Cilia are short, hair-like structure, present in large numbers in a cell, while flagella are long, hair-like complex structure and are few per cell. Cilia and flagella are hair-like appendages, extending through the surface of the living cell, they differ in their mode of beating, size, and number.
Cilia and flagella are the locomotory structure, which is the extension of the plasma membrane of the cell. Besides the locomotion, they also help in other processes like respiration, excretion, circulation, etc. They also take part in capturing food. These both are found in eukaryotic cells, but in prokaryotic cells only flagella
Both of these appendages are found in eukaryotic cells, but in prokaryotic cells only flagella are present. Although these appendages are not found in plants. In the following article, we will discuss the difference between these two structures.
Contentµ: Cilia Vs Flagella
Comparison Chart
| Basis for comparison | Cilia | Flagella |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The microscopic, slender, short hair like structure present overall on the surface of the cell, and thus support the locomotion of the cell is called cilia. | The unbranched, long, complex, filamentous, thread like structure extending through cell surface is called flagella. |
| Found in | Eukaryotic cell. | Prokaryotic cell as well as in eukaryotic cells. |
| Quantity | Numerous (hundreds) per cell. | Few (less than 10) per cell. |
| Length | Short. | Longer. |
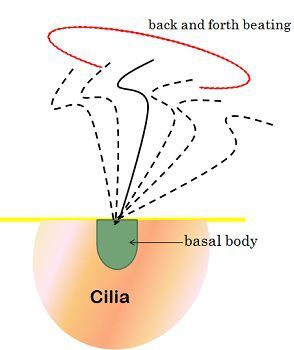
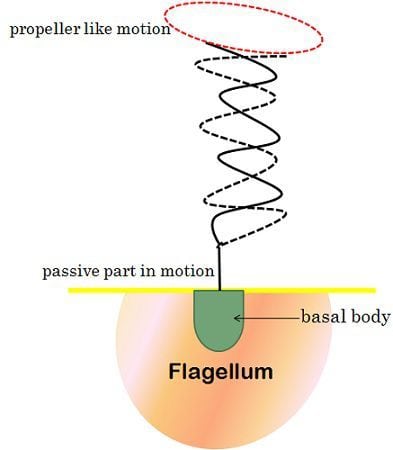
| Type of motion | Cilia show rotational motion like a motor; they are very fast moving. | Flagella show slow, wave-like, sinusoidal and undulating movement. |
| Beat | In coordination. | Independently. |
| Nexim (a protein) | Present. | Absent. |
| Role | They play their primary role in locomotion, aeration (respiration), etc. | They are helpful in locomotion only. |
| Occurs in | It occurs all over the cell surface. | It is present at both the ends or sometimes all over the surface. |
Definition of Cilia
Cilia are short, slender, hair-like appendages extending from the surface of the cell. These are present in almost all eukaryotic cells. They play a significant role the cell and overall body development.
Cilia are most active during the cell cycle progression and proliferation. The width of the cilium is less than 1 µm, and the length varies from 1-10 µm.
Cilia are broadly divided into two types – Motile and Non-motile. Motile or moving cilia are mainly present in lungs, middle ear, and respiratory tract. These kind beat rhythmically. Their work is to keep the airways clear of mucus and dust, due to which it is easy to breathe freely and without any irritation. They are also helpful in the movement of the sperm.
Motile cilia consist of ciliary axoneme, which is regarded as the microtubular backbone, they have 9+2 arrangement of the ciliary axoneme and is surrounded by the plasma membrane. In this arrangement, the nine fused pairs of microtubules arranged in a circle, while the two unfused microtubules are present in the center of the circle.
The arms ‘dynein‘ which are attached to the microtubules, act as the molecular motors. The defect in the dynein arms causes male infertility, problems in the respiratory tract.
Non-motile cilia also called as primary cilia play their role in receiving signals from other cells or nearby fluids, by acting as the antenna for the cell. For example in the kidney, the cilia send signals to the cells about the flow of urine.
Even in the eye, the non-motile cilia supports the transportation of vital molecules from one end of the photoreceptor of the retina to the other. Non-motile cilia have 9+0 microtubular arrangement.
Definition of Flagella
Flagella are the complex, hair-like filamentous structure, extending through the cell surface. Flagella are composed protein like flagellin, embedded in the cell envelope. They are responsible for motility. They can be about 5-16 µm in length and 12-30 nm in diameter.
Flagella are of three types – bacterial flagella, archaeal flagella, eukaryotic flagella. Bacterial flagella are found in Salmonella typhi, E. coli. They can be one, two or many flagella per cell. These have the helical filamentous structure that rotates like screws. These provide motility to bacteria.
Archaeal flagella show similarity with that of bacterial flagella but lack a central channel. Eukaryotic flagella are the complex projections, that beat back and forth. An example is the sperm cell, which propels itself through the female reproductive tract by using its flagellum.
Usually, flagella consist of Hook, Filament and Basal body in their body parts. The filament is the external part of the cell; the hook is in the cell envelope, and basal body is attached to the cytoplasmic membrane, through the ring-like structures. Their function is adhesion, signal transduction, sensation, movements.
Key Differences Between Cilia and Flagella
Given below are the key differences between the cilia and flagella:
- Cilia are the microscopic, slender, short hair like structure present overall on the surface of the cell, and thus support the locomotion of the cell, on the other hand, flagella are longer and few in number, complex, filamentous structure, extended through the cell surface.
- Cilia are found in eukaryotic cells only, they are present overall on the cell surface and are shorter, while flagella are longer and are few (less than 10) in numbers, they are found in prokaryotic as well as in eukaryotic cells.
- Cilia beat coordinately and show rotational motion and are very fast moving also, on the other hand, flagella show whip-like, sinusoidal, undulating, independent movement, but are slow.
- Cilia play their leading role in locomotion, aeration (respiration), excretion, circulation, etc., while flagella are helpful in locomotion only.
Similarities
- Cilia and flagella share some common characteristics like they arise from the small granular structure called the basal body. Both are the outgrowth of the plasma membrane of the cell. Cilia and flagella consist of the central filament called an axoneme. The axoneme contains eleven microtubules. Nine are present in pairs called as the doublet, and two of them present in the center are the singlet. This is called 9+2 microtubular arrangement. The drift in the microtubules of the axoneme causes the movement in the cilia and flagella. The axoneme contains proteins like dynein, tubulin, nexin.
- In some organisms like protozoans and metazoans, it helps in capturing food.
- Mainly serve as locomotory organs.
- Also helps in respiration, circulation, and excretion.
Conclusion
Cilia and flagella are the locomotory structure of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, but apart from it, they also perform certainly a physiological process like circulation, respiration, locomotion, excretion. Being structurally same, the feature that distinguishes them from each other is their number, size and beating mode.

Leave a Reply