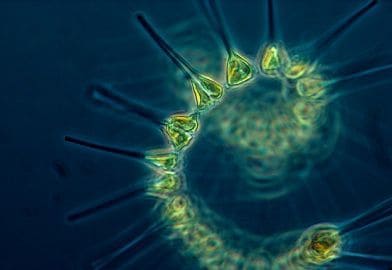
The basic difference between phytoplankton and zooplankton is that the word ‘phyto‘ is used for the small plants like diatoms and algae and word ‘zoo‘ is used for the small animals like tiny fish, crustaceans, which are the weak swimmers and just move along the currents. The word “plankton” refers to the smallest aquatic plants or animals that float and drift in the limnetic zone of water bodies.
Planktons are divided into two categories where one is called as permanent plankton and the other is called as temporary plankton. Permanent members of this category include diatoms, radiolarians, foraminifers, dinoflagellates, krill, copepods, salps, etc., they are also called holoplankton. Temporary members include sea stars, crustaceans, marine worms, sea urchins, most fish, etc., these are the larval forms which are also known as meroplankton.
All the species of plankton are adapted to certain structural adaptations, which enable them to float freely in the water. These adaptations are oil droplets, lateral spines, sheaths made of gel kind of substance, floats filled with gases, flat bodies. In this article, we will be discussing the difference between both kinds of plankton.
Content: Phytoplankton Vs Zooplankton
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Phytoplankton | Zooplankton |
|---|---|---|
| What are they | Phytoplankton are the aquatic plants. | Zooplankton are the small aquatic animals. |
| Mode of nutrition | Phytoplankton prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis (autotrophs). | Zooplanktons depend on phytoplanktons for their food and other matter found in sea (heterotrophs). |
| Habitat | As they depend on sunlight for making their food, they primarily use to live on the surface of the water. | Zooplankton lives in the darker and colder area of the water body. |
| Liberation of oxygen | Being in the category of plants, Phytoplankton releases oxygen in the atmosphere. | Zooplankton does not have such function. |
| Movement | Phytoplanktons are not the active swimmers and cannot move. | Zooplankton can swim actively or passively. |
| Ecological Importance | 1. Phytoplankton serve as the basic food source for many marine animals. 2.They also play a vital role in checking the stability in marine water, as they serve as an indicator of health of water. | Zooplankton also helps in checking the toxicity level in marine water. If there are sudden changes in water like increase in level of pollution, acidity, changes in temperature, these plankton reveal the early warning of the changes in the environment. |
| Examples | Algae and Diatoms. | Crustaceans and Small fishes, etc. |
Definition of Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton is derived from a Greek word where phytos means ‘plant’ and planktos, means ‘wandering’. One of the most common examples of the planktonic genus is Synechococcus and can reach the densities of 104-105 cells per milliliter. Whereas the Picocyanobacteria which is a very small cyanobacterium represents 20-80% of the total phytoplankton.
In most marine and freshwater environments, Phytoplankton (photosynthetic prokaryotes and eukaryotic organisms) forms the basis of primary production. The dissolved and particulate organic matter is released by the phytoplankton and is further used by heterotrophic bacteria.
A part of this material is consumed by the predators, which further releases the material and is used eventually used by phytoplankton. Iron and nitrogen can limit these activities in the different marine environment. Most importantly, phytoplanktons are producing half of the world’s oxygen.
The overgrowth of algae, also known as algae blooms, is the type of phytoplankton indicating the high level of presence of toxins. It is also known as Red Tides. It results in the die-off of marine animals and fish in that particular water body and thus creating the dead zone. The two main classes are dinoflagellates and diatoms of phytoplankton. They also play a major role in global carbon cycle.
Definition of Zooplankton
Zooplankton refers to the small animals, that swims in the water bodies. Zooplankton is classified by size by their developmental stage and size like picoplankton, nanoplankton, microplankton, mesoplankton, macroplankton, mega plankton. They range from less than 2 micrometers to 200 millimeters (almost 8 inches).
On the basis of the sizes, the zooplanktons are divided into two groups, which are meroplankton and holoplankton. Holoplankton contains Polychaetes, Larvaceans, Copepoda, Pteropods, Siphonophores, etc., these are the permanent members. Meroplankton includes crustaceans, mollusks, echinodermata and some small fishes, these are the temporary members among plankton.
Almost all the members of Kingdom ‘animalia’ like Protozoa, Cnidarians, Arthropods, Molluscs, Echinodermata, and Chordates are considered as zooplankton.
They show a very different feature called as vertical migration in which at the night time zooplankton moves towards the surface of the water and at the day time they move down to the deep water. This process protects the zooplankton from being eaten by the predators especially diurnal and also support the phytoplankton to produce their food in the presence of sunlight.
Many zooplankton moves deeper into the water during the day and gets back into the night. This migration is based on the season, size, age, and sex. Zooplankton is also affected by calcium, pH, heavy metals, calcium, and aluminum.
Key Differences Between Phytoplankton and Zooplankton
Given below are the substantial key differences between the phytoplankton and zooplankton:
- Phytoplankton is the aquatic plants, Zooplankton is the small aquatic animals.
- Phytoplankton prepares their own food by the process of photosynthesis and is called as autotrophs while zooplanktons depend on phytoplankton for their food and other matter found in the sea also called as heterotrophs.
- Phytoplankton depends on sunlight for making their food, they primarily live on the surface of the water, while zooplankton lives in the darker and colder area of the water body.
- Being in the category of plants, Phytoplankton releases oxygen into the atmosphere, whereas zooplankton does not have such function.
- Phytoplankton does not show any movement, hence they are not the active swimmers, while zooplankton can swim actively or passively.
- Phytoplankton serves as the basic food source for many marine animals.They also play a vital role in checking the stability in marine water, as they serve as an indicator of the health of the water. Zooplankton also helps in checking the toxicity level in the marine water. If there are sudden changes in the water like the increase in the level of pollution, acidity, changes in temperature, these planktons reveal the early warning of the changes in the environment.
- The example of phytoplanktons are Algae and Diatoms and the example of zooplankton are Crustaceans and Small fishes, etc.
Conclusion
Plankton consists of phytoplankton and zooplankton, where ‘phyto’ refers to ‘plants of the sea’ and ‘zoo’ refers to the’ animals’, which are tiny creatures. Phytoplankton forms the basis of life in the aquatic world’s, they influence the color, taste, and odor. Zooplankton is considered as wandering animals.
Planktons help in checking the health of the water body in terms of changes in temperature, acidity, salinity, etc. Thus we can say that plankton plays a substantial role in the aquatic environment and thus their presence is equally important as others creatures.




Parag kalita says
Thanks for the information
Chinmayee says
Got just what I wanted,
Thanks for such a clear and detailed information
Charlito Bomediano says
Very detailed differentiation.
Thanks for the information
augusta owusuwaa koranteng says
great work done with detailed information but no referencing sites or citation