To understand the importance of dopamine and endorphins, you must first know what are they!
Our body is driven by certain chemicals that balance and manipulate the emotions we feel. Happiness, sorrow, pleasure, affection, etc. are the feelings that arise from these chemical messengers. Dopamine and endorphins are two of those same chemicals responsible for happiness and relief.
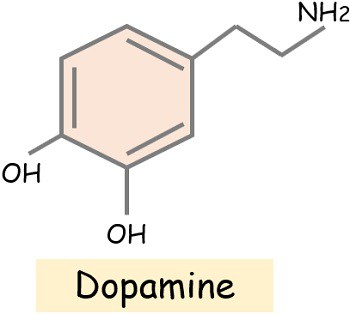
Talking about dopamine, it is basically a neurotransmitter that also serves the role of a hormone. We often refer to it as a feel-good hormone that acts as a “reward centre” for our body. Whereas the endorphins are responsible for creating a relief sensation from pain thereby generating a euphoric pleasure.
The brain secretes dopamine as a motivational component in response to some behaviour, activity or movement. In comparison, the endorphin releases when the body experiences stress, discomfort or physical pain.
The neurotransmitter dopamine belongs to the catecholamine family. While the endorphins are the group of hormones consisting of opioid neuropeptides.
The site of action of both of these chemical messengers differ. Dopamine acts on the brain. But the endorphins target both central and peripheral nervous systems.
They are the two crucial happy hormones of our body. Always remember “happy hormones means happy you”. Thus, it becomes essential to have adequate knowledge about them. This content will provide key differences between dopamine and endorphins.
Content: Dopamine Vs Endorphins
Comparison Chart
| Basis of Comparison | Dopamine | Endorphin |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It is a neurotransmitter that drives your brain to send happy, rewarding signals. They get released as a reward, especially after some pleasurable activity. | They are a group of hormones that curb physical pain. They get secreted to generate euphoria when the body experiences pain and discomfort. |
| Chemical formula | C8H11NO2 | C45H66N10O15S |
| Role | To generate or promote the motivational component for more reward. | Inhibits the mechanism that communicates the signals of pain. |
| Type | Catecholamine family | Opioid neuropeptides |
| Synthesis | Occurs in brain and kidneys | Occurs in CNS and pituitary gland |
| Precursor | L-DOPA or Levodopa | POMC or Pro-opiomelanocortin |
| Site of Action | Acts on brain | Acts on both central and peripheral nervous system |
| Binding Receptors | Binds to G-protein coupled D1-D5 receptors or human trace amine-associated receptors1 (hTAAR)1 | Binds to G-coupled opioid receptors or µ-opioid receptors |
| Endocrinal Functions | • Acts as a vasodilator of blood vessels • Enhances sodium excretion and urination in the kidney • Decreases the insulin production in pancreatic glands | • Β- endorphin influences the discharge of ACTH, prolactin, aldosterone, corticosterone and somatotropin |
| Related medical conditions | Can cause: • Tourette’s syndrome • Parkinson’s disease • Drug addiction | Can cause: • Mood swings • Depression • Obsessive-compulsive disorder |
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine plays a part in the reward mechanism of our body. It is a sort of monoamine neurotransmitter that also functions as a happy hormone. Our brain secretes it as a result of a particular action, behaviour or physical movement.
After completing certain activities, the body releases dopamine in order to make us feel good. This motivates us to want to do more of it, which will ultimately produce more dopamine. Thus, we say that it is a cycle of reward, motivation and reinforcement that drives us towards happiness.
Understanding Dopamine with Example
Any activity can flood you with plenty of dopamine as per your liking and your way of enjoyment. It can be anything from completing a given task, winning a bet, getting a good meal, doing a physical workout, listening to loud music etc.
Imagine if you get immense pleasure from eating a red velvet cake. It is your go-to comfort food. As soon as your senses come in contact with that cake-like if you smell it or taste it, your brain instantly floods you with dopamine. It will start generating a pleasurable feeling. It also reinforces this craving and aims to satisfy it in future.
Similarly, suppose if you are craving that cake for a very long time but are unable to find it anywhere, this disappointment will reduce the level of dopamine in your body. Thereby exaggerating your desire to eat it even more.
Role of Dopamine in our body
Dopamine directly or indirectly influences every aspect of our bodily function. Being a hormone, dopamine gets released directly into the bloodstream. For this reason, it influences many of the mechanism occurring nearby. This may include the way we think, sense, move, remember or behave.
It also plays a part in flight and fight response during times of danger and real or perceived stressful situations.
Apart from playing the role of a happy hormone, dopamine impacts several other mechanisms in our body such as:
- Neurological functions
- Behavioural actions
- Cognitive functions
- Movement
- Memory
- Mood
- Lactation
- Learning abilities
- Attention
- Sleep and arousal
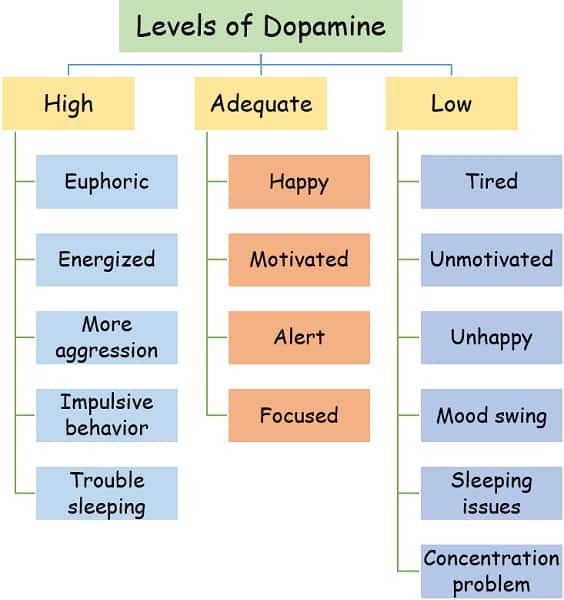
What does the level of Dopamine indicate in our body?
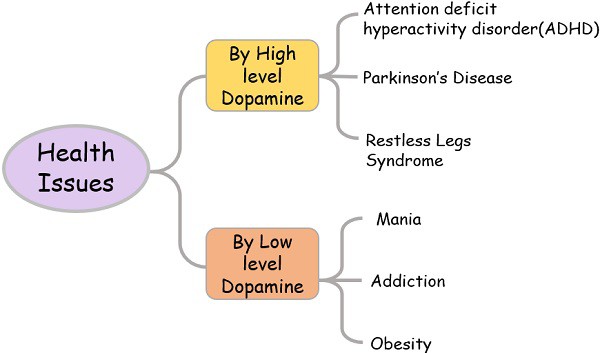
We all experience dopamine differently. Different levels of dopamine may lead to certain potential imbalances that are hard to detect which eventually affects the healthy being of your physical and mental state.
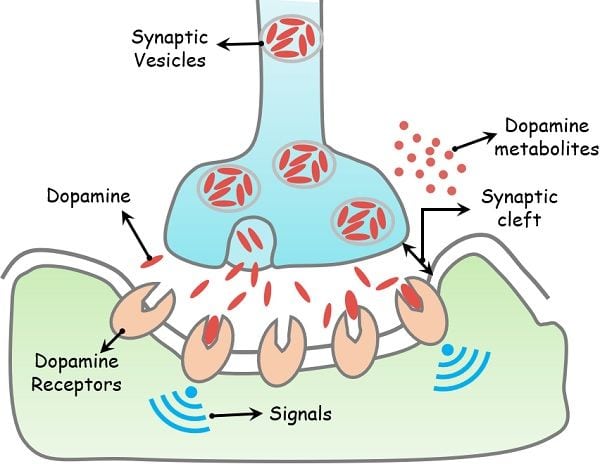
Mechanism of Action of Dopamine
Dopaminergic neurons start producing and secreting dopamine into chemical synapses as soon as the brain gets a stimulus. From there, it diffuses via the synaptic cleft towards the postsynaptic domain receptors. No sooner the dopamine reaches the nearby neuron than it adheres to that neuron’s receptor.
There, it delivers the chemical message leading to the generation of signals in the receiver nerve cell. After completing the transmission process, the dopamine is retaken and repacked into the synaptic vesicles or get digested through enzymes.
What are Dopamine Receptors?
These receptors are proteinaceous and are present in the brain and the nerves within the body. They are slow-acting metabotropic G-protein coupled receptors. The receptor and neurotransmitters function together like a lock and key mechanism.
There are five kinds of dopamine receptors at the postsynaptic end: D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5.
Health issues because of High or low levels of Dopamine
Natural methods to balance the Dopamine Level
It is highly difficult to keep a check on dopamine levels in the body as they get released by the brain. But there are several methods to balance out the dopamine concentration. This may include:
- Healthy habits and lifestyle
- Consumption of nutritious food
- Doing adventurous activities
- Keeping yourself happy by doing things of your interest at regular intervals
- Exercising to keep body and mind fit
- Celebrating small moments of your life
- Spending time with children and family
This is the list of a few activities that generally boost the dopamine level in our body.
What are Endorphins?
The endorphins are actually endogenous morphine. They are named so as they bind to the same opioid receptor to which morphine binds and produce the same effects as morphine of relieving pain. They serve the role of natural painkillers in the body during physical pain, stress or discomfort.
Apart from this, they help in distracting us from the feeling of pain and lead us towards the sensation of euphoria.
Although they do not directly induce pleasure and motivation, instead they prompt the brain to release dopamine which ultimately produces the sensation of happiness.
For instance, suppose you are engaged in any physical activity after which you are suffering from pain and discomfort. In such a situation, the body secretes endorphin that will ease your stressed muscles and pain. Thereby stimulating reward-related areas of the brain to secrete dopamine
They are a group of opioid neuropeptides. Generally, the pituitary glands and the central nervous system both release endorphins when needed.
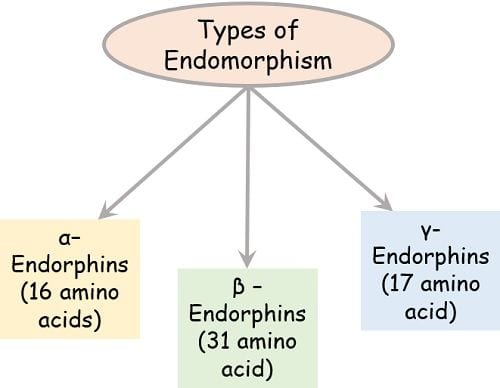
Types of Endorphins
Understanding Endorphins with Example
The actions like heavy workouts, running a marathon, climbing mountains etc., may cause pain in the body. But along with that, it brings a good feeling of euphoria and accomplishment. At this time, your body distracts from its painful experiences and enjoys the pleasure achieved from that particular activity. Thus, we can say that endorphins, on one hand, reduce pain, and on the other hand, they provide euphoria.
For instance, imagine that you are on a mountaineering or trekking trip. And your body is burning with pain. On which you hit your ankle very hard. Ultimately, your body and mind are totally in a miserable condition. But you are still climbing to reach the top of the mountain.
In such a case, as soon as you will reach your goal, the CNS will flood your body with your endorphins. This will pull your attention away from the pain and ankle injury. And will motivate you to focus on the pleasure and euphoria of reaching the top.
Functions of Endorphins
- Eases the discomfort
- Reduce the pain
- Increase pleasure and euphoria
- Enlighten mood
- Boost self-esteem
- Decrease the sense of anxiety or stress
- Prevent depressive thoughts
- Supports a healthy immune system
- Attenuates inflammation
- Supports cognitive functions
- Boost memory
Mechanism of Action of Endorphin
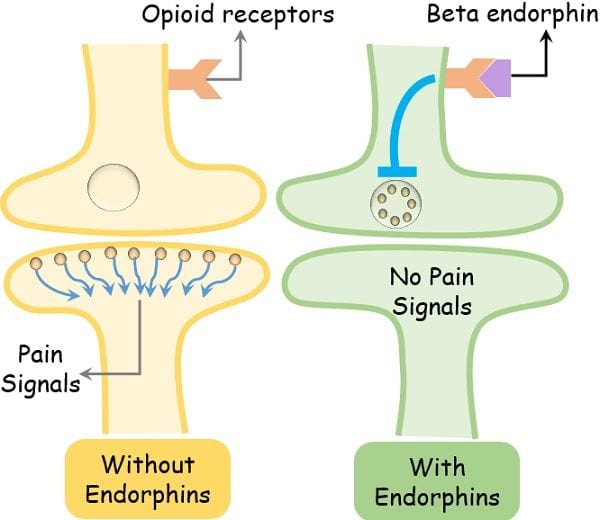
They bind to the receptors of both CNS and PNS. The beta-endorphin binds to G-coupled opioid receptors or µ-opioid receptors in the peripheral nervous system. Further, it blocks the neurotransmitters that induce the postsynaptic response causing pain.
While in the central nervous system, this same binding leads to increased dopamine secretion that brings out the euphoric feeling.
Natural methods to boost the Endorphins
These are a few activities that can naturally induce the body to secrete endorphins:
- Eating Dark Chocolate and related food
- Exercising
- Creating or Listening to Music
- Creating Art
- Dancing
- Receiving Acupuncture
- Laughing aloud
- Eating Spicy Food
- Massaging
- Sauna bathing
- Using Aromatherapy
- Watching thrilling shows on TV
- Doing adventurous stuff
Key Differences Between Dopamine and Endorphins
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that stimulates the good and happy feeling inside our body as a result of a particular action, movement or behaviour.
In comparison, the endorphins released when the body undergoes a heavy physical workout thereby is in pain, distress or discomfort. It relieves the pain and creates euphoric pleasure. - The brain (CNS) and kidneys are responsible for the regular secretion of the major proportion of dopamine in our bodies. Whereas CNS, as well as the pituitary gland, releases the endorphins when necessary.
- Dopamine comes under the catecholamine family. In comparison, endorphins are opioid neuropeptides.
- The precursor molecule of dopamine is Levodopa (L-DOPA). While the proopiomelanocortin (POMC) is the precursor for endorphins.
- The dopamine binds to the G-protein coupled dopamine receptors while endorphins bind to µ-opioid receptors.
Conclusion
Dopamine and endorphin are two of the four happy hormones. Both of them have their own importance in our bodies. They are the actual reason you feel happy, pleasured and motivated after doing a particular activity.
We should regularly engage ourselves in the activities that boost these neurotransmitters so as to stay happy and healthy. But we should avoid doing reckless things in order to attain their rush.



Leave a Reply