CT Scan uses harmful x-rays ( the form of electromagnetic radiation like light) for imaging, while MRI does not use any radiation and is based on the effect of the magnetic field, radio waves for the imaging of the organs of the body.
CT Scan gives the images of the bones in a much-sophisticated way than the x-ray and is good to check the fractures, tumors, and arthritis but MRI which is popular in detecting the damage of soft tissue. It is also seen that CT Scan is not as expensive as the MRI technique.
Over the decades, a series of modification has been developed in the field of generating x-rays in the more advanced way which can scan even smallest and delicate organs, soft tissues in a short time and with full accuracy. So for this development German physicist Wilhelm Rontgen is credited for the discovery of x-rays in 1895, as he was the first to study them systematically.
Later on computed tomography (CT) was developed in the 1970s, which was the advanced version of the x-rays as well 100 times more sensitive than the earlier one.
Nowadays magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique is considered as the enhanced version among all. It is superior from x-ray and CT scan machine as it does not use the hazardous x-rays while scanning, though costly than the other techniques but provides the result with accuracy.
Among the various radiographic tests through which we can evaluate the internal parts of the body. There are three most popular techniques we hear about and are most widely used in the diagnostic centers. First and the old technique is the X-ray which has been used around us since a long time and we can view the bones in two dimensions. But, it is still important technique and is used to check the details about the bones before going for the CT scan or MRI.
Second is the CT Scan, and the last is MRI. In this content, we will discuss the basic differences between the CT Scan and MRI along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Content: CT Scan (Computed Tomography) Vs MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | CT Scan (Computed Tomography ) | MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | CT Scan works on the same principle as that of the X-ray, where the radiowaves are made to focus on the damaged part, and the image is created. The image provided is three dimension, as well multiple images are obtained of the targeted area. | MRI works with the powerful magnet along with radio waves and a computer which shape these magnetic elements and provide the highly detailed images of the target body part. |
| Discovered by | Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack in 1972. | In the year 1977, Raymond Vahan Damadian completed the construction of the whole body of MRI scanner. |
| Radiation | In CT Scan the image is produced by combining multiple x-rays, during this, there is exposure to radiation. | There is no radiation involved in the MRI technique, rather uses strong magnetic field and radio waves to create the image of the targeted body parts. |
| Cost | Less expensive than MRI. | It is much costly than CT Scan. |
| Time taken | Very quick, usually the scan takes only 5 minutes to complete though sometimes depends on the part of the body to be scanned. | The time depends on the body part to be scanned, but it takes 15 minutes to 2 hours to complete. |
| Uses | It is best in viewing the soft tissue, bones, lungs, tumour, cancer detection. | MRI is best in viewing the slight differences in the soft tissues, for example, tendons and ligaments. It is also used to view the detailed images of cancer or other neurological disorder. |
| Limitations | 1. It may sometimes cause the allergic reaction intravenously and has the potential to damage kidneys, especially the person suffering from diabetes or any kidney related problem. 2.CT Scan is not appropriate at the time of pregnancy. | The size of the tube creates the problem in contrast to the size of the person to be examined, so for such person open MRI machines are used. Although the contrast dye used may generate problems to the person suffering from any kidney or liver related disease. |
Definition of CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
CT Scan and MRI are the forms of tomography only, where the imaging of the slices or sections of the body is possible. A CT scanner is a rotating unit of the X-ray tube with the opposing detectors. Firstly it creates the bi-dimensional image of the body which get digitally processed, and this image is further used to generate the three-dimensional image.
The new version of CT scanner contains multi-slice scanners which are multiple rows of X-ray detectors. These scanners have high scanning speed as well as high resolution and generate two-dimensional as well as three-dimensional images of the targeted area (bones).
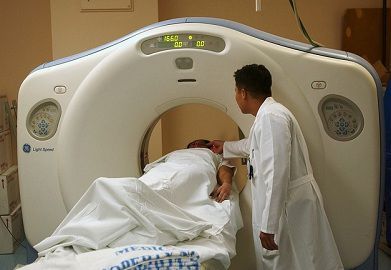
In this, the patient is made to lie on the examination table and is made to move through the scanners – the X-ray tube along with the detectors rotate around the patient. The images created are of spiral orientation or helical and thus are known as the multi-slice scanners. This technique has reduced the examination time and the discomfort which the patient feels while going through the scanner.
It requires contrast agent which is injected intravenously, in this iodine-based contrast agent are used. This agent allows the differentiation between the tissues and tumor lesions and blood flow system.
CT Scan is proven to be safe technology, but as it relies on the ionizing radiation for creating the image, the caution exists for using any X- rays even the routine chest X-rays, especially in case of pregnant women and children
Moderate-speed scanners are good for detecting the non-cardiovascular problems while high-speed is good for detecting the cardiovascular-related issues.
Advantages
- Provide the best result of the image of the bones and in orthopedic conditions, also in trauma.
- CT Scan displays the bones of the spines clearly than in MRI and so effective in diagnosing the conditions of the bones of the spine and vertebrae.
- Though CT Scan can distinguish the two separate, very close structure.
- It is also applicable in craniofacial issue including skull base, fractures, deformities, dental jaw, sinus, etc.
- It is also preferred as for examining the brain, lungs, chest, and bowel, along with chronic and acute disease like lung cancer, fibrosis, pneumonia, and emphysema.
Disadvantages
- The contrast agent used may be allergic in some cases to the patient.
- CT Scan is not ideal for scanning the soft tissues like brain, joint or muscles.
Definition of MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
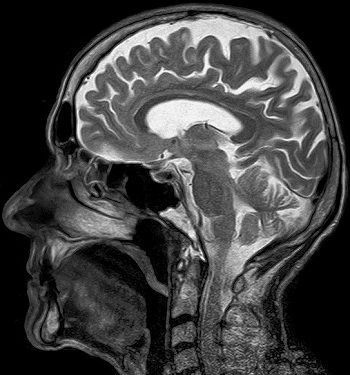
The MRI scanners use magnetic field technology which provides the excellent result of the scanned non-calcified tissues or soft tissues. It does not use the ionizing radiation as used in X-rays, rather radio waves of specified frequency are used. However, till yet there is no known side effect of using the magnetic fields, but the patient feels discomfort as it takes longer time for scanning and is louder and the tube is narrow and confined.
This technique is based on the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), where atomic nuclei are placed in the magnetic field they absorb and emit radio frequency energy. But in the MRI the hydrogen atom is used to produce a radio-frequency signal, this signal is further used by antennas close to the part or anatomy to be examined. The hydrogen atom is only used, as it is present in the body naturally and in much quantity of an organism, especially in fat and water.
Hence the MRI uses the location of fat and water in the body. Nuclear spin energy transition gets excited by the pulses of the radio waves, the detection coils present in the MRI scanner read the energy generated by the water molecules. MRI uses gadolinium-based contrast dyes. As bones are deprived of water and therefore do not create any image and leaves the black image. The data is in the two-dimensional form, illustrated through any axis of the body
Advantages
- MRI is the best for studying the diseases related to the brain, and spinal cord tissue like multiple sclerosis, brain injuries, hemorrhages, and brain tumors.
- MRI is also used to evaluate the breast tissue instead using X-ray mammography.
Disadvantages
- Patients with tattoos, cardiac pacemaker, and metal implants are at risk due to the image distortion.
- Even the patients with more than 350 lbs are considered as the overweight than the weight limit.
Key Difference Between CT Scan (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Following points differentiate between the CT Scan and MRI techniques:
- Among the method used by the radiologist to detect the exact problem in the body parts, CT Scan and MRI machines are widely used these days, CT Scan works on the same principle as that of the X-ray, where the ionizing radiations are made to focus on the damaged part, and the image is created. The image provided is three dimension, as well multiple images are obtained of the targeted area. On the other hand, MRI works with the powerful magnet along with radio waves and a computer which shape these magnetic elements and provide the highly detailed images of the target body part.
- Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack in 1972 discovered CT Scan, and MRI was discovered in the year 1977, Raymond Vahan Damadian completed the construction of the whole body of MRI scanner. But commercially it was available from the year 1981.
- Radiation in CT Scan the image is produced by combining multiple x-rays, during this, there is exposure to radiation while there is no radiation involved in the MRI technique rather uses strong magnetic field and radio waves to create the image of the targeted body parts.
- CT Scan cost low as compared to MRI and the time taken by CT Scan for scanning is only 5 minutes though sometimes depend on the of the part of the body to be scanned, whereas in MRI the time depends on the body part to be scanned, but it generally takes 15 minutes to 2 hours to complete.
- CT Scan is best in viewing the soft tissue, bones, lungs, tumor, cancer detection, whereas MRI is best in viewing the slight differences in the soft tissues, for example, tendons and ligaments. It is also used to view the detailed images of cancer or other neurological disorder.
- CT Scan may sometimes cause the allergic reaction intravenously and has the potential to damage kidneys, especially the person suffering from diabetes or any kidney related problem. It is also not appropriate at the time of pregnancy. Although the contrast dye used may generate problems to the person suffering from any kidney or liver related disease.
- In MRI size of the tube creates the problem in contrast to the size of the person to be examined, so for such person, open MRI machines are used. MRI is also expensive than the CT Scan.
Conclusion
CT Scan and MRI are the two most widely used modalities in medical imaging technologies. Both of them can be used for detecting the variety of therapeutics areas, and disease states in biopharmaceutical and medical device trials with other unique benefits too. Both the modalities have advantages as well as some disadvantages, so for this clinical study should be taken into account to use different technology.

Leave a Reply