Cereals and Pulses are the types of foods obtained from plants. They serve their individual roles in our bodies, and thus both are equally important in a balanced diet. We consume them in one or the other form daily, which makes it important for us to know more about them.
So, let’s start!
The cereals are a rich source of carbohydrates and starch. They provide the human body with immense energy so as to perform daily activities. With that, they are high in vitamins like A, B6, and C and minerals like calcium and phosphorous.
On the other side, the pulses are a rich source of proteins, amino acids, and minerals which act as the building block in our bodies.
The cereals are commercially produced on a large scaledue due to their higher demands, rich nutrient values and cheap cultivation process. Whereas pulses have fewer cultivation areas in comparison to cereals.
Mostly, all the countries, big or small, consume cereals as one of their staple foods. But the pulses are less important in comparison to that of cereals.
In this post, we will unfold the points that exhibit the major differences between cereals and pulses.
Content: Cereals Vs Pulses
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Cereals | Pulses |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Cereals are the harvested grasses, which are cultivated for its starch component. The type of fruit and botanically known as a caryopsis. | Pulses are the leguminous crop, that is harvested as the dry seed in a pod. |
| It contains | Cereals have high levels of carbohydrates. | Pulses are rich in proteins and amino acids, though they have lower contents of carbohydrates. |
| Production | Cereals are largely produced, as they are highly rich in carbohydrate, it is the major staple food in many countries. | Though pulses are rich in proteins, they are consumed in less quantity. |
| Grows in | Cereals can be grown in all kind of soil except desserts and in cold areas. | Pulses are grown in the pod, that may yield one to twelve seeds. |
| Classification | Kingdom: Plantae. Order: Poales. Family: Poaceae. | Kingdom: Plantae. Order: Fabales. Family: Leguminosae. |
| Examples | Barley, corn, wheat, rice, oats, and maize. | Lentils, dry beans, chickpeas, and cowpeas. |
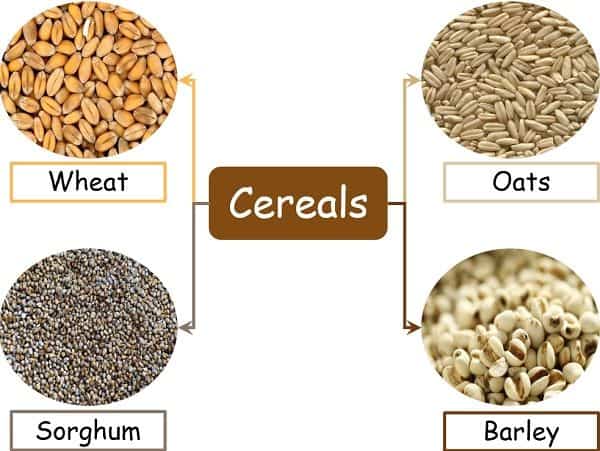
What are Cereals?
The cereals come under the grass family. They are actually seeds or grain part of the grass that is edible.
In almost all the countries, cereals are the staple food, i.e., the basic food taken in daily life. It contributes to the major proportion of the diet of any healthy individual’s plate in one or the other form.
For instance, a person belonging to India will consume chapati made up of wheat, ragi, maize millets etc., in his daily routine diet. On the other hand, an American citizen will have cereals in the form of flakes, bread or porridge.
Constituents of Cereals
The cereals are a good source of energy as they are rich in carbs and starch. Most cereals comprise 40 – 70 % starch and 5 -23 % of carbohydrates. Also, they are rich sources of vitamin E, B complex, fat, as well as fibre.
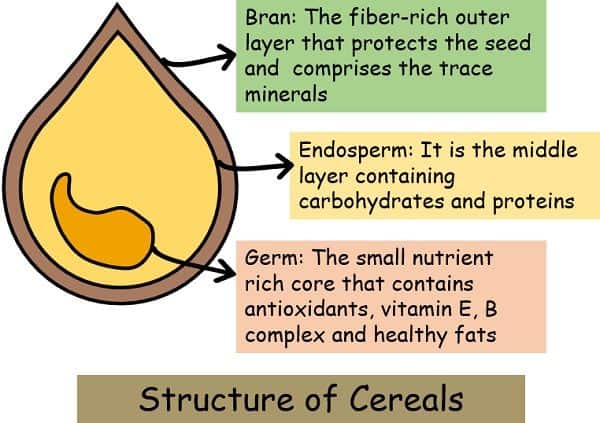
Structure of Cereal Grain
The cereals share structural similarities as all of them consist of three common parts: Bran, Endosperm, and Germ/Embryo.
1. Bran
- It is a thin outermost covering comprised of rectangular epidermal cells.
- There are five layers just below the epidermis- hypodermis, cross-layer, tube calles, testa and hyaline.
- This layer is rich in fibre and trace minerals.
- It provides protection to the internal parts of cereal grain.
2. Endosperm
- This layer is rich in starch and proteins.
- The endosperm remains surrounded by one or more layers of aleurone cells.
- The starch is present in the form of spherical granules that might be single or in clusters in a matrix of protein.
- The size and shape of the starch granule, as well as its proportion in every particular cereal grain, varies.
3. Germ/ Embryo
- It comprises its sub parts: Plumules, scutellum, radicle, and radicle cap
- Scutellum separates the germ from the endosperm. Its main function is to store the food for germination time.
- It is rich in proteins, fats and vitamins like the B complex.
Storage of Cereals
After the process of harvesting completes, the grains are taken to the warehouses for their safe storage. Precautionary measures are taken in the warehouses so as to conserve the grains from germination, infestation by pests or spoilage by moisture.
Cultivation of Cereals
Every part of the earth cultivates some type of cereal on its soil except for those with exotic climatic conditions like freezing poles or sandy deserts.
China is the topmost producer of cereals in the world. According to the census, their total production was 617 million metrics in 2017, which counts as 20.75 % of the entire world’s production. Apart from China, the United States of America, Brazil, India, and the Russian Federation are in the list top five countries for cereal production and contribute 54.42 % of the total output.
Different cereals require different climatic conditions and soil types to grow. For instance, you can grow wheat in every type of soil except for the dessert and frozen region. Whereas the grains like rye can easily be grown in less fertile soil.
Importance of Cereals
- The cereals have a large quantity of starch and carbs; thereby, they are known to provide immense energy content. They are also known to prevent some illnesses, including intestinal disorders, cancer and blood sugar.
- The bran part is rich in fibre and thus is recommended for patients suffering from constipation.
- Ranchers give the cereals to their cattle, domesticated animals and also to the poultry hens as food.
- Certain cereals are useful in synthesizing the products like oils, glues, alcohols, glucose etc.
What are Pulses?
The pulses are the crops harvested when they are completely dried. This differentiates them from the other crops that are harvested in their green state. They are the second most commonly consumed crop after the cereals.
The protein-rich pulses are the staple food of many places. For the Indian population, the pulses contribute largely to their daily routine diet. For the vegetarians whose who don’t eat proteinaceous meat, chicken etc., these pulses suffice the requirement of proteins in their bodies.
Constituents of Pulses
As mentioned earlier, the pulses contain lots of proteins. Along with that, they are rich in the compounds like:
- Amino acids
- Phytochemicals
- Anti-microbial compounds
- Enzyme inhibitors
- Lectins
- Saponins
- Oxalates
- Phytates
- Tannins
- Anti-cancerous compounds
- Anti-inflammatory compounds
- Vitamins; like folate, thiamine (B1), Riboflavin (B2), and Niacin (B3)
- Minerals; like phosphorous, magnesium, potassium, calcium and iron
Cultivation of Pulses
There are hundreds of varieties of pulses grown across the world. They are not just grown for their nutritional benefits, but the farmers also cultivate them to practise sustainable agriculture.
Most of the pulses, especially the leguminous ones, have symbiotic bacteria at their nodules. These bacteria are responsible for the nitrogen fixation in the soil, thereby making the soil more fertile, enhancing soil health, and reducing greenhouse gases.
As per the trends and research, India is the largest pulse producer in the world, with 28 % of the global contribution. Apart from that, India also accounts for the greatest consumer, contributor and importer of the pulses.
Besides India, other countries like China, Australia, USA, Brazil, Nigeria, Canada and Myanmar are the leading cultivators of the pulses.
We can cultivate the pulses even in areas having a moderate water supply since they have less water requirement.
For this reason, we can find their cultivation in the majority of places.
Importance of Pulses
- The pulses are rich in nutritional content.
- They are very healthy and helpful in keeping the sugar and blood-pressure level in check.
- Since the pulses are low in fat, doctors highly recommend them for patients suffering from cardiac disorders.
- Their cultivation enriches the soil with many important nutrients, ultimately making the soil more fertile.
Key Differences Between Cereals and Pulses
- Cereals belong to the grass family, cultivated for their starch and carbohydrate components. Pulses are the leguminous crop, harvested as the dry seed in a pod.
- Cereals have high levels of carbohydrates and starch. Whereas pulses are rich in proteins, vitamins, and amino acids, though have lower contents of carbohydrates.
- Many countries are the leading cultivators of cereals. Most of them use cereals as their staple food. Whereas the consumption of pulses is low in comparison to the cereals.
- We can grow cereals in all kinds of soils and weather conditions except in deserts and cold areas. Whereas we can grow pulses in the areas with a moderate water supply.
- Classification of cereals is as Kingdom: Plantae; Order: Poales; Family: Poaceae and that of pulses are Kingdom: Plantae; Order: Fabales; Family: Leguminosae.
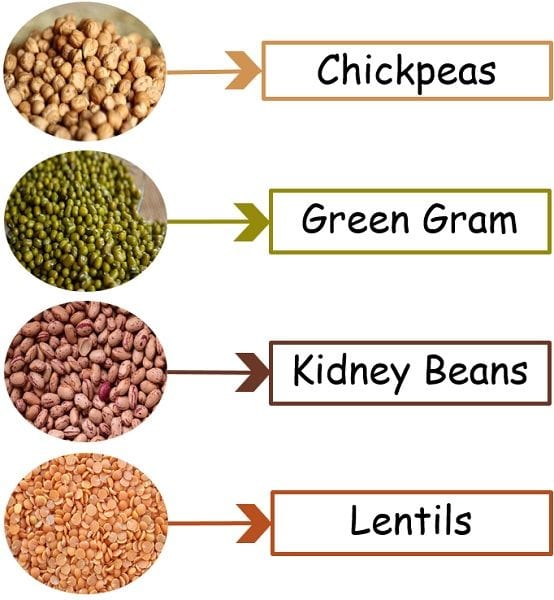
- Examples of cereals are Barley, corn, wheat, millet, rice, oats, sorghum, and maize, whereas Lentils, dry beans, golden gram, chickpeas, and cowpeas are a few varieties of pulses.
Conclusion
We can conclude by saying that cereals and pulses both have their importance in our diet, and are the rich sources of nutrition. Thus one should consume these grains in sufficient quantity in their diet, which will help in maintaining their health.


Leave a Reply