Aerobic denotes the term ‘in the presence of oxygen’ while the word anaerobic denotes the ‘absence of oxygen’. So the respiration which occurs in the presence of oxygen is called as aerobic respiration, on the other hand, respiration occurring in the absence of oxygen is known anaerobic respiration.
So accordingly the chemical reaction involving the breakdown of the nutrient molecule with the aim of producing energy is called respiration. Thus the energy required by the body to perform well which is produced by the chemical reaction. This process takes place in the mitochondria or in the cytoplasm of the cell either aerobically or anaerobically.
Below we will consider the important points which distinguish the aerobic respiration to that of anaerobic respiration.
Content: Aerobic Vs Anaerobic Respiration
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce more amount of energy is called as aerobic respiration. | The breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce energy is called as anaerobic respiration. |
| Chemical Equation | Glucose + Oxygen gives Carbon dioxide +water + energy | Glucose gives Lactic acid + energy |
| It occurs in | The cytoplasm to mitochondria. | Takes place in cytoplasm only. |
| Energy produced | The high amount of energy is produced. | Less amount of energy produced. |
| Number of ATP released | 38 ATP. | 2 ATP. |
| Final product is | Carbon dioxide and water. | Lactic acid (animal cells), carbon dioxide and ethanol (plant cell). |
| It requires | Oxygen and glucose to produce energy. | It does not require oxygen but uses glucose to produce energy. |
| It involves | 1. Glycolysis - also called Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas(EMP) pathway. 2. The respiratory chain (electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation). 3. The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle. | 1. Glycolysis. 2. Fermentation |
| Process of combustion | Complete | Incomplete. |
| Type of process | It is a long process for the production of energy. | It is a fast process in comparison to aerobic respiration. |
| Examples | Aerobic respiration occurs in many plants and animals (eukaryotes). | Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscle cells (eukaryotes), bacteria, yeast (prokaryotes), etc. |
Definition of Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration can be described as the chain of reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The mechanism involves the transfer of electrons from the molecules acting as the source of fuel like glucose to the oxygen which works as the final electron acceptor.
This is the principal pathway for yielding the energy in aerobic respiration. This scheme at the end provides ATP and metabolic intermediates, working as the precursor for many other pathways in the cell, like carbohydrates, lipid and protein synthesis.
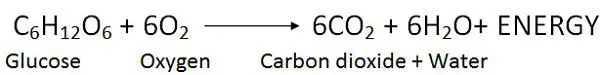
Thus the equation can be summarized as:
So the total yield of ATP is 40: Four from glycolysis, two from the TCA, and 34 from electron transport. Though 2 ATP were used in early Glycolysis, so this gives only 38 ATP at a time.
While the amount of total energy released is 2900 kJ/mol of glucose. There is no production of lactic acid. The aerobic respiration process goes on continuously in the body of plants and animals.
Definition of Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration can be distinguished from that of aerobic respiration regarding the involvement of oxygen while converting the given resources such as glucose into energy.
Some bacteria, have evolved this kind of system where it utilizes oxygen-containing salts, rather using free oxygen as the electron acceptor. The energy produced by the anaerobic respiration is useful at the time of high energy demand in tissues when the oxygen produced by aerobic respiration is not able to fulfill the required demand. Though it is produced in very less amount as compared to aerobic respiration.
Thus the equation can be summarized as:
As in the above reaction, glucose does not completely break down, and hence it produces very less energy. So the total amount of the energy released regarding kilo per joules is 120 kJ/mol of glucose. It produces lactic acid.
Key Differences Between the Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
Following are the substantial differences between both kind of respiration:
- The breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce more amount of energy is called as aerobic respiration; Whereas the
breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce energy is called as anaerobic respiration. - Chemical Equation of aerobic respiration is Glucose + Oxygen gives Carbon dioxide +water + energy whereas the equation of anaerobic respiration is Glucose gives Lactic acid + energy
- Aerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm to mitochondria, while anaerobic respiration occurs in the cytoplasm only.
- The high amount of energy is produced and 38 ATP released at a time in aerobic respiration; Less amount of energy is produced and 2 ATP are released at a time in anaerobic respiration.
- Final product in aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water, whereas Lactic acid (animal cells), carbon dioxide
and ethanol (plant cell) is the final product in anaerobic respiration. - Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and glucose to produce energy whereas in anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen but uses
glucose to produce energy. - The stages involved in aerobic respiration are – 1. Glycolysis – also called Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas(EMP) pathway; 2.The respiratory chain (electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation); 3. The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), also known as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle whereas the anaerobic respiration involves the two stages only which is 1. Glycolysis and 2.Fermentation
- Aerobic respiration shows complete process of combustion, while it is incomplete in the anaerobic respiration.
- Aerobic respiration is a long process for the production of energy whereas anaerobic respiration is a fast process in comparatively.
- Examples of aerobic respiration occurs in many plants and animals (eukaryotes) whereas anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscle
cells (eukaryotes), bacteria, yeast (prokaryotes), etc.
Conclusion
From the above article, we can say that energy is an essential factor, concerning the work performed by the body. The energy requirement is fulfilled by the two type of chemical reactions occurring inside the cell within the body of all kinds of living beings like microorganisms, plants, animals. These chemical reactions are of two types one is called aerobic respiration and the another is called anaerobic respiration, which we discussed above.
Respiration and breathing are the two different kind of process, that takes place simultaneously inside the body, where the former (respiration) is related to the production of energy, involving the breakdown of nutrient and converting it to the form of energy, while the latter (breathing) is linked to the inhalation and the exhalation process of oxygen and carbon dioxide relatively.



Nouman Arif says
Its awesome
Annie says
Thanks it’s so easy to learn
jia sanajy bhatti says
it is very easy because it is in a simple english language
Mahmooda says
ok to include
sisenkosini ndiweni says
its easy to understand than in class because its simplified
Anuj singh says
The website looks so good it is a good website in the world of biology
Nicky Takunda says
This is good
Sarthak says
A good website, it helped me to go through types of respiration very quickly and I scored good lol!
Judith says
This site meets what I need to learn.
Thank you.