We divide psychiatry into Neurosis and Psychosis for a convenient outlook and thorough studies. The professionals assert that these two terms vary greatly concerning their symptoms, pathology, treatment and prognosis.
We can understand that a neurosis is actually a group of light mental disorders. And they occur due to functional impairment rather than an organic cause. On the other side, psychosis is a personality disorder resulting from some underlying diseases.
You can consider neurosis as a maladaptive response to a busy day-to-day life, excess mental stress, phobias or OCD. In contrast, the psychosis is pretty more than that. A person who has psychosis has severe organic impairment in the brain.
Neurosis doesn’t carry any risk of self-harm as the person’s insight works properly, and he is aware of his problems. Whereas, in psychosis, the patient tends to harm himself as he has a complete loss of insight. He is unaware of the problems he is suffering from and disagrees to accept that he is sick.
Here, we will study the differences between neurosis and psychosis in detail.
Content: Neurosis Vs Psychosis
- Comparison Chart
- Why is it necessary to keep a check on your mental health?
- What is Neurosis?
- What is Psychosis?
- Key Differences
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis of Comparison | Neurosis | Psychosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Neurosis means continual struggle of an individual between his personality and behavioural pattern in case of stressful situations related to disturbance of mental or physical well-being. | Psychosis is a complete personality disorder that disturbs an individual's mental and emotional facet of life causing deep psychical illness and social unacceptance. |
| Types | Obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, neurasthenia, hysteria, somatoform, fearful neurosis are some common types of neurosis. | Schizophrenia, epilepsy, hallucinatory psychosis, senile or presenile dementia, bipolar affective disorder, paranoia are the types of psychosis. |
| Contact with Reality | Neurotic persons partially lose contact with reality due to mild hamper of insight. | Psychotic persons have considerable impairment of insight. Thus, the contact with reality is lost. |
| Personality Changes | It doesn't affect the personality. | There is an overall alteration in the individual's personality. |
| Language and Communication | There are no significant hindrances in speech, thoughts, language or communication. | The speech, communication skills and thoughts are disorganised and irrational. |
| Awareness | A person with a neurotic disorder is fully aware and realises the associated problems. | The psychotic patient might not be aware of their suffering or difficulties. |
| Organic Changes | It is a functional disorder and is rarely associated with the organic changes occurring inside the brain. | These occur due to the organic changes in the neuro-cerebral substances. |
| General Behaviour | These individuals are quite stable and can manage themselves. They rarely possess suicidal tendencies. | The psychotic are unstable individuals who can't manage their behaviour or actions. They possess strong suicidal tendencies. |
| Treatment | The treatment involves social support, counselling sessions, anti-depressants. | Here, the anti-psychotic medicines, psychological therapies, social boost etc. |
| Prognosis | Neurotic symptoms are temporary and with optimum cure, willpower and cooperation of the patient, the resultant treatment outcomes are good. | Its treatments are long term and have to be taken constantly. Even when the person recovers and appears normal, there are higher chances of relapse of psychotic episodes. |
| Self-Harm | Causes less personal harm | Causes severe personal harm |
| Type of Disorder | These are functional disorders | These disorders are associated with pathological and organic changes in the brain. |
| Causative Agents | Biological, socio-psychic climate, psychological and socio-economic conditions. | Genetic, environmental and biochemical. |
Why is it necessary to keep a check on your mental health?
It is not necessary that if you are disease-free, you are healthy. As per WHO, health is the complete physical, physiological, social, and mental well-being of an individual.
We often neglect the mental health criterion as we think it is least important to keep our minds healthy. Thus, most of the population might suffer from mental illness without even knowing it.
We can define ‘Mental health‘ as a state of self-efficiency, emotional well-being, autonomy, competence, the realisation of one’s capabilities and integrational dependence while dealing with society.
Any sort of disruption in the state mentioned above is a mental illness. This kind of illness can severely hamper the everyday routine, general behaviour and quality of life. Thus, it becomes our moral duty to give equal time and importance to our mental health in order to stay entirely fit.
What is Neurosis?
As per a psychiatrist, neurosis is the state of unconscious conflict between the individual’s personality and his pattern of behaviour. It is frequently linked with the ego defence strategies in emotional distress, irritability, sadness, anger or anxiety.
In easy words, we can say that neurosis is an individual’s internal struggle and inability to stabilise his disturbing emotions. But a neurotic patient is fully aware of his surrounding conditions and only remains partially detached from reality.
Neurotic sufferers have some typical traits like being emotionally imperfect, reckless, lack of sincerity, impatience and immaturity, etc. You may observe that these individuals have trouble in their relationships and cannot fulfil others’ expectations.
Even in such cases, these people can manage themselves in society as they are no harm to themselves or others.
Definition of Neurosis
“Exaggerated defence response to evade the intense feelings of anger, anxiety, phobia or depression is referred to as Neurosis“.
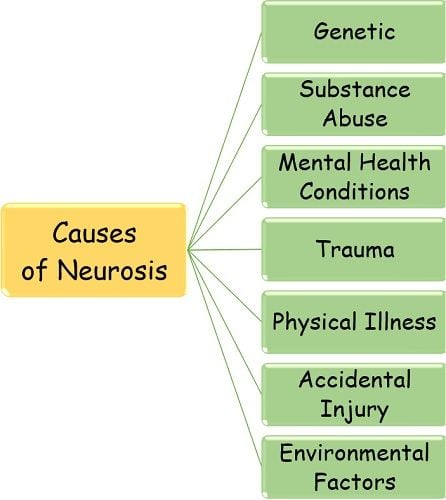
Causes of Neurosis
The causes of neurosis vary according to the individual’s condition. It mainly occurs due to the internal clash between reality and the attitude of the person. Such situations cause agitation and discomfort, which further get converted into a neurotic disorder.
Characteristics of Neurosis
Researchers often debate over this topic and give more than one explanation about the common traits of neurosis. But they agree on the presence of certain characteristics mentioned below:
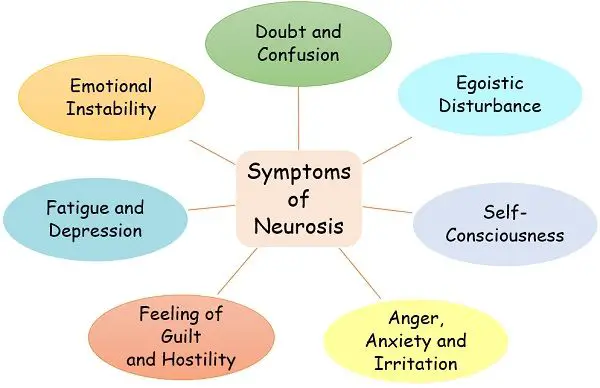
- Emotionally Imperfect: Neurotic individuals have trouble stabilising their emotions in certain situations. They are over-expressive about their feelings. For this reason, their personal and professional lives both get disturbed.
- No loss of contact with reality: These individuals are fully aware of their condition as their insight remains well-maintained. Moreover, there is no loss of contact with the real world.
- Barely affects thoughts, speech and communication: There is no significant damage to ones thinking abilities or communication skills.
- It is a conflict between two psychic incidents: As per Swiss scientist Carl Gustav Jung, neurotic disorders result from a clash between conscious and unconscious events in our brains.
- It is a part of the defence mechanism: Famous neurologist Sigmund Freud defined neurosis as the coping mechanism of our mind’s defence system. He explained it as the explosion of repressed emotions that can be due to any unpleasant experience.
Symptoms of Neurosis
Types of Neurotic Disorders
Anxiety Neurosis
Anxiety is nothing but a state of fear or panic due to some person, thing or situation. One of its primary reasons is overthinking and overanalysing something. In such cases, an individual is apprehensive and starts behaving weirdly or inversely to his natural behaviour. Researchers term this condition anxiety neurosis.
During this, a person might suffer from a dry throat, numbness, fainting, heart palpitation, chills etc.
Phobia
Phobias are the irrational fear of a person, an object or a situation. These are extreme responses generated by the mind against certain things. And due to this, a person might undergo bad experiences in doing some work or using something.
The sufferer is fully aware that his fear is irrational, but still, it is very difficult for him to overcome it. As a result, they behave differently in a situation that might seem normal to others.
For example, a claustrophobic person might not be able to travel in lifts due to its closed structure. While for others, it is a normal experience.
Depressive Neurosis
This type of neurosis has a core reason behind its occurrence. It can be past trauma, accident, relationship trouble, social pressure, work-life imbalance, economic crisis etc.
A person having depression has a constant feeling of sadness, hopelessness, despair, guilt or fear. Such individuals might look and behave normally in public places but are in a continual emotional conflict.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
OCDs are some persistent intrusive thoughts of a person that make him obsessed with something. An individual suffers from an irrational fear of doing something or getting rid of something. If not done so, they might feel severely anxious.
In some cases, the obsession is not regularly followed by compulsion. But in the majority ones, it becomes compulsive to follow the obsession.
One of the prevalent examples is the OCD of germs. In this situation, the person will always feel germs on his hands and body. And may repeatedly feel the urge to bathe or wash hands.
Eating Disorders
They are very similar to that of OCDs, where people start feeling that their food pattern may harm their body shape and size in a bad way. Due to this, after every meal, they feel anxious about getting fat or obese.
Anorexia nervosa is one of the famous eating disorders that women mainly experience. In this, the person has an obsession or feeling to get rid of the food taken in. And for this, they excessively use laxatives or do continuous vomiting until their stomach is empty.
Bulimia nervosa is also one such eating disorder where a person does binge-eating and then feels deep guilt. To overcome the guilt or compensate for their diet, they vomit or starve for several days.
Combat Neurosis
It is the type of neurosis that occurs as a consequence of war or combat. Also referred to as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). People who have experienced war may suffer from trauma for the rest of their life.
What is Psychosis?
Psychosis is a common term of psychiatry that professions often use to point out unstable mental behaviour.
You cannot mention it as a core disease as it is an actually symptomatic indication of some severe mental disorder. In easy words, you can understand it as a by-product that gets generated due to some underlying mental condition.
A person who has psychosis loses his insight and ability to rationalise. Thereby, he experiences difficulty in social interactions and daily routine tasks. They cannot handle themselves on their own and strictly require medical aid.
They see, hear or smell the things that don’t exist in reality. It occurs because of delusion or hallucination. During the constant progression of the disease, the patient gradually loses contact with the real world. And starts living in the world created by his mind.
Due to the conditions mentioned above, the person tends to remain confused, disturbed and distrustful between what’s real and what’ not!
Definition of Psychosis
“Individuals’ mental state that breaks his contact with reality due to delusions, hallucinations, false judgements and disorganisation of thoughts is called Psychosis”.
Symptoms of Psychosis
The four cardinal symptoms of psychosis are as follows:
1. Delusion
The delusion can be any false belief or thought that a person strangely holds. For this reason, they remain suspicious and frightened over everything happening around them.
We can categorise delusion into two primary types based on their plausibility:
a. Bizarre Delusions
It involves weird thoughts and feelings about the patients’ life, family or surroundings.
For example, the patient might believe that some family member has changed.
b. Non-Bizarre Delusions
These are due to excessive fear or over-protectiveness towards something or someone.
For example, someone feels that his partner is cheating on him.
2. Hallucination
It is a wakeful sensory experience where the patient sees, smells or hears the things that are not present in reality. The patient often feels scared about someone following to harm him.
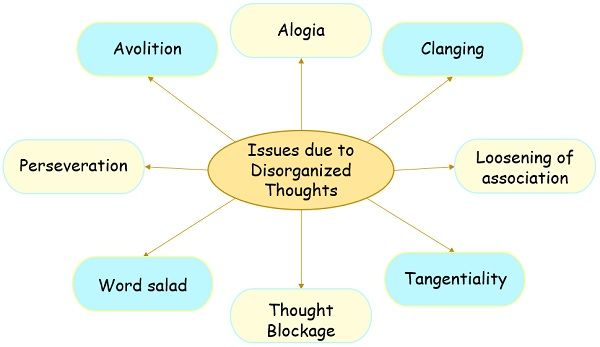
3. Disorganisation of Thoughts
The thoughts of the person are illogical and remain scattered in different directions. Thereby he is unable to focus on any particular thought or conversation. He might face difficulty expressing his feelings and problems due to the hindrance in speech and language.
The following are some problems associated with the disorganised pattern of thoughts:
4. Aggression and Agitation
The person during his psychotic episode may become violent and aggressive. He might not be able to control his aggression and might cause harm to himself or, in severe cases, to others.
Causes of Psychosis
As mentioned earlier, the psychosis itself is not a disease, but it is a by-product of underlying mental or physical issues.
We can classify the causatives of psychosis as Primary and secondary illnesses.
Primary Causes
The primary disease may include the following reasons:
- Functional: Mental issues like schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophreniform disorder etc.
- Organic: These causes are due to the organic changes occurring in the patients’ minds. Such as tumours, chemical imbalance etc.
- Substance Abuse: The intake of psychoactive drugs like hallucinogens, barbiturates and amphetamines can trigger psychotic episodes.
Secondary Causes
The secondary causes can involve the health issues like:
- Stroke
- Thyroid
- Adrenal diseases
- Wilson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
Types of Psychosis
The following are the common type of psychosis:
- Bipolar Psychosis: Bipolarity refers to sudden changes in mood. Like from happy to very sad or the alterations of emotions from time to time. The psychotic episodes occurring by this are bipolar psychosis.
- Brief Psychotic Disorders: These psychotic episodes last for a shorter period of time. The main cause behind them is the stressful routine, anxiety etc.
- Delusional Psychosis: This type of psychosis is due to an individual’s false, bizarre and irrational beliefs.
- Postpartum or Postnatal Psychosis: After the child’s mother undergoes many hormonal changes. Due to this, they experience severe dep[ression and grief, leading to psychosis.
- Schizoaffective Psychosis: Schizophrenia is responsible for this type of psychosis.
- Substance-Induced Psychosis: This occurs because of certain drugs and chemicals misuse.
Key Differences Between Neurosis and Psychosis
- Neurosis is a functional disorder that causes the struggle between an individual’s personality and behaviour. While psychosis is not an illness, it occurs as a by-product of any other mental disorder.
- Neurosis is a functional psychical disorder, but psychosis is because of organic changes.
- The neurotic person is fully aware of his situation and can handle himself without any medical help. But the psychotic persons remain in denial about their mental issues. Thereby cannot take care of them on their own and require medical assistance.
- An individual suffering from neurosis doesn’t have significant effects on his personality. But the psychotic person’s personality traits change.
- There is no loss of contact with reality in the case of neurosis. In contrast, there is a complete loss of contact with the real world.
- A neurotic patient’s insight is partially affected. While of psychotic person has a significant impairment of insight.
- There are no suicidal tendencies in neurosis. Whereas they are often found in psychotic patients.
Conclusion
Both neurosis and psychosis are two separate branches of psychiatry. Anyone who is suffering from either of them needs proper help and support from family and society. Simultaneously a suitable medical treatment and professional guidance should also be provided to the patient.
Mental health is an important aspect of human life as our brain controls and manages the way we live on earth. Thus, in case of any mental issue, you should seek the necessary help before it is too late.









Leave a Reply