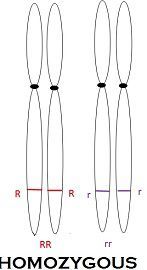
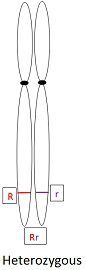
Individual organisms carrying two identical alleles (for example RR or rr) are called as homozygous. While individual organisms bear different alleles (for example Rr) are called heterozygous.
A homozygous trait is when the same kind of two alleles associate to form a trait. A heterozygous is a trait when different kinds of two alleles associate to form a trait. In this type, dominant and regressive alleles are present in the pair, and the dominant will represent the kind of trait the offspring will show.
As humans are diploid organisms, containing two copies of every chromosome, which inherit a complete set of chromosomes from their mother and a complete set from their father. These two chromosomes which correspond to each other are called homologous chromosomes. Even the locus (location) is same of these genes in homologous chromosomes.
For example, here we are talking about hair colour and let’s consider that we have two alleles for this gene – one allele codes for black hair colour (R) and the other allele codes for brown hair colour (r).
The homologous pairs of chromosomes consist of either same alleles (both black or brown) or different alleles (black and brown). On the groundwork of these possible outcomes, we can differentiate whether they are same alleles, i.e. homozygous or different alleles i.e. heterozygous.
Content: Homozygous Vs Heterozygous
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Homozygous | Heterozygous |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | If the diploid organisms carry two copies of each gene, they may be identical alleles so called homozygous. | But if the diploid organisms carry two copies of each gene, which can be different (dominant and regressive) alleles, can be said as heterozygous. |
| Results in | It brings similar individuals, means it is pure for a trait and breeds true. E.g., RR, rr | It brings dissimilar individuals, which means heterozygous individual is rarely pure and produces offspring with different genotype. E.g. Rr |
| It carries | Homozygous carries similar alleles of a trait. E.g. RR, rr. | Heterozygous carries dissimilar allele e.g. Rr. |
| Type of alleles | Homozygous individual can carry either dominant or recessive alleles, but not both at a time. | Heterozygous individual has both, i.e. one dominant and one recessive alleles. |
| Type of gametes produced | Only one type of gametes are produced. | Two types of gametes are produced. |
Definition of Homozygous
Homo means’same‘, and zygous refers to ‘having zygotes of a specified kind‘, so we can elaborate it by saying that “when both alleles present on the homologous chromosomes for a given gene are same, they are called homozygous.
When two genes share readily detectable sequence similarities (nucleotide sequence in DNA or amino acid sequence) in proteins they encode, are homologs. If two homologous genes occur in the same species as they are said to be paralogous and their protein products are paralogs.
An organism is said to being homozygous at a specific locus when it brings two indistinguishable (identical) copies of the gene affecting a trait present on the two reciprocal homologous chromosomes. (e.g., the genotype is RR or rr when R and r refer to the different possible alleles of the same gene). Such a cell or such an organisms are called homozygote.
Definition of Heterozygous
Hetero means ‘different’ and zygous means ‘having zygotes of a specified kind‘. So we can explain it by saying that “when both the alleles present on the homologous chromosomes for a given gene different.
For example, one chromosome in homologous pair contains brown hair (R) and another chromosome contains black hair (r). So the resultant genotype is Rr.
Diagrammatic representation of Homozygous Vs Heterozygous
Key Differences Between Homozygous and Heterozygous
- If the diploid organisms carry two copies of each gene, they may be identical alleles so-called homozygous, whereas if the diploid organisms carry two copies of each gene, which can be different (dominant and regressive) alleles, can be said as heterozygous.
- Homozygous results in similar individuals mean it is pure for a trait and breeds true. E.g., RR, rr; whereas it brings dissimilar individuals, which means the heterozygous individual is rarely pure and produces offspring with a different genotype. E.g. Rr
- Homozygous carries similar alleles of a trait. E.g. RR, rr, while heterozygous carriers dissimilar allele e.g. Rr.
- A homozygous individual can carry either dominant or recessive allele, but not both at a time; a Heterozygous individual has both, i.e. one dominant and one recessive allele.
- Only one type of gamete is produced in homozygous, while in heterozygous two types of gametes are produced.
Conclusion
We conclude that homozygous and heterozygous are the two genetic terms used in the identification of traits, occurring in an organism. When two organisms breed, they produce a trait which is a combination of either series of dominant or regressive alleles. The way these alleles are combined will identify as they are either homozygous or heterozygous.


Leave a Reply