The fracture is a hard tissue injury thus it affects bones. On the other hand, the sprain is a soft tissue injury and it damages soft ligaments. The fracture is generally due to a break, crack or twist in the bone. Whereas, the sprain occurs due to the overstretching or tearing of the ligaments.
A sprain is constrained to some particular regions only; such as ankle, wrist, thumb and knee. Contrarily, the fracture can happen wherever there is a bone in the body. The sprains are not that severe and thus can easily be tackled at home. But the fractures require the doctor’s supervision and clinical assistance for its recovery.
Symptoms of both fracture and sprain are very much similar thus people often get confused between these two. In the following content, we will learn the common difference between these two injuries with the help of a comparison chart, brief description, types and ways to their treatment.
Content: Fracture Vs Sprain
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Fracture | Sprain |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Fracture is a breaking of bones in arms, elbow, wrist, hands, legs, ankle, foot, toe. | Stretching of ligaments especially in ankle or wrist. |
| Diagram | 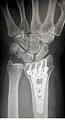 |  |
| Causes | Accidents fall, sports injuries or from osteoporosis (bone weakening). | Falling, hitting or twisting can cause the sprain. |
| Symptoms and Signs | 1.The patient is unable to move the affected area, swelling, pain, bruising. 2.Angulation: The bone of the affected area bent at an unusual angle. 3.Deformity in the affected area. | Pain, Swelling, Bruising, not able to move the joint. |
| Diagnosis | X-Ray, MRI, Bone Scan, CT scan. | There will be pain, swelling, redness, numbness. |
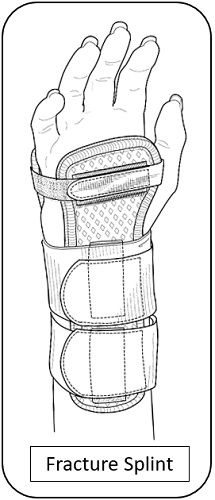
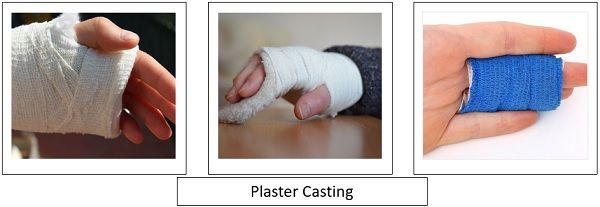
| Treatment | Treated by Cast or Splints. | Mostly sprain get recovered with time but in few cases physical therapy or surgery ae required, but best is RICE formula i.e. Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. |
What is Fracture?
The term fracture means “crack or break”. Fracture is a hard tissue injury and thus we generally use this term when we have a break or crack in the bone. The fracture may lead to the change of shape and orientation of the bone.
The damage might occur in the entire length of the bone or in a specific area of the bone. In cases of severe injuries, the fractures may split the bone into two or crush it into numerous pieces.
Symptoms of Fracture
The symptoms of fracture may vary depending upon the cause of injury as well the type of injured part. The general symptoms in all kinds of fracture are:
- Deformity of bone.
- Change in the orientation of bone.
- Rise of ridges and bulges on the injured part.
- Severe oedema
- Bruising and redness
- Inability to move the injured limb
- Unbearable pain
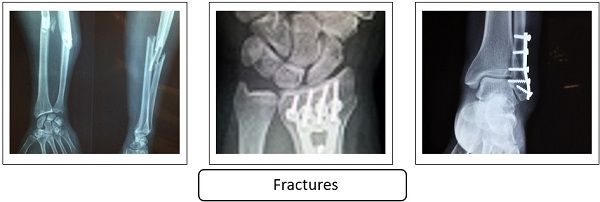
Types of Fractures
There are a lot of different types of fractures, but doctors usually describe them as displaced, non-displaced, closed, and open fractures. Healthcare providers can usually categorize a bone fracture based on its features. The categories include:
- Displaced Fractures: When the bone is dislocated from its original place due to which the edges of the bones move apart from each other. Here, there is no break or crack in the bone.
- Non-displaced: The bone is either cracked or is broken but still remain intact and aligned at their respective positions.
- Complete Fracture: Where the bone directly breaks into two or more pieces.
- Partial Fracture: When the break doesn’t entirely go along the length of the bone.
- Spiral Fracture: Generally, occurs in the long bones. Here, the bone is broken and twisted making a spiral shape.
- Open fracture: During intense accidents, the bone breaks and comes out from the skin.
- Closed fracture: The bone is broken or cracked but doesn’t puncture the bone.
- Greenstick fracture: This is very common in children as their bones are soft. In this kind of fracture, the bone bends and then cracks.
- Transverse Fracture: When the fracture occurs in the perpendicular direction of its original position.
- Oblique Fracture: Here, the bone is cracked diagonally.
- Comminuted fracture: The bone in this type of fracture is disintegrated in multiple fragments.
- Buckled fracture: It is a type of incomplete fracture or torus fracture. It occurs when a bone cracks, bends and elevate its edge to form a buckle shape.
- Compression: Then bone when is flatted and cracked due to the overstress.
- Avulsion: In this type, the tendons and ligaments attached to the bone are pulled apart. This makes the joints weak and thus the bone is cracked.
- Pathological Fracture: Those fractures occur due to the weakening of the bones.
Diagnosis of Fracture
There are various scientific approaches to detecting fractures. Some of them are:
- X-rays: Fracture can easily be detected with the help of X-rays imaging. A two-dimensional picture of the break is generated from X-rays.
- Bone Scan: It is a type of nuclear radiological technique that is used to identify physical and chemical variations in the bone.
- CT scan: It is used only for severe cases to take the detailed information of the injured bone. It studies the bone in small cross-sections using computers and radiations.
- MRI: Here, the strong magnetic resonance is utilized for fracture detection. It gives a detailed picture of the stressed bone.
Cure and Treatment
Treatment of bone fracture can be done by a plaster cast, metal plates, and screws, intramedullary nails, extra fixators. Healing of bone is a natural process, which takes two-eight weeks to get re-join and become functional. till then, the patient is advised for bed rest and to keep the fractured part immobilized.
More than 99% of the body’s calcium is found in bones and the rest 1% is found in the blood. Hence it is necessary to maintain that level by taking a properly balanced diet that has an adequate amount of calcium like milk, cheese, green leafy vegetables. Importantly sunlight, eggs, and fishes are also good sources of vitamin D. Along with that one should do physical exercise which helps in strengthening the bones.
Note: In women’s due to menopause the level of calcium decreases resulting in the weakening of bones, hence it’s necessary to maintain that level.
What is Sprain?
The sprain is a soft tissue injury; thus, it mainly affects the delicate and soft connective tissues such as ligaments.
Ligaments are soft but stiff and firm tissues. They are the stretchy bands that are typically found near the joints of the bones. Their primary roleplay is to maintain the bones in place and so provide joint stability.
These ligaments can only stretch to a certain extent. If these bands are stretched beyond their breaking point, they will rupture or tear completely. Sprains occur as a result of such circumstances. Thus, you can say that the sprain is caused by exerting excessive force and pressure on the soft tissue. Sprains can be excruciatingly painful and unpleasant to deal with.
Symptoms during sprain
The prime signs and symptoms of a sprain are:
- Severe pain around the injured part.
- Redness and swelling
- Sometimes bruised skin
- Difficulty in moving the injured part
- Popp sound or sensation during the injury.
- Seldom sprains are so serious to need surgery.
Since the sprain causes similar symptoms as like fracture, it is often confused with it.
Reasons Behind Sprain
The cause of the sprain could be anything. There is no one type of damage that guarantees a sprain. It can happen as a result of:
- Thumb sprain: Overextension, skiing, or racquet sports such as table tennis, badminton, and tennis can all cause a thumb sprain.
- Wrist sprain: A wrist sprain is usually caused by an abrupt twist or overstretching. This could happen if you trip and fall on your hands.
- Knee sprain: Occurs when a man falls over his knees, for example, when training in the gym or as a result of sudden accidents.
- Ankle sprains: They are most commonly caused by jogging, running, or leaping. It can also happen while landing unevenly after a jump.
Types of Sprains
On the basis of the level of severity and pain, the sprains can be classed under three following degrees:
- Mild: No major damage just some overstretching of the ligaments.
- Moderate: Here, the ligament is moderately damaged with overstretching as well as minor tears.
- Severe: This is when the sprain has progressed to the point of severe swelling, unbearable pain, and the inability to fully move the joint. This occurs when the ligament is completely torn off.
Diagnosis of Sprain
- To determine whether the injury is a fracture, strain, or sprain trained doctor will do the physical examination of the movability of joints, soreness of nearby muscles, swelling etc.
- Alternatively, imaging procedures such as X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRIs may be used to provide a thorough evaluation of your injuries.
Treatment of Sprain
A sprain is not a very severe injury but if not taken seriously might lead to dangerous outcomes. A normal sprain can easily be treated at home with RICE therapy.
R: R stands for Rest. Proper resting of the injured parts will help it to heal faster. Lesser the movement, the faster the recovery.
I: I is for Ice. Applying ice to the sprained portion will reduce the swelling and will soothe the pain.
C: C is for Compression. It means to apply continuous pressure on the sprained body part. This reduces the swelling. Generally, ACE bandages are wrapped around the injured part. The combination of heat and pressure has a magical action in the healing of sprain.
E: E stands for Elevation. The injured part if kept elevated will soothe the pain and will also decrease the swelling. For this., the sprained part is held above the heart level. This can easily be done with help of a pillow.
Along with this, you can also take, pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory tablets, physiotherapy for fast relief. One should consult a doctor if the pain and swelling don’t get reduced even after therapy or tablets.
Very few cases of a sprain are so severe that they require surgery.
Key Differences Between Fracture and Sprain
Both the words like Fracture and Sprain are closely related, common people may get confused for the same but the following are the main differences, which may be helpful in making out the difference.
- A fracture is a hard tissue injury but a sprain is a soft tissue injury.
- Fracture is the breaking, cracking or twisting of bone, whereas Sprain is the overstretching or tearing of ligaments.
- The fracture can happen in any part of the bones like left, hands, toe, ankle, foot, wrist, arms, but sprains usually occur in joints like ankles, wrist, knees and thumb.
- The fracture may cause due to accidents fall, sports injuries or osteoporosis (bone weakening), while sprain occurs due to falling, hitting or twisting can cause the sprain.
- The fracture can be treated by plaster cast or splint; sprain is treated by RICE therapy.
Summary
Fracture and sprain are very common cases occurring everywhere. People should take care of themselves by taking proper diet, by doing proper exercise and being careful while driving. As fracture and sprain result in body ache, and proper rest is required for healing.

Leave a Reply