, while exothermic reactions are those chemical reactions where the energy is released or evolved in the form of heat.
- As discussed earlier, in the endothermic process there is the requirement of energy in the form of heat, whereas in the exothermic process energy is evolved or released.
- ΔH is positive, as heat is absorbed in the endothermic reaction, while in exothermic reaction ΔH is negative, as heat is evolved.
- A few common examples of endothermic reactions are conversion of ice into water vapour through boiling, melting or evaporation; breaking of the gas molecules; production of anhydrous salt from hydrate. Whereas formation of ice from water, burning of coal (combustion), the reaction between water and strong acid are examples of exothermic reactions.
Conclusion
From the above article, we conclude that there are various types of reactions that takes place, whenever molecules interact with each other. Endothermic and Exothermic reactions are the two types of chemical reactions categorized by their behaviour during the chemical reaction, and we found these words opposite of each other.

Leave a Reply