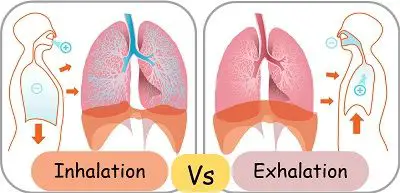
The inhalation and exhalation are the two basic mechanisms involved in the process of breathing. These processes facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
During the process of inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves in a downward direction. And the ribs move outwards and upwards. These movements cause an increase in the intrapulmonary volume and the expansion of the thoracic cavity.
As the volume inside increases, the intrapulmonary pressure falls down. So, in order to balance it, the gas molecules travel from the outer atmosphere into the lungs. This process is referred to as inhalation.
In contrast, the diaphragm relaxes and moves in the upward direction during exhalation. The ribcage moves in and down to its normal positioning. These changes lead to the contraction of the thoracic cavity and reduce the intrapulmonary volume.
When the volume decreases, the internal pressure automatically increases beyond atmospheric pressure. Thereby leading to the movement of gas molecules from inside the lungs to the outer atmosphere. This process is termed exhalation.
In this post, we will study the difference between the process of inhalation and exhalation in brief.
Content: Inhalation Vs Exhalation
- Comparison Chart
- Components of Respiratory Tract
- Mechanism of Breathing
- What is Inhalation?
- What is Exhalation?
- Key Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Inhalation | Exhalation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Inhalation is the process of intake of air into lungs. | Exhalation is the process of letting air out from lungs. |
| Type of process | Inhalation is an active process. | Exhalation is a passive process. |
| The role of diaphragm | They contract during the inhalation and get flattens by moving down. | They relax during exhalation and turned into dome-shaped by moving up. |
| The role of intercostal muscle | Internal intercostal muscles relaxes and external costal muscles contract. | Internal intercostal muscles contract and external intercostal muscles relax. |
| The volume of lungs | It increases during inhalation means it get inflated. | It decreases during exhalation means it gets deflated. |
| The size of chest cavity | Increases. | Decreases. |
| It results | Air rich in oxygen is taken into the blood. | Carbon dioxide is pushed out. |
| Effect of intercostal muscles | Due to the effect of intercostal muscles rib cage moves upward and outward. | Due to the effect of intercostal muscles the rib cage moves downward. |
| The composition of air | The air which is inhaled is oxygen and nitrogen mix. | The air which is exhaled is carbon dioxide and nitrogen mix. |
| Air pressure | Decrease in air pressure (below atmospheric pressure). | Increase in air pressure. |
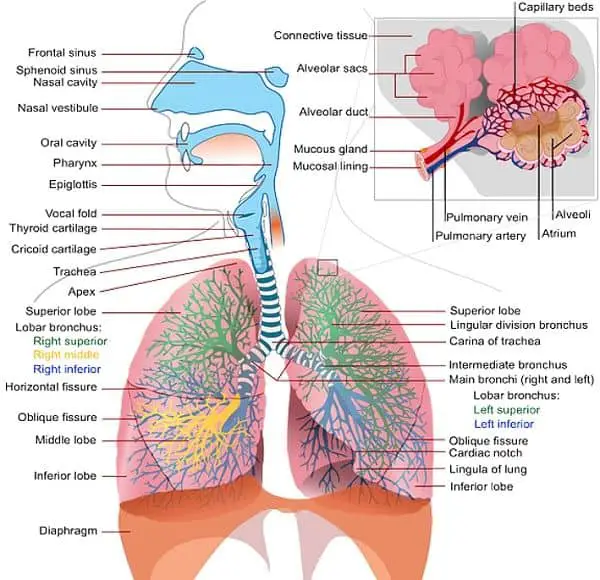
Components of the Respiratory Tract
Firstly, let us study the components of the respiratory system. You can see in the diagram the detailed view of the respiratory tract. The primary parts are the nostrils, nasal passage, larynx, trachea, bronchi and the lungs.
The lungs remain surrounded by a type of serous membrane known as visceral pleura. Above which there is another serous layer surrounding it called parietal pleura. Between these two layers, there is a pleural cavity filled with pleural fluid.
The bones enclosing the entire respiratory system form a cage-like structure called a ribcage. The ribs remain interconnected by the intercostal muscles.
Mechanism of Breathing
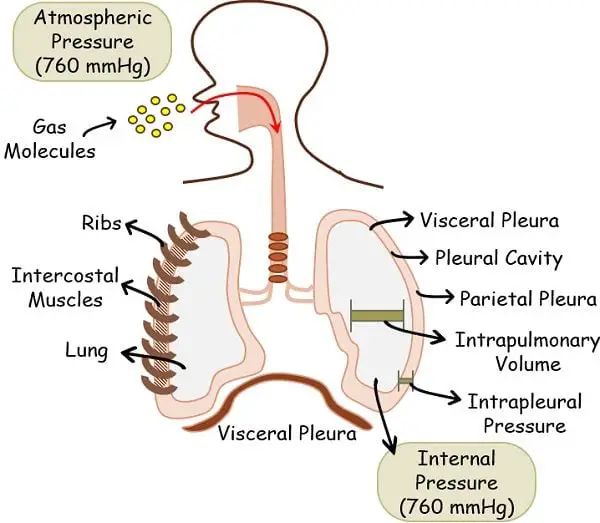
The breathing mechanism relies on one most important phenomenon that any gas tends to move from the area of higher concentration to that of lower concentration. You can understand it similar to that of diffusion.
The atmospheric pressure outside the body remains constant at 760 mmHg. Similarly, the intrapulmonary pressure inside the lungs is also 760 mmHg complementing the external pressure.
What is Inhalation?
The term inhalation simply means to inhale the air inside. The process of inhalation is also known as inspiration.
Process of Inhalation
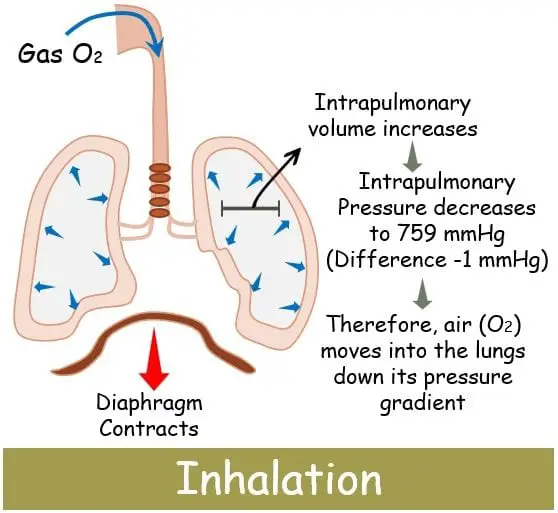
The process of inhalation begins when the diaphragm contracts in a downward direction. The intercostal muscles between the ribs stretch, pulling the ribcage upwards and forwards.
These movements expand the area of the thoracic cavity and the intrapulmonary volume inside the lungs increases. This led to the decreased intrapulmonary up to 759 mmHg, i.e. 1 mmHg negative difference below the atmospheric pressure.
And as we know that the gases tend to move from higher to lower pressure zone. Thus, the air will start flowing from the outer environment inside the lungs down its pressure gradient to establish the balance again.
Do you know, What happens inside the lungs?
As soon as the lungs expand, air enters through the nose or mouth. This air travels downward through the windpipe and into the lungs. The air certainly reaches the alveoli, after passing through bronchial tubes.
The air passes to the nearby capillaries (blood vessels), through the thin walls of the alveoli. Now, this air (oxygen) moves to the blood from the air cavity with the help of a protein called haemoglobin.
Simultaneously, on the other side, the carbon dioxide also shifts from capillaries to air sacs. The movement of gas is through the pulmonary artery into the bloodstream from the right side of the heart. Further, this blood rich in oxygen is carried to the pulmonary veins through a network of capillaries.
The role of the pulmonary vein is to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the left side of the heart. This side of the heart pumps the blood to the rest of the body. From there the blood moves into the surrounding tissues.
Characteristics of Inhalation
- The inhalation process allows the intake of oxygen in our bodies.
- The two most important muscles in the inhalation are- the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm.
- The shape of the diaphragm turns flat due to its contraction, which expands the thoracic cavity.
- The external intercostal muscles contract while the internal ones relax to raise the sternum and ribs, expanding the thoracic cage in the outward direction.
What is Exhalation?
Exhalation is the process where the body exhales out the air from the lungs. The process of exhalation automatically begins after inspiration.
Process of Exhalation
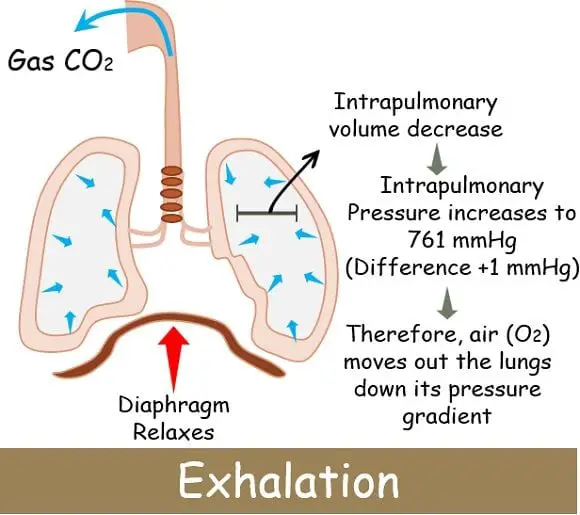
As soon as the inhalation ends, the diaphragm relaxes and comes to its original position. This causes the rib cage to move inwards and downwards, thereby decreasing the area of the thoracic cavity.
Ultimately the lungs contract, and the intrapulmonary volume inside decreases. This decrease in volumes leads to the increased intrapulmonary pressure inside to 761 mmHg. The pressure increases by positive 1 mmHg from the outer atmospheric pressure.
The randomness of the gas molecules taken in via inhalation rises, intensifying the pressure. Gradually, the area in the chest gets decreased and air rich in carbon dioxide is forced to move out of the lungs.
So as per the rule, the gases, including air, tend to flow from higher to lower concentrations. Thus, the air molecules start moving from the lungs to the outer environment down its pressure gradient to balance again.
Characteristics of Exhalation
- Exhalation is expelling carbon dioxide from the lungs to the environment.
- During exhalation, the diaphragm moves up and contracts the thoracic cage.
- The external intercostal muscles relax while the internal ones constrict.
Key Differences Between Inhalation and Exhalation
- Inhalation is the process of intake of air into the lungs, whereas exhalation is the process of letting air out from the lungs.
- Inhalation is an active process which requires energy. But exhalation is a passive process that doesn’t need energy.
- The diaphragm contract during the inhalation and get flattens by moving down. Whereas they relax during exhalation and turned into dome-shaped by moving up.
- The intercostal muscles relax and external costal muscles contract during the inhalation process. But while the exhalation process internal intercostal muscles contract and external intercostal muscles relax.
- The volume of the lungs increases during inhalation which means it gets inflated. But the volume decreases during exhalation means it gets deflated.
- The size of the chest cavity increase in inhalation while it decreases during exhalation.
- During the inhalation, the body intakes oxygen-rich air into the blood. In contrast, the body expels carbon dioxide in the exhalation process from the blood.
- Due to the effect of intercostal muscles rib cage moves upward and outward in inhalation, while in exhalation the rib cage moves downward.
- The air inhaled constitutes oxygen and nitrogen. While the air exhaled comprises carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
- Inhalation results in a decrease in air pressure (below atmospheric pressure). In exhalation, there is an increase in air pressure.
Conclusion
Simply we can say that the giving and taking process is called breathing. In this process, while breathing we take in air rich in oxygen from the atmosphere and give out the carbon dioxide back to the atmosphere. This air (carbon dioxide) is utilized by the plant during the daytime in the process of photosynthesis. And hence the cycle goes on continuously, which is significantly important for all living beings.

Anatomy Students Trying Understand says
Hello,
Thank you so much for creating this website! It has been a very informative and fantastic resource! Without this site, we would have never been able to comprehend the primal human function.
Thank you,
MadDog and Slippe
P.S. We think that we did well on our project, thanks again! Keep up the great work:)
musaib says
Got very much information from this article.
best website,keep it up,
Nayyab Amjad Malik says
Thanks for this information. This really help me.
Rujula says
Its a very good website .There are answers for all question in this web site. it given all information about science a very goo plat form. Keep it up 🙂