Mitosis has the diploid number of chromosomes and produces two identical daughter cells with 46 chromosomes, on the contrary in Meiosis four genetically distinct daughter cells with each having 23 chromosomes in the human cells are produced which have the haploid number of chromosomes. Secondly, Mitosis occurs in Somatic cells while Meiosis happens in Sex cells or Gametic cells.
The above points are the critical one to distinguish between the two, though there are many more to focus, which will make the reader much clear about the terms Mitosis and Meiosis.
Life starts from a single cell, which further divides and grow and start functioning for the task they have been assigned; with the purpose of growth and development of the body and to transfer the parental DNA to their offsprings. Hereby, we will be studying the distinct features of Mitosis and Meiosis and how they vary from one another.
Content: Mitosis Vs Meiosis
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Mitosis is the process of cell division which occurs in all types of cells (excluding sex cells), with the purpose of the asexual reproduction or the vegetative growth. | Meiosis is the process occurs in the specialized type of cell called as meiocytes, which supports the sexual reproduction by the gametogenesis. |
| Discovered by | Walther Flemming. | Oscar Hertwig. |
| Steps required to complete the cycle | Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. | Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I; (Meiosis II), Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II and Telophase II. |
| Occurs in | Somatic cells. | Germ cells. |
| Other Features | There is no process of synapsis and crossing over. | Synapsis and crossing over take place of the Homologous chromosomes during meiosis I. |
| The genetic identity remains same even after the mitotic division. | Genetic variation is noticed during meitoic divison. | |
| There is only one nuclear division. | There are two nuclear divisions. | |
| There is no pairing of Homologs. | Pairing occurs of Homologs. | |
| Mother cell can be diploid or haploid. | Mother cell is always diploid. | |
| There is the production of two daughter cells, which are diploid. | There is the production of four haploid daughter cells. | |
| The number of chromosomes remains same. | The chromosome number is reduced by half. | |
| The pairing of chromosomes does not occur. | The pairing of chromosomes occurs during zygotene of prophase I and continue till metaphase I. | |
| Does not produce sex cells. | In this stages, only sex cells are produced which can be either male sperm cells or female egg cells. | |
| Nucleoli appear again in telophase. | It is absent in telophase I. | |
| Karyokinesis takes place during Interphase, but Cytokinesis occurs during telophase. | Karyokinesis takes place in Interphase I. Here Cytokinesis happens in Telophase I and II. | |
| Chiasmata is absent. | Chiasmata are seen during prophase I and metaphase I. | |
| Spindle Fibres completely disappear in telophase. | Present in telophase I. | |
| The splitting of centromeres takes place during anaphase. | There is no such splitting of the centromere in anaphase I and II. | |
| The duration of Prophase is short (of few hours only) and is a very simple process. | The process is Prophase is complicated and is longer (it may last for days). | |
| There is no exchange of two chromatids of a chromosome in prophase. | Exchange of two chromatids of the Homologous chromosomes takes place at the time of crossing over. | |
| Functions | They are functional at the time of cellular growth. | This process a major role in gamete formation and in sexual reproduction. |
| Active during the body repair and healing mechanisms. | These are active in maintaining the number of chromosomes. |
Definition of Mitosis
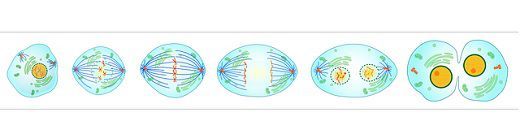
The method of cell division, where a nucleus of a cell divides into two daughter nuclei. These daughter cells contain the equal number of chromosomes as that in the parent nucleus. As this is the process of asexual reproduction, it is essential for the single-celled eukaryotes. Apart from it, in the multi-celled eukaryotes, it has many roles such as in body growth, repair mechanism, etc. Mitosis may complete in minutes or hours; it depends on the cells, species, temperature, place and day.
Mitosis is completed in by undergoing through various stages. These stages are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, beside this there are few more stages also, which are further discussed.
Interphase – This is the preparatory stage, which is technically not the part of mitosis but plays a vital role. Interphase starts and ends mitosis, by duplicating DNA and preparing the cell to grow fully for the division. When an identical set of DNA is arranged in a cell, it is ready to undergo the process of mitosis.
Prophase – This is the first stage of mitosis, where the chromosomes get thick and condense. In this, the spindle fibers start to form, and the nuclear membrane disintegrates.
Metaphase – Here the chromosomes, each having there duplicate chromatids gets align in the midline of the cell.
Anaphase – In this each chromatid pair gets separate and is pulled in the opposite direction towards the end of the cell, with the support of the spindle fibers.
Telophase – Here the chromosomes again decondensed, the spindle fibers and the nuclear membrane start forming again around nucleoli. The cytoplasm also divides into two daughter cell, having the equal number of chromosomes. The cell again gets ready for the interphase.
Definition of Meiosis
The process where the division of cell occurs by sexually reproducing organisms, following two nuclear division (meiosis I and meiosis II) and results in the production of four haploid gametes or sex cells. Each cell contains a pair of the homologous chromosomes, which means paternal and maternal chromosomes randomly distributed among the cells.
Meiosis give rise to the non-identical sex cells, having two consecutive nuclear divisions, first meiotic division (or meiosis I) and second meiotic division (meiosis II). The nuclear division also has four stages which are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
In interphase the cells are duplicated, the chromosomes condense and pull towards the opposite ends and pair with their homologous at the time of crossing over. Further, the cell divides and forms two cells. These are the process of the meiosis I and then in these two newly formed cells undergoes the process of meiosis II.
Now, these two cells further divide into two more cells, which contains decoupled chromatids and thus four genetically different haploid cells are formed. Meiosis is the vital process where the chromosomes are reduced to the half and produce variation by different genetic recombination and independent assortment.
Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Given below are the essential difference in order to distinguish the two main types of cell division occurring in living organisms:
- The process of cell division which occurs for the replacement of the somatic cells (excluding sex cells), and is helpful in body repair mechanism and growth is known as mitosis. They are known to happen in case of vegetative reproduction or in asexual reproduction. On the other hand, the process of cell division known to occur for the production of sex cells like egg cells or sperm cells, and supports the sexual reproduction by the gametogenesis is called as meiosis.
- Mitosis was discovered by Walther Flemming, while meiosis was discovered by Oscar Hertwig.
- Steps required to complete the cycle in mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, but in case of the meiosis, where the division splits into two main stages like, Meiosis I – Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I; and Meiosis II – Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II and Telophase II.
- Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, and so there is no process of synapsis and crossing over, while meiosis happens in germ cells and synapsis and crossing over takes place of the Homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.
- As the primary purpose of mitosis is for the growth of the body so even after the cell division the genetic identity remains same even after the division.
But in case of meiosis of genetic variation is noticed during division, as these cells are helpful in the production of sex cells. - Mitosis has only one nuclear division, no homologous chromosome are involved in the pairing, on the contrary meiosis has two nuclear division and pairing occurs of homologous chromosomes.
- Mother cell can be haploid or diploid, which give rise to only two daughter cells (diploid) in case of mitosis, but mother cell is always diploid and give rise to four daughter cells (haploid) in meiosis.
- The number of chromosomes remains same in mitosis, but the chromosome number is reduced by half in meiosis.
- Nucleoli appears again in telophase, but chiasmata is absent even Karyokinesis takes place during interphase, but Cytokinesis occurs during telophase in the mitosis, whereas in meiosis, nucleoli is absent in telophase I, chiasmata is seen during prophase I and metaphase I, even Karyokinesis takes place in Interphase I; Cytokinesis happens in Telophase I and II.
- In mitosis the splitting of centromeres takes place during anaphase, Spindle Fibres completely disappear in telophase, while there is no such splitting of the centromere in anaphase I and II, and Spindle Fibres is present in telophase I.
- The duration of Prophase is short (of few hours only) and is a simple one in mitosis. On the other hand, the process is Prophase is complicated and is longer (it may last for days).
- Mitosis is functional at the time of cellular growth and active during the body repair and healing mechanisms. Meiosis plays a significant role in gamete formation and sexual reproduction and is active in maintaining the number of chromosomes.
Similarities
- Mitosis and Meiosis both occur in the nucleus of the cell and are observable under the light microscope.
- Both the process involves the division of the cell.
- Mitosis and Meiosis happen in M-phase of the cell cycle.
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase are the typical stages in both the cycle. - Synthesis of DNA occurs in both the cycles.
- There is no involvement of the cells of the cardiac muscles tissue and the nervous tissue in the process of Mitosis and Meiosis as they once formed, do not undergo further any division.
Conclusion
Cell division gives rise to the new daughter cells, and it is an important event that occurs in every living organisms. Thus we can say that in general, the parent’s cell splits and produce two or more cells. Sometimes the error in such division may lead to disease also. In this section, we reviewed the essential differences between the two processes and explained the reason of occurrence.


rabab awad says
full thanks for this covenant in formations
kennedy ouma says
excellent