The biological process, where ammonium gets converted into nitrate is called nitrification. Further, when this nitrate is converted or reduced into nitrogen gas, it is called denitrification. These steps involve various microorganisms, and it is important biologically as well as economically.
Both the steps are a significant part of the nitrogen cycle, which is one of the most important cycles for our atmosphere. Around 78% of the atmosphere contains nitrogen, which is even an essential biological molecule found in proteins and nucleic acid and thus marking it important part of all living being.
The nitrogen cycle is completed in five simple steps: nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification. In this article, we will be discussing the two steps only and how they differ from each other.
Content: Nitrification Vs Denitrification
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Nitrification | Denitrification |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The part of nitrogen cycle where ammonium (NH4+) is converted into nitrate (NO3-) is called nitrification. | Denitrification is the level where reduction of nitrate (NO3-) is made into nitrogen gas (N2). |
| The process involves | Nitrifying bacteria like Nitrobacter, Nitrosomonas. | Denitrifying bacteria like Spirillum, Lactobacillus, Pseudomonas, Thiobacillus. |
| Grows slowly. | Grows rapidly. | |
| Requires aerobic condition. | Requires anaerobic condition. | |
| The microbes | Autotrophic. | Heterotrophic. |
| Precursor | Ammonium . | Nitrate. |
| End product | Nitrate. | Nitrogen. |
| pH and Temperature | The process occurs at the pH between 6.5 to 8.5 and temperature between 16 to 35 degree C. | The process occurs at the pH between 7.0 to 8.5 and temperature between 26 to 38 degree C. |
| Importance | Provides nitrate to the plant, which acts as the important nitrogen source. | Denitrification is used in wastewater treatment and is beneficial for aquatic habitats. |
Definition of Nitrification
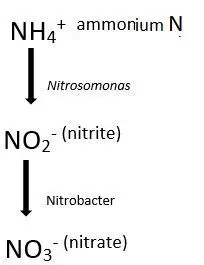
Nitrification is an oxidation process (loss of electrons or gain of the oxidation state by an atom or compound takes place). This process starts with the ammonium which gets oxidized into nitrite (NO2-), this action is performed by the bacteria Nitrosomonas sp. Later on, this nitrite (NO2-) gets oxidized into nitrate (NO3-), and this action is performed by the Nitrobacter sp.
The bacteria are autotrophic, and the reaction is performed under aerobic condition. The importance of this step in the nitrogen cycle is the conversion of ammonia into nitrate, as nitrate is the primary nitrogen source present in the soil, for the plant. Though nitrate is toxic to the plants.
The activity of nitrifying bacteria gets slower in acidic solution, and are best at pH between 6.5 to 8.5 and temperature vary from 16 to 35°C.
Definition of Denitrification
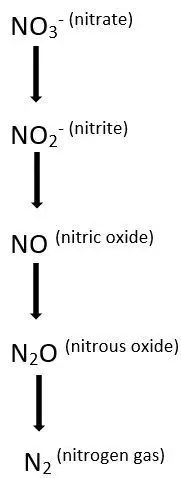
Denitrification is the reduction process, where the nitrate is removed in the form of nitrogen and is converted to nitrogen gas. The action is performed by bacteria like Bacillus, Aerobacter, Lactobacillus, Spirillum, Pseudomonas.
The bacteria are heterotrophs, and the action is completed under anaerobic condition. Even the small amount of oxygen may hamper the process, but there is a need of organic carbon. Denitrification is useful for wastewater treatment, aquatic habitats.
The denitrification is performed best at pH between 7.0 to 8.5 and at the temperature between 26 to 38°C.
Key Differences Between Nitrification and Denitrification
Given below are the important points which differentiate both the process:
- The biological process where ammonium (NH4+) is oxidized and converted into the nitrate (NO3-) is called as nitrification, while denitrification is biological process involves the conversion of nitrate (NO3-) into nitrogen gas (N2).
- The nitrifying bacteria like Nitrobacter, Nitrosomonas are involved in nitrification process, while in denitrification process bacteria such as Spirillum, Lactobacillus, Pseudomonas, Thiobacillus shows their involvement.
- In nitrification process the microbes are autotrophic, require anaerobic condition (presence of oxygen) to grow, and even their growth is slow, on the other hand in denitrification process the microbes are heterotrophic, require an anaerobic condition (absence of oxygen), and they show rapid growth as well.
- The precursor of the nitrification process is ammonia, and the end product is nitrate, whereas nitrate is the precursor of the denitrification process and nitrogen is the end product.
- Nitrification is performed best at pH between 6.5 to 8.5, with temperature varying from 16 to 35 degree C. Though denitrification is best at pH between 7.0 to 8.5 and temperature ranging from 26 to 38 degree C.
Conclusion
We all know that nitrogen is the substantial part of the atmosphere, as well as plants and animals also. As nitrogen cannot be used directly and so is transferred in through various sources. In the provided content we focused on the distinction between the nitrification and denitrification and found variations in their products and needings.


Patricia says
Helpful article.
Sudhakar says
Usefull Artical