Monera is a unicellular organism, they have a prokaryotic cellular organization, which means they lack well-defined, membrane-bounded organelles and nucleus. On the other hand, Protista is also unicellular organisms, but consist of eukaryotic cellular organization and well defined,membrane-bounded organelles and nucleus, this is the main difference between them.
All forms of life on earth are divided into five categories on the support of the nutrition and energy they obtain, kind of cell (single cell or multi-celled), structural complexity, etc. These five kingdoms are Monera, Protists, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Monera is the most primitive types of organisms which include blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), eubacteria and archaebacteria. While Protista represents the early evolution of eukaryotic cells.
Given below are the key differences between Monera and Protista, as well brief description on them:
Content: Monera Vs Protista
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Monera | Protista |
|---|---|---|
| Cellular level | Monera are unicellular organism's having prokaryotic cellular structure. | Protista are also unicellular organisms though possess eukaryotic cellular organisation. |
| Other organelles | Cellular organelles are absent. | Well defined as well membrane-bounded cellular organelles are present. |
| Complexity | Monera are simple in structure, with no complexity. | Protista are complex in structure. |
| Contains | Small microorganisms. | Organisms are larger than Monera. |
| Mitochondria/ Chloroplast | Not present. | Present for cellular respiration, chloroplast for photosynthesis. |
| Cell wall | Cell wall is present. | They have well developed cell wall. |
| Nucleus | Monera's does not posses a true nucleus. | Protists has it's own nuclei, bounded with nuclear membrane. |
| Mode of Nutrition | It can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. | It can be holozoic or parasitic or photosynthetic. |
| Presence of Flagella and Cilia | Not found in monera. | It is used for locomotion in some organisms, some also have pseuopodia. |
| Mode of reproduction | Asexual by binary fission or budding. | Both Asexual (binary fission or multiple fission) or sexual. |
| Found | They are cosmopolitan, which means they are found everywhere. | They are found partially in aquatic environment, moist soil, shady places, etc. |
| Classified as | Archaebacteria, bacteria, cyanobacteria. | Diatoms, Algae, molds and protozoans. |
| Examples | Mycobacteria, Bacillus, Sporohalobacter, Clostridium, Halobacterium. | Green algae, red algae, slime molds, euglena, and water molds are the examples of protists. |
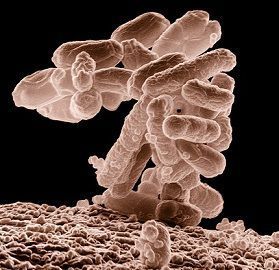
Definition of Monera
As said above, these are the unicellular, prokaryotic organisms lacking well-defined organelles and nucleus. But these are found abundantly among all types organisms present on earth, due to their adaptability in all kinds of habitat. It is estimated that a single fall of water contains around 50 billion bacteria. They are found in living as well as in the non-living environment.
They have their vital role in the nitrogen cycle and carbon cycles. They reproduce through asexual reproduction, by binary fission, budding or fragmentation. DNA is double stranded, suspended in the cytoplasm of the cell of organisms termed as the nucleoid. These are metabolically active and uses a variety of substances to gain energy. The cell wall is rigid.
Because of their capability of surviving in harsh and extreme climatic conditions like in deserts, hot springs, acidic soils, etc., monerans are present everywhere. They can be autotrophic, heterotrophic, saprophytic, symbiotic, commensalism or parasitic.
The realm of kingdom monera is Cyanobacteria, Eubacteria, and Archaebacteria, Mycoplasma, etc. Monerans circulation is through the process of diffusion and movement is through flagella. They reproduce sexually (transformation, conjugation, or transduction) or asexually (by binary fission).
Cyanobacteria-They is also called blue-green algae. They are photosynthesizing prokaryotes. Cyanobacteria are found in all kinds of aquatic habitats right from the fresh water to ocean.
Eubacteria-These are two types gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Their cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan and murins, which is a kind of carbohydrates. They are found everywhere which includes water, soil, or on large organisms.
Archaebacteria-Archaebacteria is considered as the most primitive kind of bacteria and is said to evolve just after first life on earth. They usually live in extreme environments like salt lakes, marshlands, oceans and hot springs.They are of three types halophiles, thermophiles, and methanogens.
Economic Importance of Monera (bacteria)
- They are used in the fermentation process in industries.
- Used in bioremediation process.
- Used as pesticides in pest control mechanism.
- In making therapeutic proteins.
- Preparation of medicines.
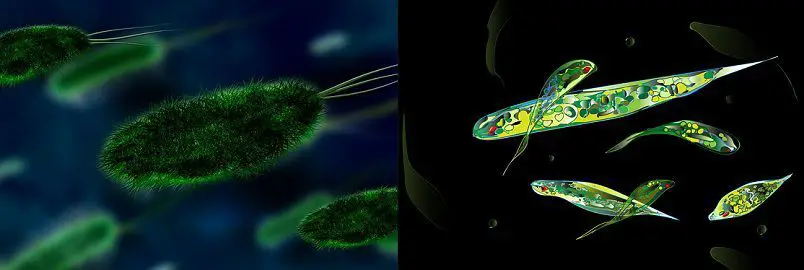
Definition of Protista
Protista is considered to be the predecessor of the plants, fungus, and animals. In 1866, Ernst Haeckel used the word Protista for the first time. Protista are said to be the first eukaryotic forms of life. So they have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Protista is the large group, consisting of around 16 phyla. Maximum members of this category are aquatic in nature. Some of them are responsible for causing serious human diseases like sleeping sickness and malaria.
These are the simplest eukaryotic organisms. Mostly live in the aquatic region, moist soil or in the body of plants and humans. They have mitochondria for cellular respiration, while some contain chloroplast for photosynthesis. The nuclei have multiple DNA strands.
Their movements are through flagella or cilia. Their mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Protists reproduce either sexually or asexually through mitosis or meiosis.
Green algae, red algae, brown algae, water molds, dinoflagellate, amoeba are few examples of protists.
Economic Importance of Protists
- Source of medicine – as an anti-cancer compound, blood coagulants.
- Source of food – used as edibles.
- Source of commercial products – They are the producer of antiseptics, agar, carrageen, algin.
- Helpful in biological research.
- Source of minerals – They are a good source of minerals.
Key Differences Between Monera and Protista
Given below are the noteworthy key differences between Monera and Protista:
- Monera are unicellular organism’s having prokaryotic cellular structure while Protista is also unicellular organisms though possess eukaryotic cellular organization.
- Cellular organelles are absent in Monera; whereas Protists have well defined as well membrane-bounded cellular organelles.
- Monera is simple in structure, with no complexity at the cellular level while Protista is complex in the structure at the cellular level.
- Monerans contains very small microorganisms and are found everywhere while in protist, organisms are though microscopic but larger in size than monerans.
- Mitochondria/ Chloroplast are not present in Monera; whereas mitochondria are present for cellular respiration and chloroplast for photosynthesis in Protista.
- Monerans does not possess a true nucleus whereas Protists has its own nuclei, bounded with the nuclear membrane.
- Mode of nutrition can be autotrophic or heterotrophic in Monera, whereas it can be holozoic or parasitic or photosynthetic in Protists.
- Flagella and Cilia are absent in Monera; It is used for locomotion in some organisms, some also have pseudopodia in Protists.
- Mode of reproduction is asexual by binary fission or budding and if sexual then through conjugation, transformation or transduction in monerans; and in Protists it is either through asexual (binary fission or multiple fission) or sexual.
- Monerans are cosmopolitan, which means they are found everywhere, due to their ability to survive in harsh conditions also; Protista is found in moist soil region, and in the partially aquatic environment.
- Monerans are classified as Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Cyanobacteria whereas Protista is classified as Diatoms, Unicellular algae, Molds, and Protozoans.
- Examples of monera are Mycobacteria, Bacillus, Sporohalobacter, Clostridium, Halobacterium while Green algae, red algae, slime molds, euglena, and water molds are the examples of protists.
Conclusion
In the provided article we discussed the monera and protists, which are among the five kingdoms of classification, under which all kinds of life present on earth is classified. Monera is said to be the ancient form of life living on earth and even still they exist generously as well ubiquitously.
While protists are considered as the forebear of the eukaryotes, they are unicellular animals and are distinctive from plants, animals and fungi category. Both of them important from natures as well as economic and biological point of view. Both of them important from natures as well as economic and biological point of view.



Mohammed aneesuddin says
Superb and useful information …thanks a lot
Sristi Crma says
Was very helful…..