Epithelial tissue is present just below the basement membrane, while connective tissues are found all around the body, along with the nervous system, separating and supporting the various tissues and organs. Epithelial and connective tissues are among four of the major and vital kinds of animal tissues.
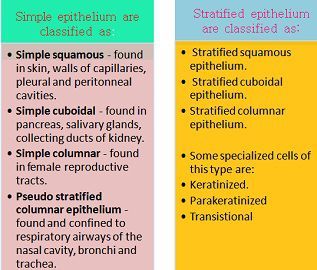
Mainly there are three types of epithelial tissues, based on their shapes: simple, columnar and cuboidal, and are also classified on the basis of organization of layers of cells present which can be simple epithelium (single layer) or stratified epithelium (two or more layers ).
Every connective tissue differs from three segments: cell or lymph, ground, and fibers substance. Blood and lymph do not contain fiber segment. Below we will differentiate between two types of tissue and a small description on them.
Content: Epithelium Vs Connective tissues
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Epithelial tissue | Connective tissue |
|---|---|---|
| Made up of | Cells and small amount of intercellular matrix. | Cells and a huge amount of intercellular matrix |
| Role | 1.Mainly forms covering of the organs, internally and externally. 2.Helps in transcellular or intercellular transportation. 3.In selective absorption, protection of cells. | 1.Support and anchors other tissue and organs. 2.Helps in muscles and bone formation. 3.Also helps in working of blood and lymph. |
| Develops from | It develops from the endoderm or mesoderm or ectoderm from the embryological germ layer. | Develops from mesoderm (embryonic mesodermal origin). |
| Arrangement | These cells are arranged in layers which can be either single or multi layer. | Here cells are present in scattered form in the matrix and does not show any arrangement. |
| Surrounded by | Does not surrounded by blood capillaries. | These cells are surrounded by blood capillaries. |
| Location | These tissues lie above the basement membrane. | These tissues lie below basement membrane, called lamina propia. |
| Nutrition | As epithelial cells are not bounded by blood capillaries and they gain their nutrition from the cellular membrane. | These types are bounded by blood capillaries and hence gain nutrition from there. |
| Bounded by | Special proteins, desmosomes and hemidesomes. | Blood capillaries and materials like elastic or collagen fibres. |
| Can be found | Lungs, kidneys, skin, mucous membranes. | Bones, nerves, ligaments, tendons, blood. |
Definition of Epithelium tissue
Epithelial cells are present in the arranged pattern, below the basement membrane. They get derived from embryological germ layers which can be from endoderm (e.g from the lining of the gastrointestinal tract), from mesoderm (e.g from the inner linings of body cavities), from ectoderm (e.g from the epidermis). Skin is one of its kind.
On the basis of different shapes, sizes and arrangement, epithelial tissues are divided into following principal categories:
- Columnar epithelium – These are column-like cells.
- Squamous epithelium – These are flattened and scale-like cells.
- Cuboidal epithelium – These are present in the cube shape.
By the presence of a number of layers, the epithelium is classified is as either simple epithelium, which is only one cell thick i.e. uni-layered or stratified epithelium, which are two or more cells thick i.e. multilayered.
Simple epithelium is present just below the basement membrane and is directly in contact with it, it also separates underlying connective tissue. Mainly take part infiltration and absorption.
Epithelial cells are found abundantly in cell junctions, they help in cell-cell communication, cell junction act as the main communication point between tissue cells and plasma membrane. These tissue helps in protection, sensing the external shocks, excretions, secretions, etc.
Definition of Connective tissue
These tissues have a wide networking of nerves and blood capillaries. These tissues connect, separate and support tissues and organs of the body. As these are enclosed within the matrix of elastic, cartilaginous and collagen tissue, fibroblast is the most common among all. Others are plasma cells, mast cells, adipocytes, leukocytes.
Additionally, connective tissues also perform the function of insulation (adipose tissue), functions performed by blood and lymph like in distribution of nutrition and oxygen throughout body’s tissue, as well in supporting network of bones and muscles.
It is responsible for the formation and organizing skeleton, blood and muscles, fat and the nerves. Among all organs, connective tissues play a vital and important role among all.
Types of Connective tissue
1. Blood.
2. Adipose tissue.
3. Cartilage.
4. Bone.
5. Fibrous connective tissue.
6. Loose connective tissue.
Key Differences Between Epithelium and Connective tissues
Following are the substantial difference between epithelial and connective tissues:
- Epithelial tissue is made up of the cell and a small amount of intercellular matrix, while connective tissues are made up of the cell and a huge amount of intercellular matrix.
- Epithelial tissues mainly form a covering of the organs, internally as well externally, helps in transcellular or intercellular transportation, in selective absorption, and in the protection of cells; connective tissues support and anchors other tissue and organs, helps in muscles and bone formation, also helps in working of blood and lymph.
- Epithelial tissue develops from the endoderm or mesoderm or ectoderm from the embryological germ layer; connective tissue develops from mesoderm (embryonic mesodermal origin).
- The arrangement of epithelial cells are either single or multilayer; In connective tissue cells are present in a scattered form in the matrix and does not show any arrangement.
- Epithelial tissues are not enclosed by blood capillaries while in connective tissue, cells are enclosed by blood capillaries.
- Epithelial tissues lie above the basement membrane; connective tissues lie below basement membrane, called lamina propia.
- Cells of epithelial tissues are not bounded by blood capillaries and they gain their nutrition from the cellular membrane; cells of connective tissues are bounded by blood capillaries and hence gain nutrition from there.
- Bounded by special proteins, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes are epithelial tissues; connective tissues are bounded by blood capillaries and materials like elastin or collagen fibers.
- Epithelial tissues can be found in lungs, kidneys, skin, mucous membranes and connective tissues are found in bones, nerves, ligaments, tendons, blood.
Conclusion
Organs are made up of tissues and tissues are made up of cells which are known to perform different functions. Among four major kinds of tissues present in animal body’s, epithelial and connective tissues are the two most important one.
These two types of tissues form a dense structural network in the body, which helps in connecting different organs and even in protection from toxins, macrophages, foreign bodies as well as from external shocks.
Important is that, apart from being different in function, origin, and constituents, they work in a synchronized manner with the aim of keeping the body fit and in proper function. So it’s one responsibility to understand this amazing functions of the body and try to maintain its lifetime.

Angel Borrero says
Thank you I now have a clear understanding of Epithelial tissue functionality , location comparison to connective tissue . I’m studying to be a medical coder and your references , explanation is concise compare to the book I’m reading for human anatomy course.