Both yeast and mould belong to kingdom fungi. But still, they exhibit many differences, including their appearance, habitat, method of reproduction, growth conditions etc. At present, there are around 1500 types of yeast, whereas 400,000 species of moulds are found on earth.
On the one hand, the yeasts are unicellular microorganisms with a round or oval-shaped, colourless appearance. Contrastingly the moulds are filamentous, thread-like, multi-coloured fungi.
The growth conditions also vary for both of them. The yeast can grow between the pH range of 4.0 to 4.5, whereas the moulds are capable of growing in a broad range of pH.
The yeasts are non-sporing species; they reproduce via budding or binary fission. Contrastingly, the moulds bear spores and can reproduce via both sexual and asexual means.
The following post will help you know the primary differences between yeast and moulds with and comparison chart and other characteristic features.
Content: Yeast Vs Mould
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Yeast | Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Yeast is a type of single cell microorganism, falls under kingdom fungi. | Molds are multicellular microorganisms, usually colorful and also fall under kingdom fungi which grow in a multicellular filaments called hyphae. |
| Kind of cell | Single cell. | Multicellular. |
| Shape | Filamentous or Threadlike. | Round or oval. |
| Presence of Hyphae | Pseudo-hyphae i.e. they don't have true hyphae. | Hyphae (microscopic filaments). |
| Presence of Spores | Non-Sporous fungi. | Sporous fungi. |
| Types | There are 1500 types of yeast. | There are 400,000 types of molds. |
| Mode of Reproduction | Asexual through mitosis. Common method is budding and spores formations. | Sexual or asexual. |
| Colour | Colourless and smooth (usually white). | Colourful, wooly and fuzzy (green, orange, black, brown, pink, purple). |
| Aerobic/Anaerobic | Yeast can grow in aerobic as well as in anaerobic conditions. | Mold grow only in aerobic conditions. |
| Uses | Yeast is used in beverages production like alcohol and also in making of baking, bioremediation, food additive. | Useful in biodegradation, food production (cheese), in making antibiotics. |
| Health Hazards | Yeast may weaken the immune system of the body and may contribute in asthma, crohn's disease. | Molds may cause allergies, respiratory problems. |
| Examples | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baking yeast), Cryptococcus neoformans, etc. | Mucor, Penicillium, Rhizopus, Aspergillus, etc. |
What is Yeast?
You may have eaten pizzas, bread, cakes and doughnuts with spongy airy textures. The fact might amaze you, but most of the time, the yeast is used for this texture in the above food items.
Yeasts are the least in number when we talk about the species of fungi found on the earth. They are eukaryotic microorganisms but with a single-celled appearance.
Let us know more about them!
Structural/Microscopic Appearance
- It is a unicellular microorganism.
- Mainly round or oval in shape.
- Slimy appearance.
- Yeast does not have distinguished body parts like filamentous hyphae, mycelia etc.
Colour
They are present in lesser colour varieties. Sometimes they are white or even colourless.
Habitat
They can be found on fruits, berries, and even in the stomach and skin of mammals.
Colony morphology
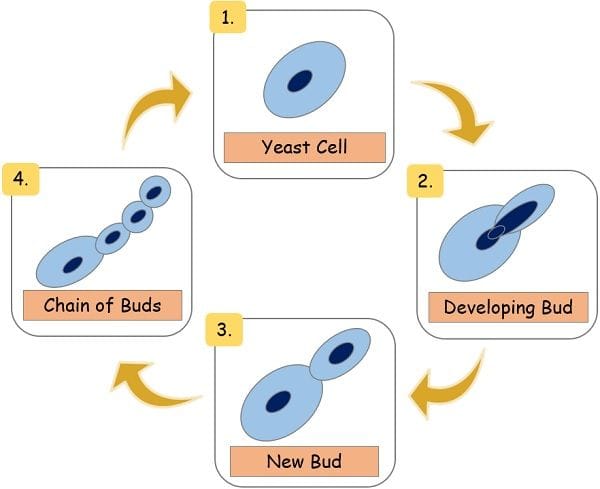
- They produce visible colonies in the form of clusters and chains by budding.
- Their colonies are soft, opaque and cream-coloured.
- Some species manifest multicellular characteristics with developing strings by connecting the newly budded cells. They resemble the structure of hyphae but are not true and are called pseudohyphae.
Energy Production
They perform anaerobic fermentation reactions that convert carbohydrates to alcohol and release carbon dioxide as a by-product.
Also, they obtain carbon from hexose sugar.
Reproduction
They mainly reproduce asexually via budding. But of, the yeast species are even capable of reproducing by binary fission.
Their asexual spores are Blastopore.
Conditions for growth
- Nutrition: The yeast needs organic matter with a good amount of moisture to obtain the nutrition. They require organic hosts to derive nutrition and have the ability to break down carbohydrates and cause fermentation to produce energy either aerobically or anaerobically
- Incubation Temperature: The optimal incubation temperature is between 25-30 (room temperature) °C.
- Incubation Time: They grow within 24-36 hours after their inoculation in media.
- Requirement of Air: They can grow in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
- pH range: They can grow optimally within the pH range of 4-4.5.
Diagnostics/Identification
We identify them on the basis of physiological tests and morphological differences.
Presence of Hyphae
- The yeasts do not bear true hyphae.
- But they have hyphae-like structures called pseudohyphae.
Related risks
- In comparison to other fungi, the yeasts are less involved in the processes like food spoilage. But sometimes due to excess fermentation there occurs spoilage which is easily detectable as an ‘off-flavour” of the food.
- They may cause infection in people by compromising the immune system like candidiasis in humans is caused by yeast candida and may contribute to asthma, and Crohn’s disease.
Uses
- Yeast has the capability to convert carbohydrates to alcohol and carbon dioxide. Due to these reasons, they are used in the production of ethanol for alcoholic beverages, in baking, etc.
- The industries cultivate yeast to obtain several chemical products, including essential enzymes.
Examples
- Cryptococcus cerevisiae
- Cryptococcus neoformans
Number of Species
There are around 1500 species of yeast currently discovered on the earth.
What is Mould?
You may have seen the bread often developing a cottony thread-like appearance on its surface when kept in an open moist area. These fuzzy filamentous structures are nothing but moulds.
The moulds are multicellular types of fungi that possess identical nuclei. Let’s look at some of the common characteristics of the mould.
Habitat
- Moulds are generally found everywhere where there is moisture. They just require an organic material with a little bit of water in order to establish their entire colony in a few hours.
- Moulds grow rapidly in the dark, damp areas like rotting bread, veggies etc.
Microscopic appearance
- They appear multicellular when visualised under the microscope.
- They have a cottony or woolly texture with numerous fuzzy filaments called hyphae.
- Tubular hyphae possess lots of nuclei that share an identical genetic framework.
Methods of reproduction
- They are capable of reproducing both ways- sexually and asexually.
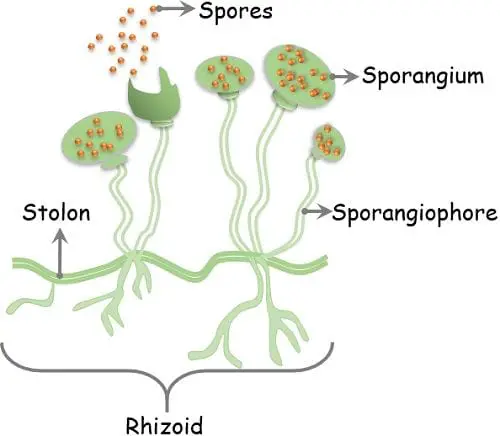
- They are sporing species that displace the aerial spores on the substrate. Further, these spores start to grow above or below the surface of the substrate.
- The sexual spores are referred to as zygospores, ascospores and basidiospores.
- The asexual spores are termed sporangiospores or conidia.
Presence of Hyphae
They bear the microscopic thread-like filaments called hyphae.
Colony Morphology
- The colonies of the mould are easily visible by the naked eyes.
- The colony is a filamentous type with vegetative as well as aerial hyphae.
Colour
They appear in many colours, including brown, green, black, purple, black, orange and pink.
Conditions for growth
- pH Level: The moulds can cultivate in a wide range of pH, including highly acidic and basic.
- Requirement of Air: They can grow only in an aerobic environment.
- Incubation Temperature: The routine incubation temperature usually ranges from 25-30 °C.
- Cultivation Time: They take a comparatively longer time to completely grow. They have a slow growth rate after their incubation in the media.
Diagnosis/Identification
- The clinical identification involves their microscopic examination
- Also, the study of ontogeny and morphology of their spores can help in the identification process.
Energy Production
Moulds realise hydrolytic chemicals that degrade biopolymers like starch, cellulose and lignin into simpler substances that can be absorbed.
Related Risks
- Certain moulds also can be hazardous to health that can cause allergies, other respiratory problems, headaches, rashes, itching, etc.
- Moulds also cause greater problems related to food spoilage, particularly in moist food items and sanitation concerns.
Uses
- Some of the moulds are useful in food production.
- Used in the production of cheese, rennet, beverages, tofu and salami.
- Penicillium is used in the making of medicines, especially antibiotics like penicillin.
- Other medicines like Lovastatin (cholesterol-lowering), and cyclosporine (immunosuppressants) are also produced.
- Moulds act as decomposers by decomposing nature’s organic wastes. They are elementary in the breakdown of organisms on the earth.
Number of species
There are around 400,000 species of moulds discovered on the earth up till now.
Examples
- Alternaria
- Fusarium
- Mucor
- Rhizopus
- Penicillium
- Trichophyton
Key Difference Between Yeast and Mould
- Yeast is a single-celled organism, which reproduces asexually mainly by binary fission or budding. Whereas moulds are multicellular and reproduce sexually or asexually.
- There are 1500 types of yeast while 400,000 types of moulds are present on the earth.
- Yeasts are commonly present in fruits, vegetables, as well as on the skin of mammals. While you can observe moulds in damp, dark or steam filled areas.
- Yeast is a colourless, oval or round-celled fungus. Whereas moulds are present in many colours with a thread-like cottony appearance.
- Some of the variants of yeasts possess hyphae-like structures but they are not true, thus we refer to them as pseudohyphae. Contrastingly, the moulds have true and dense filaments of hyphae.
- The yeast can grow both in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. But the moulds are obligatory aerobes.
- Yeast comes in use while preparing food beverages, fermented food products, alcohol, etc.
Moulds are useful in the making of cheese, rennet, and antibiotics (penicillin), Lovastatin.
Conclusion
Yeast and Molds both are types of fungi, though having different characters and uses.
As above discussed, Yeast is a type of fungi which exists as a single cell and reproduces asexually used in food beverages, alcohol, etc. On the other hand, Molds are multicellular with hyphae and can reproduce sexually or asexually; they are used in making antibiotics, cheese making, etc.
This post will help you to know a detailed explanation of all the differences between yeasts and moulds


Leave a Reply