Mitochondria are known for generating energy for the cell in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) by using nutrients and oxygen. The chloroplast is present in green plants and few algae, they are known as the place, where the process of photosynthesis occurs.
In the cell of the eukaryotes, there are only three organelles, which are bounded by the double membrane structure – the nucleus, the mitochondria, and the chloroplast. There is the higher level of diversity on the surface of the planet. Living things inquisitively, perplexingly uses the sources present here and grow. They have populated the land, water, and molded the surface of the earth.
Living things are not only restricted to the domain of the land, water, instead found in depth of the ocean, in the mud of hot volcanoes, beneath the frozen surface of Antartic and deeply buried in the earth crust. In this section, we will consider the two main units of the eukaryotic cells – The Mitochondria and the Chloroplast.
The first one is the most significant body present in the living cell, they are the producer of energy to the cell, and it’s organelles by the process of cellular respiration. Their shape and function resemble bacteria, even they have their own circular DNA and ribosomes and their tRNA, like that of bacteria.
The latter – Chloroplast, is the another enclosed membrane of the eukaryotic cell. These are found in selective types of the cell as said above. Chloroplast performs the function of the preparation of the food that is photosynthesis, by using the sources like sunlight, water, and air. Even it is acceptable that chloroplast had their genome and originated from the symbiotic photosynthetic bacteria.
Content: Mitochondria Vs Chloroplast
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Mitochondria | Chloroplast |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A large, membrane-bound, bean-shaped organelle found in almost all kind of eukaryotic organism, also known as 'powerhouse of the cell'. Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration and energy metabolism. | The chloroplast is found only in green plants and in few algae, they are the sites of photosynthesis. This organelle of the cell is much more complex and larger than the mitochondria. |
| Found in | Mitochondria are present in the cells of all types of aerobic organisms, like plants and animals. | Chloroplast is present in green plants and green algae, protists like Euglena. |
| Colour | Mitochondria are the colourless organelles. | The chloroplast is green in colours. |
| Shape | Bean shape. | Disc shape. |
| Chamber | Mitochondria have two chambers: matrix and the cristae. | Chloroplast also has two chambers stroma and thylakoid. |
| Inner membrane | The inner membrane of mitochondria is folded into cristae. | The inner membrane of the chloroplast rises into flattened sacs called as thylakoids. |
| Pigments | Mitochondria do not possess any pigments. | The thylakoid membrane in chloroplast contains carotenoids, chlorophyll and photosynthetic pigments. |
| Other characteristics | Mitochondria convert sugar (glucose) into chemical energy called as ATP (adenosine triphosphate). | In the chemical bonds of glucose, the solar energy is stored. |
| It consumes oxygen. | It liberates or releases oxygen. | |
| Mitochondria release energy by the breakdown of the organic food and produce carbon dioxide and water. | Chloroplast helps in storing the energy and uses carbon dioxide and water to make glucose (energy). | |
| Mitochondria are the site of beta oxidative, photorespiration, oxidative phosphorylation, ETC. | The chloroplast is the site of the photorespiration and photosynthesis. |
Definition of Mitochondria
Mitochondria is derived from the Greek word where ‘mitos‘-thread and ‘chondrios‘-granule. Mitochondria are also known as the ‘powerhouse of the cell‘ as it’s the main function is to produce energy in the form of ATP.
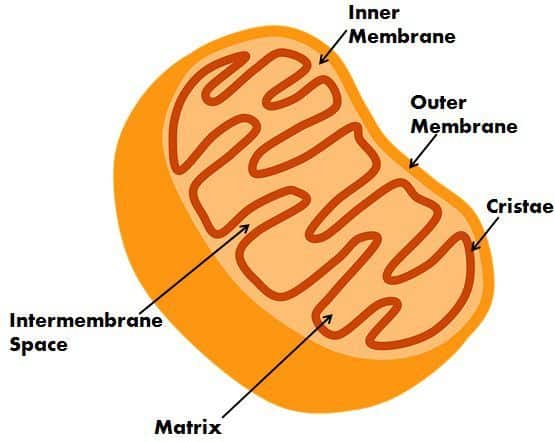
The mitochondria are the bean or rod-shaped structure. The diameter ranges from 0.75-3um, but vary in sizes. In a typical cell, it occupies around 25% of the total cell volume. In a cell, the number of mitochondria present depends on the metabolic requirements of that particular cell and therefore it can be thousand or a few. It is the double membrane structure, the outer and the inner membrane.
The outer membrane is made up of lipid and protein (phospholipid bilayers) and is highly permeable, though protecting the organelle also. The inner membrane is also made up of lipid and protein. The inner membrane is folded to form cristae, and the internal chamber is called as the matrix.
In the process of synthesizing energy that is ATP, the mitochondria use the oxygen and nutrients, this process is called as Aerobic respiration. This is the much more efficient way of producing ATP than in anaerobic respiration.
Apart from the synthesis of energy for the cell, mitochondria also help in cell signalling, regulation of cell cycle, cell growth, cell death, as well in cellular differentiation.
The exception is the mature mammalian red blood cells, where mitochondria are absent. It is believed that mitochondria used to exist as the independent prokaryotic cell once. But due to the process of endosymbiosis, they got engulfed and became the part of the eukaryotic cell. This is the reason, that why mitochondria contain its own DNA, and shows similarity with the prokaryotic cell (bacteria).
Though cellular respiration is not a simple process, the process involves three main steps: glycolysis, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and ATP synthesis. Further, the ATP released from the mitochondria is used by the other organelles, present in the cell.
Definition of Chloroplast
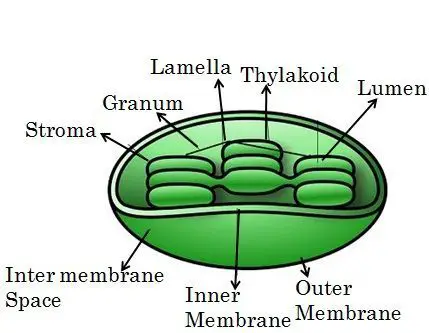
As said above, chloroplast is one of the double-membrane organelles of the cell. These are found in green plants and green algae. The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis, having their genome. These are the complexed structure, having the size of around 10um and 0.5-2um in thickness.
The structure of the chloroplast has the rigid cell wall, most importantly it contains thylakoids, which is the flat disc shape structure. Numerous thylakoids, which makes the bundle known as grana. These grana are present in the central area of the stroma.
Another important part is chlorophyll, which is a green pigment and plays its role in capturing the sunlight, this is also present in thylakoid. The thylakoid membrane also contains enzymes and other light-absorbing pigments, that are used in producing energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Key Differences Between Mitochondria and Chloroplast
Following are the key difference between the two most important organelles of the cell:
- Mitochondria are the large, membrane-bound, bean-shaped organelle found in almost all kind of eukaryotic organism, also known as ‘powerhouse of the cell’. Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration and energy metabolism. Conversely, Chloroplast is found only in green plants and in few algae, they are the sites of photosynthesis. This organelle of the cell is much more complex and larger than the mitochondria.
- Mitochondria are present in the cells of all types of aerobic organisms like plants and animals, whereas Chloroplast is present in green plants and some algae, protists like Euglena. Mitochondria is the colourless, bean shape organelles. Chloroplasts are green colour and disc shape organelles.
- Mitochondria and Chloroplast have two chambers inside them which is the matrix and the cristae in mitochondria, stroma, and thylakoids in a chloroplast.
- The inner membrane of mitochondria is folded into cristae while that of a chloroplast, rises into flattened sacs called as thylakoids.
- The thylakoid membrane in chloroplast contains carotenoids, chlorophyll, and photosynthetic pigments, but these are absent in mitochondria. Mitochondria convert sugar (glucose) into chemical energy called as ATP (adenosine triphosphate), it uses oxygen and release energy by breaking the organic food and in turn produces carbon dioxide along with water. In chloroplast the solar energy is stored, this organelle helps in storing the energy, further it also uses carbon dioxide and water to make glucose. Chloroplast liberates or releases oxygen.
- Mitochondria are the site for beta oxidative, photorespiration, oxidative phosphorylation, ETC; Chloroplast is the site for the photorespiration and photosynthesis.
Similarities
- Both are double membrane structure.
- Both the organelle contains their DNA and RNA.
- They both provide energy to the cell.
- Both the organelles contain enzyme and coenzyme.
- There is the involvement of the oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Another unique feature is that both the organelles can move from one place to another within the cell.
Conclusion
From the above article, we came to know that, being one of the most important parts of the eukaryotic cell, both the organelles are essential and contribute equally to the growth and function of the cell. It is also concluded that earlier mitochondria were the free-living aerobic bacteria, which became part of the eukaryotic cell due to some process.
Chloroplast, is not the part of all eukaryotic cell, as it is found in green plants and few algae. As these play the main role in process photosynthesis, through which plant prepare their food with the help of sunlight.

ms.springs says
very educational and interesting. .
jonathan t says
this was educational