Carpel and Pistil are the reproductive part of a flower in a plant, and they have a very slight difference between them. As carpel is composed of the stigma, style and ovary, while pistil is the union of the carpels or it can be the single carpel, so we can say that pistil is the fusion of carpels. One can easily distinguish the number of carpels by checking the number of … [Read more...] about Difference Between Carpel and Pistil
Botany
Difference Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
When the plants are grown with the medium like sand, gravel or water but without soil is known as hydroponics. On the other hands, aquaponics is considered as the subset of the hydroponics, where the plants are grown in water, (without soil), and nutrients are provided from the by-products of fishes. We all are aware of the process known as photosynthesis, where the plants … [Read more...] about Difference Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
Difference Between Liverworts and Mosses
Liverworts and Mosses are the non-vascular and non-flowering plants that are found in wet and terrestrial environments. Though numerous essential differences lie between them. For instance, Liverwort belongs to the division - 'Marchantiophyta' or often term as'Hepaticophyta', while mosses fall under division - 'Bryophyta'. Secondly, liverworts have thallus or foliose that … [Read more...] about Difference Between Liverworts and Mosses
Difference Between Plants and Trees
The initial stage of a grown tree is the plant, so we can say that 'plant may or may not grows into a tree', but vice versa is not true. Among the five-kingdom classification, plants and tree fall into the same kingdom 'Plantae'. This is one of the major kingdoms which includes grass, herbs, shrubs, vines, bushes, mosses, ferns, green algae and trees. Plants and trees are … [Read more...] about Difference Between Plants and Trees
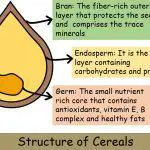
Difference Between Cereals and Pulses
Cereals and Pulses are the types of foods obtained from plants. They serve their individual roles in our bodies, and thus both are equally important in a balanced diet. We consume them in one or the other form daily, which makes it important for us to know more about them. So, let’s start! The cereals are a rich source of carbohydrates and starch. They provide the human … [Read more...] about Difference Between Cereals and Pulses