Any matter can undergo two types of changes: Physical or Chemical changes. The physical changes are those actions that generate no new substance. Instead, the older substance only changes in its size, structure and sometimes texture. Whereas the chemical changes give rise to a very new substance. And the older one loses all its characteristic properties.
The physical changes are reversible as the original matter can be brought back together after proper treatment. They are a temporary type of change. While in comparison, the chemical changes are irreversible as the reactant losses its originality. Besides, these changes are permanent ones.
The physical changes do not hamper the chemical composition of the substance. And there is no making or breaking of bonds. Whereas, in chemical changes, the chemical composition of the matter is also changed. This is because the continuous making and breaking of bonds occur here.
This section will discuss the differences between physical and chemical change.
Content: Physical Vs Chemical Change
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Physical changes are those changes, where there is no change in the mass of the substance and even the internal properties of the molecules remain same. Such changes are temporary. These changes involves the transformation in different phases of matter like from solid to liquid; liquid to gas or vice versa. | Chemical changes are those changes, where there is the formation of the new substance and such changes are permanent. There are the breaking and formation of new bonds to make the new compounds. |
| It affects | It affects only physical properties of the material like size, colour and shape, etc. | It affects physical as well as the chemical properties of the material. |
| Produces | No new substance is formed, that means the molecules and atoms are arranged in the same way in products as were in reactants. | Chemical changes always produce new substances, the atoms and molecules rearrange themselves and form a new compound. |
| Energy | There is no energy production during physical changes. | The energy is always required or produced in the form of light, heat or sound during the chemical changes. |
| Reversible/Irreversible | Physical changes are generally reversible. | Chemical changes are irreversible or some time reversible also. |
| Examples | 1. Changing of ice into water or vice versa. 2. Tearing of paper. 3. Shaping the clay in different shapes. 4. Cutting a wooden pile. 5. Switching on/off electric equipment. | 1. Digestion of food. 2. Burning of a matchstick, fuels. 3. Cooked or riped vegetables, fruits. 4. Getting old. 5. Formation of curd. |
What are Physical Changes?
The physical changes are responsible for transforming the outer appearance of any substance. This can be related to the colour, structure, shape, size, volume etc. But these changes never disrupt the molecular makeup of the given matter. There are no alterations in the chemical properties, thereby are easily reversible.
Definition of Physical Change
We can define physical changes as:
“The process that changes in the external physical features of the substances leading to the change in shape, size, texture etc., is a physical change”.
Characteristics of Physical Change
- The physical changes are reversible in nature. We can regain the original material after some physical processes.
- These changes don’t generate any sort of energy during the course of a reaction.
- Since the final product can easily be transformed back into the original substance. Thus, they are temporary changes.
- The initial substance doesn’t lose its substantial or characteristic identity.
- There is no change in the substance’s molecular configuration during the physical reactions.
- The molecules might rearrange themselves by increasing the intermolecular spaces. But the chemical composition of the molecules is never altered.
- The significant reason for the above is the absence of bond breaking or making during the physical changes.
- These changes give rise to no new substances. Instead, the original product changes either in size, shape, structure or texture.
- The physical reaction might not release energy, but they need to absorb the energy to carry out the process in some cases.
- These changes are fast to occur, but they tend to last for a very shorter span of time.
What happens during a Physical Change?
During the physical changes, the physicality or the external structure modifies. But the matter’s uniqueness and chemical makeup remain unchanged.
For example, when the water (liquid) transforms into water vapour (gas). Or when ice (solid) melts into water (liquid), in every form, the chemical composition remains the same, i.e., H2O.
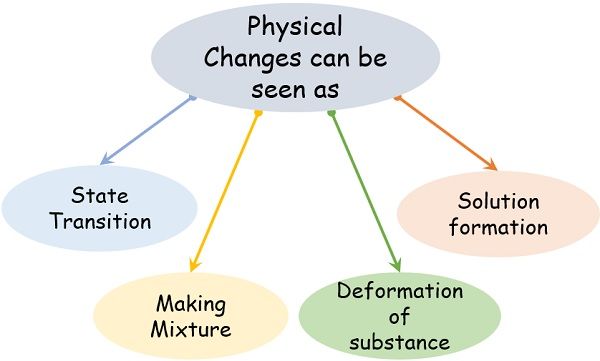
At the time of physical changes, we can observe the following physical transformation processes:
- State transition
- Deformation of the matter
- Generation of a mixture
- Formation of solution
Examples of the Physical Changes
1. Boiling Water: The water from its liquid state changes into vapours i.e., its gaseous state. Here, the chemical composition of water remains the same. Only the state transition occurs.
2. Crushing the Can: On applying force the structure of the can gets disrupted. But still, you can easily identify it as a can as there is no major chemical change. You can reverse back the original structure of the can.
3. Melting of Ice: The ice is a solid form of water which when melts gets converted to water. Here too, the state transition occurs.
4. Formation of Mixture: Mixing two or more substances generates a mixture. As the matter here doesn’t undergo any chemical or molecular interaction. Thus, it is a physical type change.
5. Cutting Paper Strips: When the paper is cut fragmented into smaller strips but never losses its uniqueness or chemical structure. Therefore, it also is a physical change.
What are Chemical Reactions?
We often refer to these changes as a chemical reaction. Chemical changes are those which alter the chemical composition of the initial substance. These changes result in the rearrangement of atoms and molecules present in the original material. Thereby they generate newer substances with totally different properties than their parent compound.
The components that we take at the beginning of the reaction are reactants. These reactants serve the typical role of ingredients for any given recipe. Later, as the reaction terminates, the end result is the product of the reaction.
The reactant molecules constantly make and break the chemical bonds for this conversion. As a result, either some amount of the energy will be absorbed, or the energy will be liberated.
Definition of Chemical Changes
We can define the chemical changes as
“The process that changes both structural and molecular properties of the reactant either due to making or breaking of the chemical bond, thereby developing a new product”.
Or
“An irreversible or permanent change alters the molecular configuration of the substance to give rise to the product”.
Characteristics of Chemical Change
- During the chemical changes, the energy evolves or get absorbed either in the form of heat or light.
- These changes are irreversible in nature as the initial reactant losses all its properties. And thus, cannot be regained easily.
- As we cannot transform the product back into the reactant, they are considered to be permanent changes.
- Completion of chemical reactions produces a new substance or substances with new properties.
- These changes take time to occur and tend to last for a longer span.
- Chemical changes transform both the chemical and the physical properties of the reactants.
What happens during the chemical change?
During the chemical change, the process of breakdown and formation of the bonds constantly occurs. This leads to the alteration in the energy of the reaction. This change in energy facilitates the formation of a new substance with changed features. Such as altered melting point, boiling point, colour, texture etc.
For example, burning the thin ribbon of magnesium generates white powdered ash of magnesium oxide. Further, if we mix this ash with water, it will produce an aqueous solution of magnesium hydroxide. All the components here have different structural and chemical properties.
Along with the product, the chemical changes can also lead to:
- Emission of heat, light or radiation
- Production of sound
- Change of odour or generation of any other significant smell
- Formation of bubbles
- Evolution of gas
- Change in colour of the reaction mix
- Fluctuation in the temperature
Examples of Chemical Change
1. Baking of Cake: Baking provides heat energy to the molecules. On heating, the molecules become excited for the formation or breakdown of the bonds. Thus, a new product is generated.
2. Burning of Wood: When we burn the wood, it is a combustion reaction. It chemically alters the wood into ash and generates several other gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide as byproducts.
3. Cooking Eggs: The eggs are all proteins and fats. As the temperature rises during the cooking process, the egg proteins start getting denatured. Thereby changing the molecular orientation and chemical composition of the molecules.
4. Lightening Candle: Burning a candle too converts the wax into several other compounds thereby changing its chemical properties. Thus, it is a chemical change.
5. Curdling of Milk: During the curdling, the milk proteins coagulate. This changes their chemical composition. And the milk produces a completely new product i.e., Curd; having different properties than its parent compound.
Key Differences Between Physical and Chemical Changes
- In Physical changes, the material the mass of the substance and the internal arrangement of the molecules and atoms remains the same. On the contrary, when changes involve the formation of the new substance from the original substance it is a chemical change.
- Physical changes are temporary and they involve the transformation in different phases of matter. Like from solid to liquid; liquid to gas.
Whereas chemical changes are permanent as it participates in the breaking and formation of new bonds to make the new compounds. - The physical change affects only the physical properties of the material like shape, size, colour. Whereas chemical properties affect not as physical as well as the chemical properties of the material. This is because there is an internal change in the atoms and molecules of the material.
- No new substance is formed in physical changes while in chemical changes always produce new substances. , the atoms and molecules rearrange themselves and form a new compound, and these can be irreversible or reversible.
- There is no energy required or produced during physical changes, but in the chemical change, there is always the requirement of energy. The energy is either absorbed or released in the form of light, heat or sound.
Conclusion
From the above article, we tried to focus on the points on which the physical and chemical changes differ. As these are some of the common things that occur every then and now and one should know of this. We also provided a few common instances which will be helpful for the readers to understand.











Leave a Reply